100 Million Years Old Sediment Map of Alabama

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
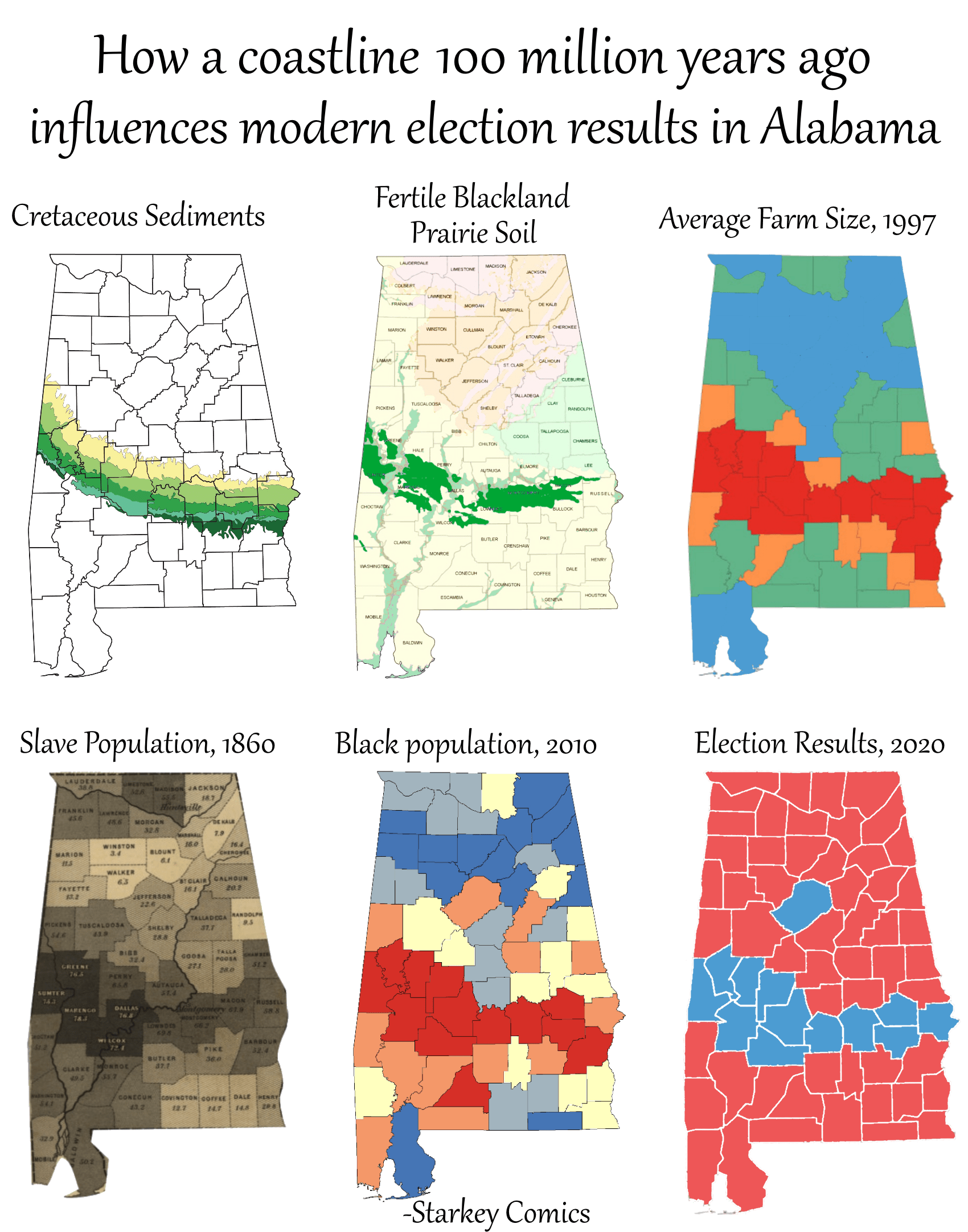
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the distribution and characteristics of sediment deposits in Alabama that are approximately 100 million years old. This ancient sediment provides a window into the geological history of the region, revealing how past environmental conditions have shaped present-day landscapes. The visualization highlights areas where these sediments are most prevalent, inviting a deeper understanding of their impact on the state’s ecology, hydrology, and even socio-economic factors today.
