Ethnic Composition of the Middle East Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
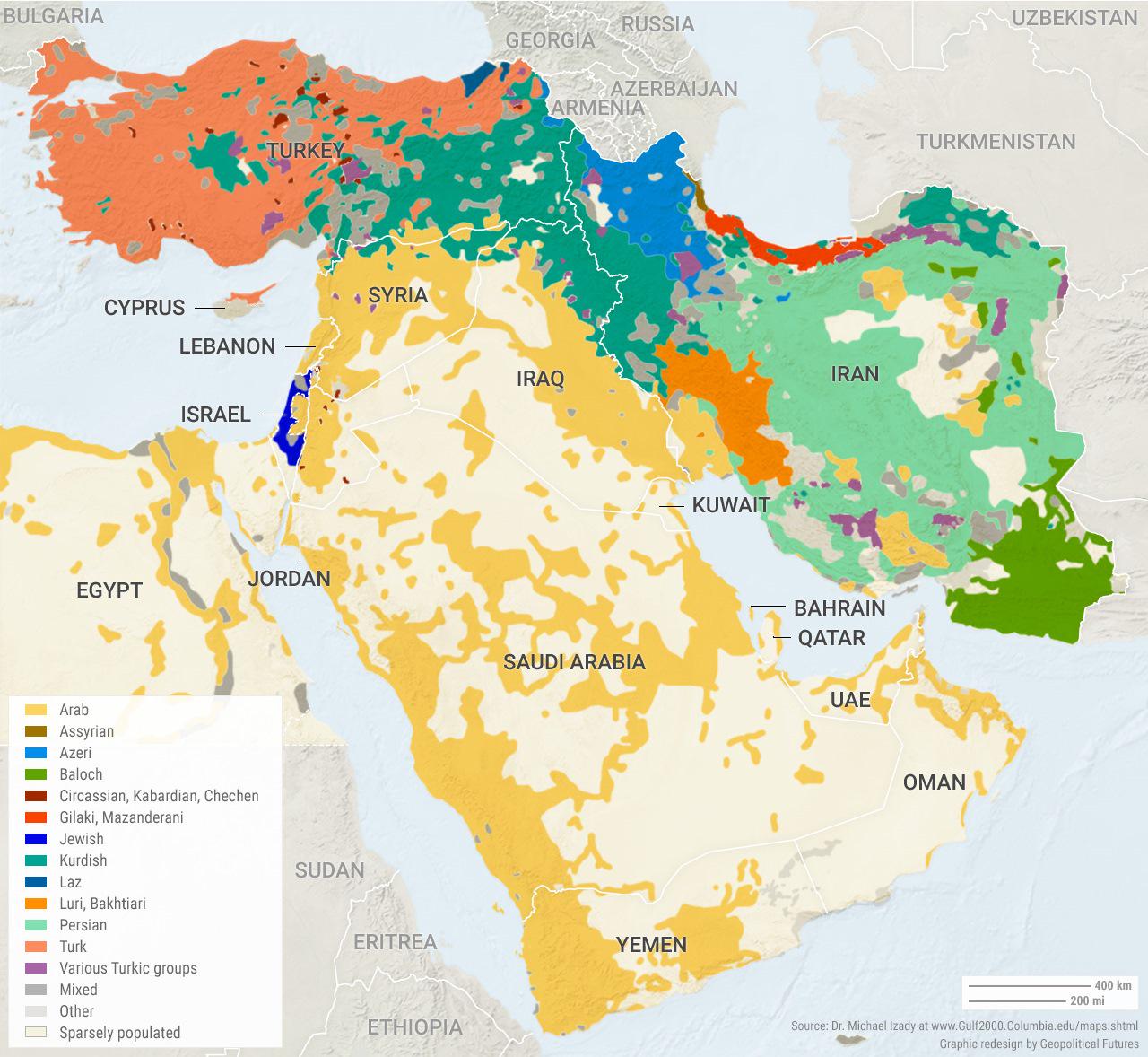
What This Map Shows
The "Ethnic Composition of the Middle East" map provides a detailed overview of the diverse ethnic groups residing in this historically rich and complex region. It visually represents the distribution of various ethnic communities across countries like Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Syria, and the Gulf states, highlighting the intricate tapestry of identities that coexist here. Understanding the ethnic landscape is crucial, as it shapes not only the cultural dynamics but also the political and social frameworks of these nations.
