Genders of Capital Cities in Poland Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
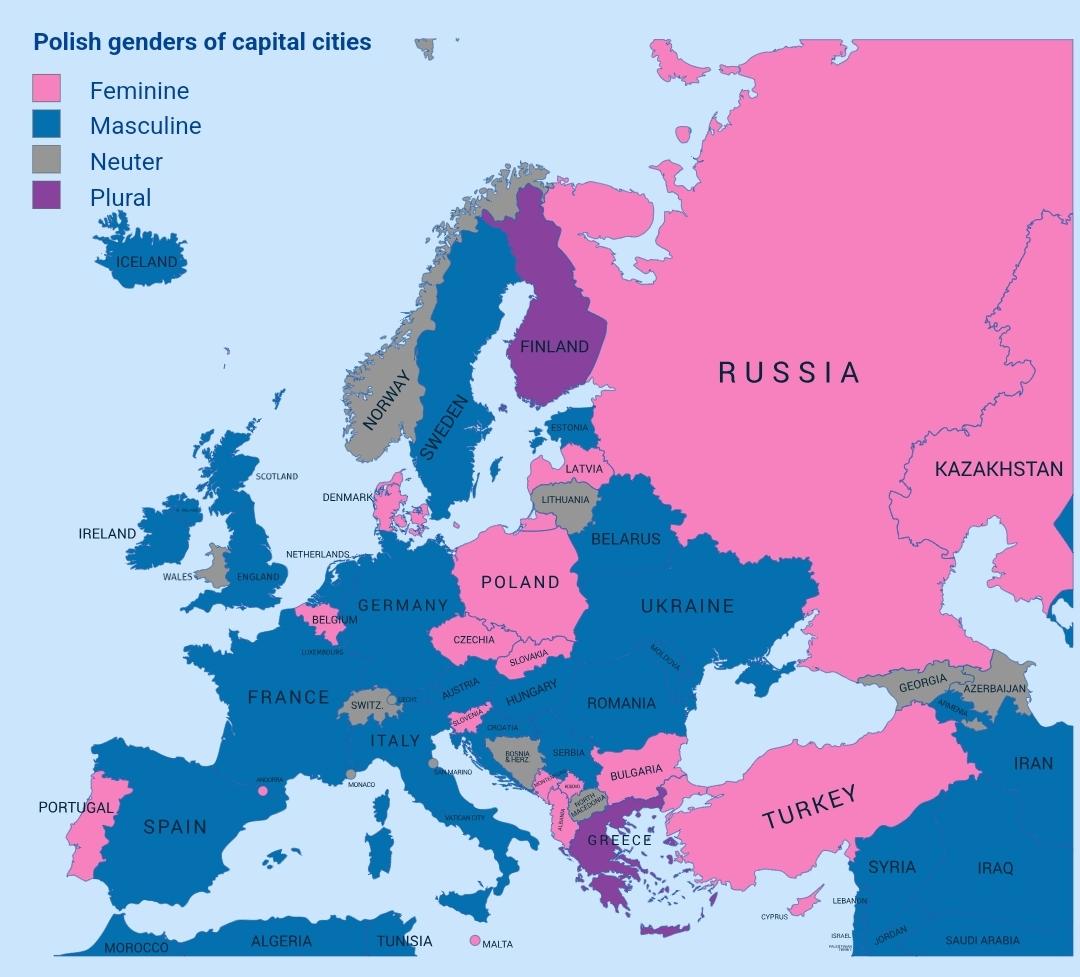
What This Map Shows
The "Genders of Capital Cities in Poland Map" provides a unique perspective on the linguistic aspect of Polish capital cities. This visualization categorizes each capital based on the grammatical gender of its name in the Polish language: masculine, feminine, or neuter. Interestingly, this seemingly simple classification unveils a deeper layer of cultural and linguistic identity in Poland's urban landscape.
Deep Dive into Grammatical Genders in Polish
Grammatical gender is a fascinating aspect of the Polish language that affects nouns, adjectives, and even verbs. In Polish, every noun is assigned a gender, which can significantly influence the way individuals perceive the world around them. Capital cities, as prominent places of governance and culture, reflect this linguistic phenomenon.
You may wonder why gender matters in language. In Polish, masculine nouns often denote strength or authority, while feminine nouns may evoke care and nurturing qualities. The neuter gender, on the other hand, tends to be associated with inanimate objects or abstract concepts. As such, the gender of a capital city can offer insights into historical and cultural perceptions.
For instance, Warsaw, the capital, is feminine (Warszawa), while Wrocław and Poznań are masculine (Wrocław and Poznań). This distinction might seem trivial, but it can influence local identity and pride. Additionally, names like Kraków highlight the importance of historical context, as cities were often named after figures or characteristics that resonate with their current identities.
Interestingly, many cities have undergone name changes throughout history, often reflecting political shifts. For example, the evolution of names during various partitions and the impact of World War II have shaped the current linguistic landscape. The gender of a city name can also be indicative of historical significance; cities that were once strongholds of culture and politics may retain masculine names, suggesting a legacy of power.
Furthermore, the interplay between gender and urban development is noteworthy. Cities labeled with feminine names often nurture a sense of community and family, perhaps influencing urban policies that focus on social welfare and education. In contrast, cities with masculine names may prioritize industrial development and economic growth. This connection between grammar and urban policy is an area ripe for exploration.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map regionally reveals interesting patterns in the gender distribution of capital cities. For instance, in the southern region, cities like Kraków and Katowice, both masculine, symbolize historical strength and resilience. They are known for their rich cultural heritage and robust economic sectors. In contrast, northern cities such as Gdańsk and Szczecin, where names are feminine, often highlight maritime culture and community-oriented initiatives.
Moreover, if we examine the central region, we find that Warsaw stands out as a feminine capital, showcasing a blend of modernity and tradition. It acts as a hub for political power, business, and education, reflecting a balance between masculine and feminine qualities in its urban planning. Interestingly, this duality could suggest a more inclusive approach to governance.
However, the map also illustrates the geographical disparities in urban development across genders. For example, while masculine cities may dominate in terms of economic output, feminine cities often excel in social metrics such as education levels and healthcare access. This begs the question: how do these gendered perceptions shape the lived experiences of residents?
Significance and Impact
Understanding the grammatical gender of capital cities in Poland is more than an academic exercise; it carries real-world implications. As language shapes thought, the way we refer to cities can influence attitudes and policies. For instance, if a city is perceived as nurturing (feminine), it may attract more family-oriented businesses and social services.
Moreover, as Poland continues to evolve in the global landscape, the significance of gender in urban identity could affect tourism and cultural heritage initiatives. Policymakers may need to consider how these linguistic nuances could shape urban branding and marketing strategies.
Current trends indicate a growing interest in linguistic diversity and its impact on urban development. As global conversations around gender and identity gain traction, the way we discuss and perceive our cities will undoubtedly evolve. This shift could lead to a more nuanced understanding of how language influences not just culture, but also economics and social dynamics.
In conclusion, the "Genders of Capital Cities in Poland Map" serves as a compelling reminder of the intricate relationship between language and identity. By delving into the grammatical gender of these urban centers, we uncover layers of meaning that enrich our understanding of Polish culture and its cities.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 5, 2025
- Views
- 48
Comments
Loading comments...