Deep Dive into Ancient Sediments
Sediments, the result of erosion, weathering, and deposition, have a profound effect on the geology and ecology of a region. In Alabama, the sediments that date back 100 million years are primarily composed of materials from the Late Cretaceous period, a time when dinosaurs roamed the Earth and the region was covered by a shallow sea. This period is crucial for understanding not only the geological formations but also the biodiversity that emerged in the region.
Interestingly, these ancient sediments are primarily found in the Gulf Coastal Plain of Alabama, where they contribute to the formation of various geological features, including the state’s sand hills and river basins. Sedimentary rocks, such as limestone and clay, formed from compacted sediments, play a significant role in groundwater systems. In fact, Alabama relies heavily on its aquifers, many of which are fed by these ancient layers of sediment. Have you ever noticed how the landscape changes from the rolling hills in the north to the flat plains in the south? This is largely due to the sedimentary processes that have occurred over millions of years.
What's fascinating is how these sediments impact not only the physical landscape but also the flora and fauna of Alabama. The nutrients found within these deposits support diverse ecosystems, from lush forests in the northeastern part of the state to wetlands in the coastal regions. Understanding sediment composition can help in conservation efforts, especially as climate change threatens these delicate ecosystems.
Moreover, these ancient sediments have economic significance as well. They are sources of clay, gravel, and other materials used in construction and manufacturing. The presence of these sediments can dictate where industries are located and how they develop, thus influencing local economies. Recent studies have shown that regions rich in these ancient deposits often see increased development and investment, tying the geological past to modern economic trends.
Regional Analysis
When examining Alabama's sediment distribution, it's important to consider regional differences. For instance, the northern part of the state, characterized by the Appalachian foothills, features sedimentary deposits that are markedly different from those found in the southern coastal plains. In the north, the sediments often include sandstone and shale, which contribute to the region's unique geological formations, such as the mountains and valleys that attract hiking and outdoor activities.
In contrast, the southern region is dominated by softer sediments, primarily clay and silt, which have implications for agriculture. The fertile soils here support Alabama's robust agricultural sector, particularly in cotton and soybean farming. Interestingly, counties like Baldwin and Mobile, situated along the Gulf Coast, are not only significant for their agricultural outputs but also for their tourism, driven by beautiful beaches formed from millions of years of sedimentation.
The interplay between these sediment types and land use is crucial. For example, areas with clay-rich sediments tend to have higher water retention, making them suitable for certain crops but also susceptible to flooding. Understanding these regional variations helps in crafting effective land management strategies that consider both environmental sustainability and economic viability.
Significance and Impact
The significance of studying these ancient sediments in Alabama cannot be overstated. They are not just relics of the past; they are active players in the current ecological and economic landscape. As climate change continues to alter weather patterns and affect water resources, understanding sediment dynamics becomes critical. For instance, sediment erosion can lead to water quality issues in rivers, impacting both ecosystems and human health.
Moreover, as urban development encroaches on natural landscapes, the preservation of these ancient sedimentary areas is vital for maintaining biodiversity. Conservation efforts can be better informed by understanding sediment types and their historical significance. Current trends show an increasing awareness of the need for sustainable practices that preserve these natural resources while allowing for responsible development.
In conclusion, the map illustrating the distribution of 100 million-year-old sediment in Alabama serves as a reminder of the intricate connections between our geological past and the present. The sediment underfoot tells a story of environmental change and resilience, shaping the land we inhabit and the lives we lead. By recognizing the importance of these ancient deposits, we can better appreciate the rich tapestry of Alabama's geography and its implications for the future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 13, 2025
- Views
- 142
Comments
Loading comments...