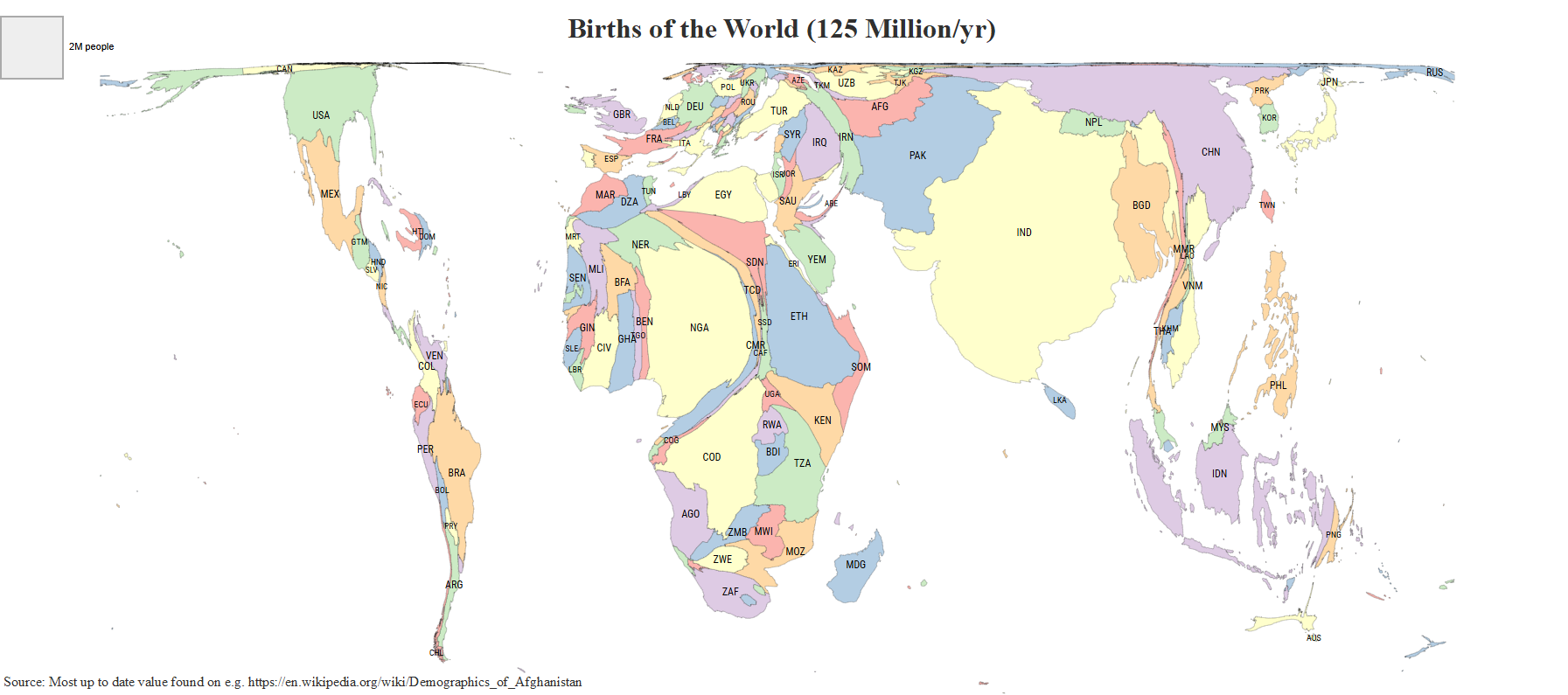
Map of Global Birth Rates by Country

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The interactive map titled "This is where the world's babies are born" provides a compelling visualization of birth rates across various countries. It highlights how many babies are born per 1,000 people in each nation, showcasing the demographic landscape of the globe. This information is vital for understanding population dynamics and trends, which can influence everything from economic policies to healthcare services.
Deep Dive into Global Birth Rates
Birth rates are a critical indicator of a country's demographic health and fertility patterns. The world’s average birth rate has seen significant changes over the past century, largely driven by social, economic, and health factors. Interestingly, the global average birth rate has dropped from approximately 40 births per 1,000 people in the 1960s to around 18 births per 1,000 today. This decline is attributed to increased access to education, particularly for women, advancements in healthcare, and a shift in societal norms regarding family size.
Countries with high birth rates, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa, often have rates exceeding 30 births per 1,000 people. For instance, Niger, one of the countries with the highest birth rate, reports around 44 births per 1,000 in recent years. This phenomenon can be linked to numerous factors, including cultural preferences for larger families, lower access to contraception, and higher child mortality rates, which encourage families to have more children.
In contrast, nations with low birth rates, such as Japan and Italy, report figures around 7-9 births per 1,000. These countries are grappling with aging populations and declining workforce numbers, leading to serious economic implications. The low birth rates here are often associated with high costs of living, career prioritization, and societal shifts towards smaller family units.
Interestingly, what’s also noteworthy is the impact of migration on birth rates. Countries that attract a significant number of immigrants often see variations in birth rates due to the different cultural backgrounds and fertility preferences of the arriving populations. For example, the United States has a relatively stable birth rate, but the influx of immigrants from high-birth-rate countries has contributed to localized increases in fertility rates in certain communities.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can identify distinct regional trends in birth rates. In Africa, the birth rate is predominantly high, with countries like Chad and Mali also reporting numbers above 30 births per 1,000 people. This region is characterized by youthful populations and rapid population growth, which can present both opportunities and challenges for developmental policies.
Conversely, Europe exhibits some of the lowest birth rates globally. Countries like Germany and Spain have struggled with rates below 10 births per 1,000. This situation has resulted in various initiatives to encourage higher fertility rates, including parental leave policies and financial incentives for families. However, these measures have yet to produce significant changes in birth patterns.
Asia presents a mixed bag; countries like India maintain moderately high birth rates (around 20 births per 1,000), while others like South Korea face severe declines, reportedly below 8 births per 1,000. The differences can often be explained by economic development levels, urbanization rates, and cultural attitudes towards family size.
Significance and Impact
Understanding birth rates is crucial for several reasons. From a socio-economic perspective, high birth rates can indicate potential for population growth, which might lead to a larger workforce. However, they can also strain resources, including education and healthcare systems, if not matched with adequate infrastructure.
On the other hand, low birth rates present their own set of challenges, such as an aging population and potential labor shortages, which can impede economic growth. Countries facing this dilemma are increasingly looking to immigration as a solution to bolster their workforce.
Looking ahead, trends suggest that global birth rates will continue to decline, particularly as education and healthcare access improve worldwide. However, the implications of these changes are vast and complex, impacting everything from economic growth to social stability. Have you noticed how these demographic shifts are influencing global policies and international relations? The way nations respond to these trends will shape the future of our global society.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 6, 2025
- Views
- 40
Comments
Loading comments...