Rail Infrastructure Density Map of Europe

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
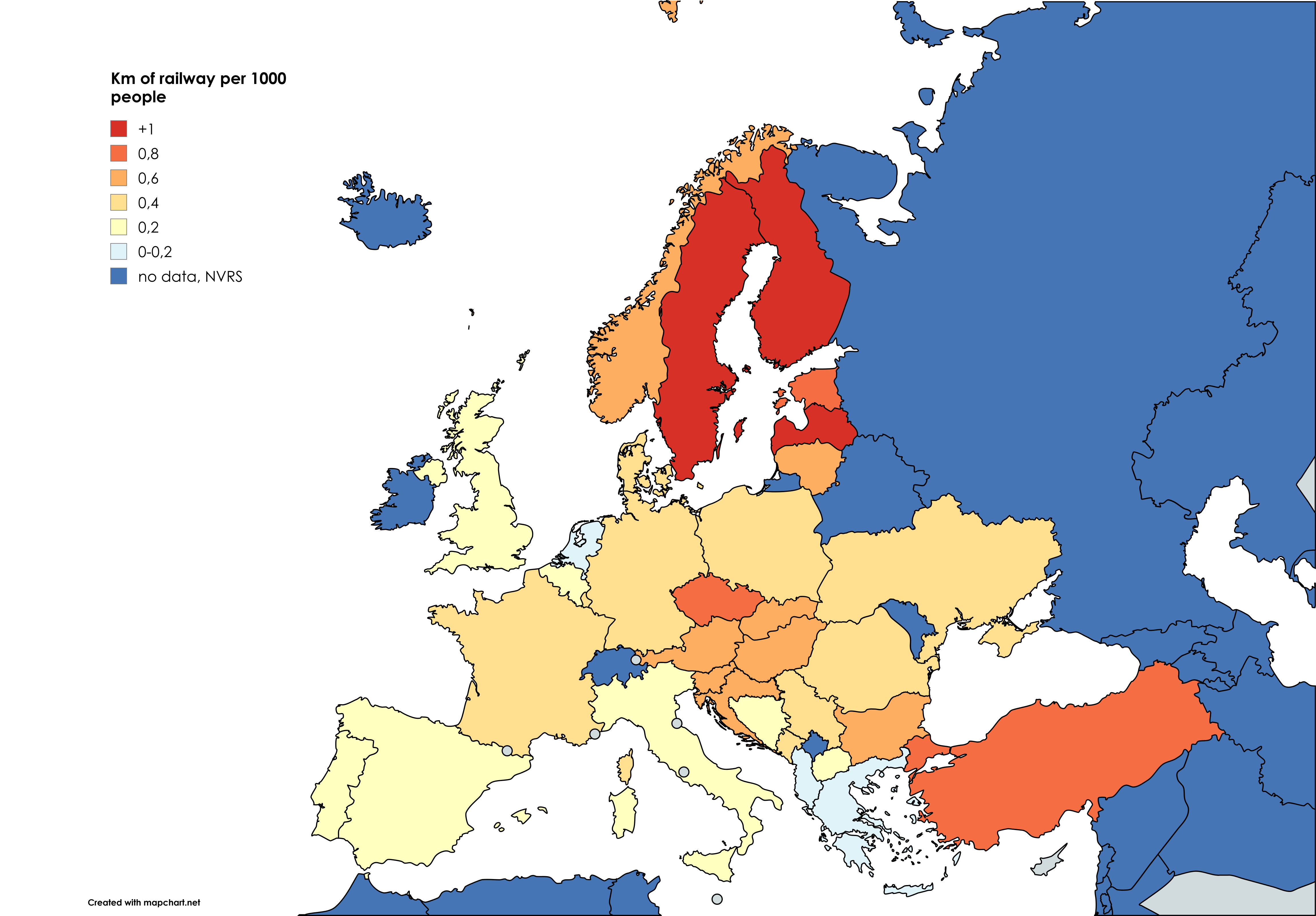
The visualization titled "Km of Rail per 1000 People" uses Eurostat data to provide a comprehensive overview of the rail infrastructure density across various European countries. By illustrating the kilometers of railway available for every 1,000 individuals, this map serves as a powerful indicator of how well-connected a nation is through its rail networks. Railways are not just lines on a map; they are vital arteries for both economic productivity and social mobility. This article will delve deeper into the significance of rail networks, their historical context, and their impact on modern society.
