Accurate Map of Venice 1729

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
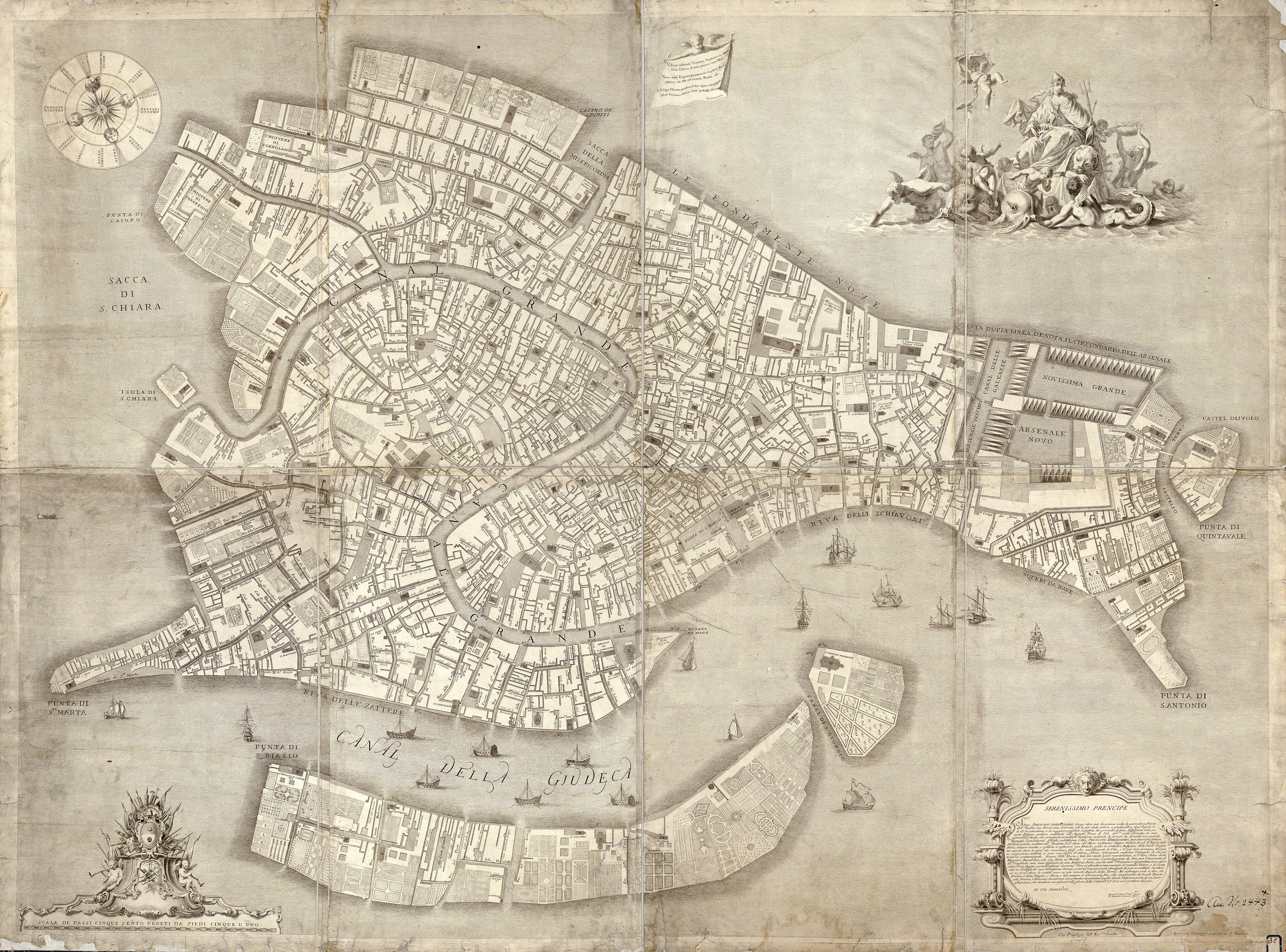
What This Map Shows
The 1729 map of Venice stands as a monumental achievement in cartography. This visualization captures the intricate layout of Venice, showcasing its canals, bridges, and buildings with unprecedented accuracy for its time. It reflects not just the geography of the city, but also its cultural and economic significance during the 18th century. The map highlights the unique relationship between land and water in this iconic city, and its detailed representation reveals the urban planning and architectural styles prevalent during the Venetian Republic.
Deep Dive into Venice’s Geographic Landscape
Venice, renowned for its stunning canals and rich history, is built on a lagoon, which is home to over 100 small islands. The 1729 map emphasizes the city's striking network of waterways, which are vital for transportation, trade, and daily life. