Nomad Empires of Europe Migration Routes Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
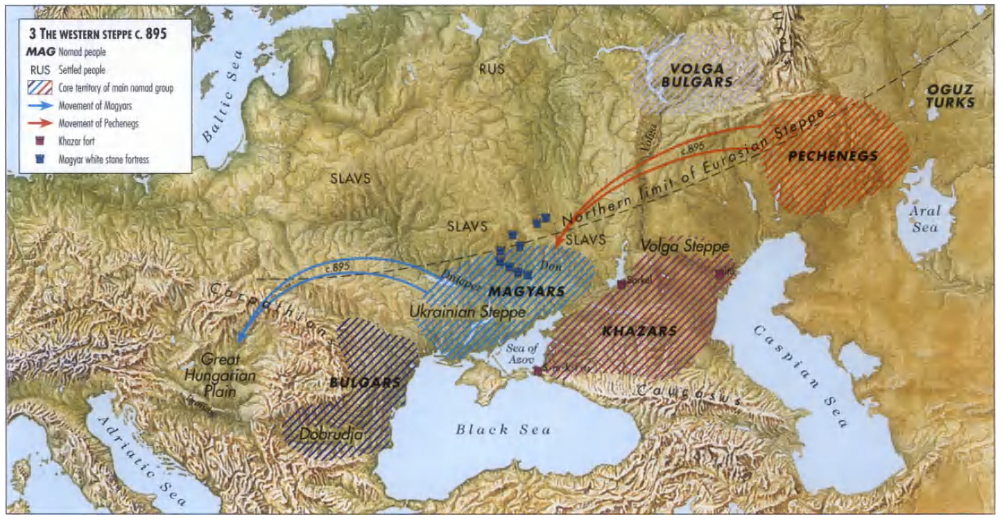
What This Map Shows
This map vividly illustrates the migration routes of various nomadic empires across Europe, highlighting their expansive territories and the paths they traversed throughout history. Nomadic empires like the Huns, Mongols, and Vikings played crucial roles in shaping the geopolitical landscape of Europe. These routes not only depict movement but also reflect cultural exchanges, trade networks, and sometimes, conflicts that influenced the region's development.
Deep Dive into Nomadic Empires
Nomadic empires have existed for millennia, characterized by their mobile lifestyles, which often contrasted with the sedentary agricultural societies surrounding them. The Huns, for instance, emerged in the 4th century AD and were known for their horse-riding prowess and swift hit-and-run tactics. They migrated from Central Asia into Eastern Europe, significantly impacting the Roman Empire and leading to its eventual decline. Interestingly, their movement was not just about conquest; it was also about seeking new pastures for their livestock, a necessity for survival in their harsh environment.
Another prominent nomadic group was the Mongols, who, although primarily associated with Asia, extended their influence into Eastern Europe during the 13th century. Under Genghis Khan, they created one of the largest empires in history, and their migration routes included key areas such as present-day Ukraine and Poland. The Mongol invasions not only altered the political boundaries of Europe but also facilitated trade along the Silk Road, introducing goods and ideas that would shape European culture.
Perhaps one of the most well-known nomadic groups in Europe are the Vikings. Originating from Scandinavia, the Vikings were skilled seafarers who established trade routes and settlements across Europe, stretching from the British Isles to the Mediterranean and even reaching North America. Their migration was driven by a combination of overpopulation, seeking wealth, and the quest for new lands. The Viking Age, which lasted from the late 8th century to the early 11th century, left a lasting legacy on European history, influencing language, culture, and trade.
Notably, these nomadic empires shared common characteristics: they were adaptable and skilled in navigating diverse terrains, whether it be the steppes of Central Asia or the rivers of Europe. This adaptability was essential for their survival, allowing them to thrive in various environments. Furthermore, their interactions with settled societies led to significant cultural exchanges, with nomads often adopting elements of local customs while also imparting their traditions.
Regional Analysis
Examining the migration patterns of these nomadic empires reveals fascinating regional variations. For example, in Eastern Europe, the Huns and later the Mongols moved through the steppes, which provided ample grazing lands for their herds. The fertile plains of Hungary, for instance, became a significant battleground during the Mongol invasions, showcasing the strategic importance of this area for nomadic groups.
In contrast, the Vikings were primarily maritime nomads who utilized their longships to navigate the coastal waters and rivers of Europe. Their routes often led them along the rivers of France and Germany, where they established trading posts and settlements. One notable example is the city of Paris, which was heavily influenced by Viking raids and trade.
Interestingly, the Iberian Peninsula also saw nomadic influences, particularly from the Moors, who, while not traditional nomads in the same sense, brought a different kind of movement and cultural exchange to Europe. Their migration routes through Spain and Portugal led to significant advancements in agriculture, science, and architecture, leaving an indelible mark on the region.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the migration routes of nomadic empires in Europe is crucial not just for historical knowledge but also for recognizing the ongoing impacts of these movements. These migration patterns shaped the political boundaries we see today and influenced cultural identities. Moreover, the legacy of nomadic empires can be observed in contemporary discussions about migration, identity, and globalization.
Current trends show a resurgence of interest in nomadic lifestyles, particularly in the context of sustainability and environmental consciousness. As people grapple with the challenges of urbanization and climate change, the adaptability and resilience demonstrated by historical nomadic peoples offer valuable lessons. It's fascinating to think about how these ancient migration patterns can inform our understanding of modern societal shifts.
In conclusion, the migration routes of nomadic empires across Europe represent more than just paths on a map; they signify a complex web of interactions that have shaped the continent's history and culture. As we continue to explore our own migration narratives, the stories of the Huns, Mongols, and Vikings remain relevant and inspiring.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 29, 2025
- Views
- 52
Comments
Loading comments...