Deep Dive into Rail Infrastructure
Rail systems have played a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of Europe. With a rich history dating back to the early 19th century, railways were initially designed to facilitate the movement of goods. However, as cities and industries expanded, passenger transport became increasingly significant, leading to the establishment of extensive rail networks across the continent.
Interestingly, rail transport remains one of the most efficient means of moving large numbers of people and goods. It is often more environmentally friendly than road transport, as trains can carry more weight while producing fewer emissions per ton-kilometer. According to the European Commission, rail transport emits 75% less carbon dioxide than road transport per passenger-kilometer. This makes rail infrastructure not just a matter of convenience but also a critical component in the fight against climate change.
Each country on the map shows varying levels of rail density, revealing insights into not just transportation but also economic disparity and urban planning. For instance, countries like Germany and France boast high rail density, with extensive networks that are crucial for commuter travel and freight movement. In contrast, nations such as Romania and Bulgaria show lower figures, indicating that these regions may struggle with accessibility and economic integration.
As urbanization continues to rise, the demand for efficient rail systems has never been more urgent. The European Union has recognized this need and is actively investing in railway projects, including the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T) initiative, which aims to enhance connectivity across member states. Have you ever wondered how this investment impacts local economies? The answer lies in job creation and improved access to markets, which ultimately contribute to national growth.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map regionally, it's clear that Western Europe generally enjoys a more robust rail infrastructure compared to Eastern Europe. For example, countries like the Netherlands and Switzerland not only have high rail density but also modern systems that prioritize speed and efficiency. In contrast, countries in Eastern Europe, while improving, often face challenges related to outdated infrastructure and limited investment.
Take Poland, for example. The rail density is growing, but many lines still need modernization. Interestingly, Poland's rail system is undergoing significant upgrades, with EU funding helping to revitalize old tracks and introduce high-speed trains. This investment is crucial, as it not only enhances connectivity within the country but also links Poland more effectively with its Western European neighbors.
Another interesting case is Italy, which, despite having a well-developed rail network, faces challenges related to regional disparities. Northern Italy enjoys high-speed trains and well-connected urban centers, while the southern regions still grapple with slower services and less frequency. This disparity often mirrors economic conditions, as regions with better rail access tend to thrive economically.
Significance and Impact
The significance of rail infrastructure cannot be understated. Quality rail systems facilitate commerce, enhance regional integration, and provide a sustainable alternative to road transportation. They also have social implications, allowing people from various backgrounds easy access to education, employment, and leisure activities.
As we look to the future, the trends in rail infrastructure development are promising yet challenging. With initiatives aimed at reducing carbon footprints, the European rail landscape is expected to evolve rapidly in the coming years. The European Green Deal emphasizes investments in sustainable transport modes, including railways, to achieve climate neutrality by 2050.
However, there are hurdles to overcome. Aging infrastructure, regional disparities, and the need for technological advancements pose challenges. Countries must prioritize investments that address not only the physical state of railways but also their integration into broader transportation networks. What's fascinating is how rail transport may shape the urban landscapes of tomorrow, potentially leading to more sustainable and interconnected communities.
In conclusion, the "Km of Rail per 1000 People" map serves as a vital tool for understanding the current state of Europe's rail infrastructure. As we move forward, it will be crucial for policymakers, urban planners, and citizens alike to recognize the importance of investing in railways, ensuring that they continue to serve as the backbone of European connectivity and economic vitality.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 14, 2025
- Views
- 28
Comments
Loading comments...