Obesity Rates Map of Adults Aged 18 and Older

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
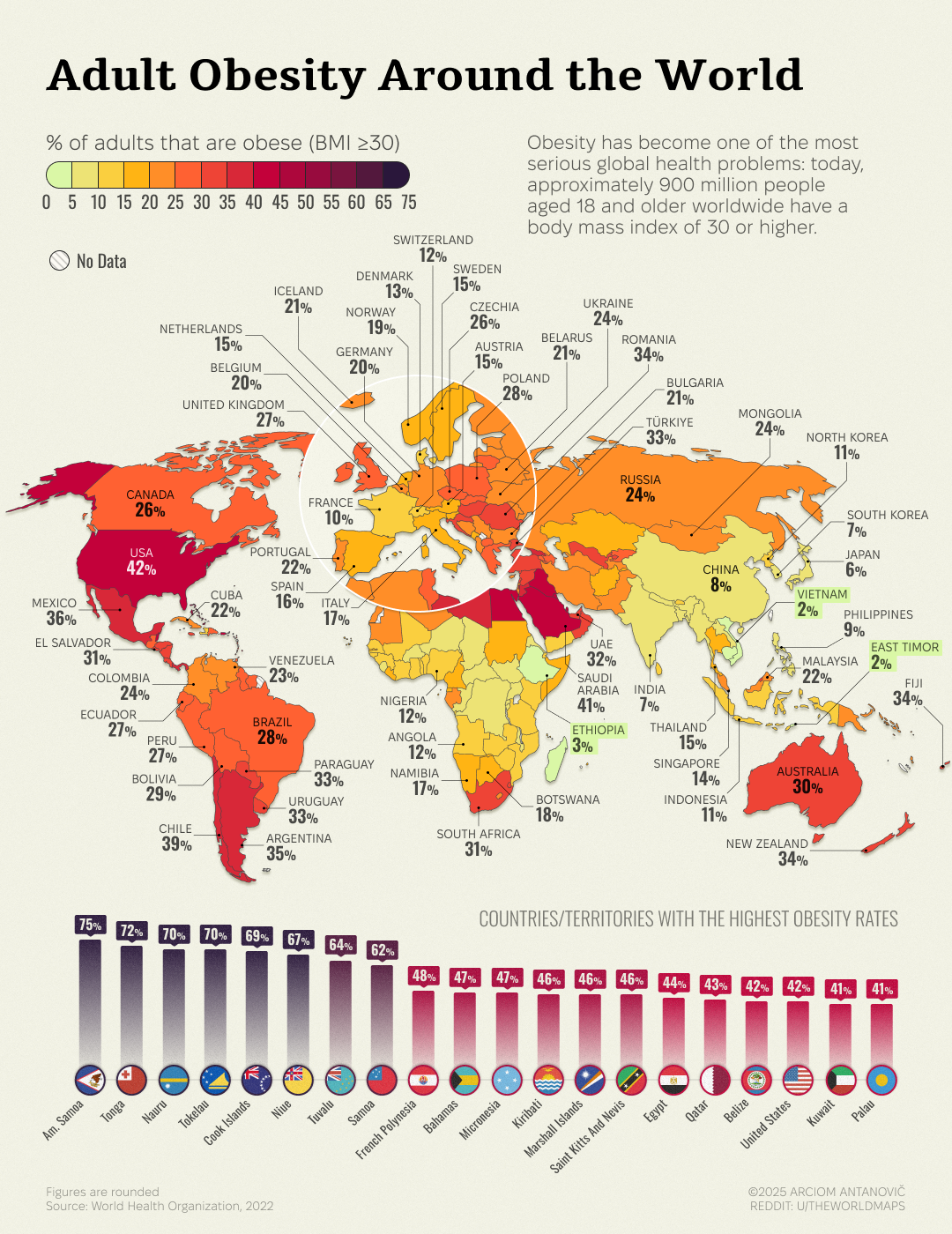
What This Map Shows
This map visually represents the percentage of adults aged 18 and older who are classified as obese in various regions. Through color coding, it offers a clear snapshot of obesity prevalence across different areas, highlighting how this public health issue varies geographically. The visualization prompts us to consider not just the numbers, but the underlying factors contributing to such disparities.
Deep Dive into Obesity
Obesity is a complex health issue that affects millions of individuals and is defined by a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. It has been linked to a myriad of health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Interestingly, the causes of obesity are multifaceted, encompassing genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors.
One significant driver of obesity is dietary habits. In many urban areas, access to healthy food options can be limited, leading to higher consumption of processed foods that are calorie-dense but nutrient-poor. Conversely, regions with vibrant local markets or agricultural production often showcase lower obesity rates. Have you ever noticed how accessibility to fresh produce can influence dietary choices?
Physical activity levels also play a pivotal role in obesity rates. Urban settings may present challenges for outdoor activity due to limited green spaces, while rural areas might encourage more physical labor and outdoor pursuits. Additionally, cultural attitudes towards body image and health can greatly affect lifestyle choices. For instance, in some cultures, being overweight may not carry the same negative connotations it does in others, which can influence individuals' health decisions.
The prevalence of obesity is not static; it has been steadily rising over the past few decades. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the global prevalence of obesity nearly tripled between 1975 and 2016. What's fascinating is how different countries and regions respond to this growing crisis. Some have enacted public health initiatives aimed at curbing obesity through education and promoting healthier lifestyles, while others grapple with the economic implications of a population burdened by weight-related health issues.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map of obesity rates, distinct regional patterns emerge. For instance, the Southern United States often showcases higher obesity percentages compared to the Northeast. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) frequently highlights states like Mississippi and Arkansas with obesity rates exceeding 35%. In contrast, states like Colorado and Hawaii typically report much lower rates, around 25% or less.
Interestingly, urban versus rural dynamics also play a role. Cities such as New York and San Francisco, despite their high population densities, often promote healthier lifestyles through walkable environments and a plethora of healthy dining options, leading to comparatively lower obesity rates. On the other hand, rural areas may face higher obesity rates due to limited access to healthcare and recreational facilities.
Internationally, the trends are equally compelling. Countries like Mexico and the United States report high obesity rates, while many Asian countries have lower percentages. However, emerging economies are witnessing rising obesity as lifestyles change and western diets are adopted. This shift raises alarm bells about the long-term health implications in these regions, where healthcare systems may not yet be equipped to handle the surge in obesity-related conditions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding obesity rates is crucial not only for public health planning but also for addressing broader socioeconomic issues. The implications of high obesity rates extend beyond individual health; they affect healthcare costs, workforce productivity, and overall quality of life. As healthcare systems strain under the weight of preventable diseases, communities must engage in proactive measures to address the root causes of obesity.
Current trends indicate a dual challenge: while some regions are successfully implementing strategies to combat obesity, others remain stagnant or are even seeing increases. Future projections suggest that without concerted efforts, obesity rates could continue to rise, leading to a plethora of health complications. This is a call to action for governments, communities, and individuals alike. Ever wondered what role you could play in promoting healthier lifestyles around you? It starts with awareness and education, paving the way for a healthier future for all.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 5, 2025
- Views
- 18
Comments
Loading comments...