Deep Dive into Ethnic Composition
The Middle East, often referred to as the cradle of civilization, is home to a multitude of ethnic groups, each with its own unique history, traditions, and languages. The predominant groups include Arabs, Persians, Kurds, Turks, and smaller communities such as Assyrians, Armenians, and Druze.
Interestingly, Arabs are the largest ethnic group in the region, primarily concentrated in countries like Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Egypt, and Iraq. Their cultural influence is significant, given that the Arabic language is a unifying factor across many nations. However, the Arab identity is nuanced, with various dialects and cultural practices that vary from one country to another.
Persians, primarily found in Iran, make up the second-largest ethnic group. The Persian language, Farsi, is a key aspect of their identity, and Iran’s rich historical context adds layers to its cultural fabric. It’s fascinating to note that despite the regional tensions, many Persians share a cultural heritage with their Arab neighbors, dating back to ancient empires.
Kurds represent another vital ethnic group, mainly inhabiting the mountainous regions of Turkey, Iraq, Iran, and Syria. As one of the largest ethnic groups without a state, the Kurdish population has long pursued autonomy and recognition. The ongoing struggles for Kurdish rights and identity have significant implications for regional stability.
The Turks, predominantly in Turkey, have a unique cultural identity influenced by a blend of Central Asian, Middle Eastern, and Balkan heritages. The Turkish language is one of the most widely spoken in the region, and their geopolitical position has historically made them a bridge between Europe and Asia.
Other smaller ethnic groups, such as the Assyrians and Armenians, have also contributed to this mosaic. They often face challenges in preserving their languages and cultures amid larger dominant groups. For instance, the Assyrian community, primarily Christian, has seen significant declines in population due to conflicts and persecution.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map closely, one can see distinct ethnic concentrations throughout the region. For example, in Iraq, the Arab and Kurdish populations dominate, but the presence of Turkmen and Assyrians adds to the country’s diversity. The complex interplay between these groups has historically led to both collaboration and conflict, particularly in the context of political power struggles.
In Syria, the ethnic landscape is equally complex. The Alawite minority, a sect of Shia Islam, holds significant political power, while Sunni Arabs form the majority. The civil war has intensified ethnic and sectarian divides, leading to a humanitarian crisis that affects millions.
Interestingly, Lebanon is another example where ethnic and religious identity is paramount. The country’s confessional political system is designed to maintain a balance among its various communities, including Christians, Sunni Muslims, and Shia Muslims. This delicate balance is continually tested by regional tensions and internal divisions.
In contrast, countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE showcase a more homogeneous Arab identity, though they are home to significant expatriate communities from South Asia, the Philippines, and other regions, which contribute to their multicultural environments.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the ethnic composition of the Middle East is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. Ethnic identities play a crucial role in shaping national policies, social dynamics, and international relations. For instance, the ongoing conflict in Syria demonstrates how ethnic and sectarian identities can escalate into violence, with profound humanitarian consequences.
Furthermore, as globalization continues to influence the region, there are emerging trends in inter-ethnic relations. The younger generation, more exposed to global cultures through technology, is beginning to challenge traditional boundaries and prejudices. This shift could lead to new forms of identity that integrate multiple ethnic influences.
Looking ahead, the ethnic composition of the Middle East will remain a critical area of study. As countries navigate issues of nationalism, migration, and conflict, the way these ethnic identities interact will undoubtedly shape the future. Understanding this map is essential for grasping the complexities of the region, as it provides insight into not just who lives there, but how they live and interact within an evolving geopolitical landscape.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 2, 2025
- Views
- 52
Comments
Loading comments...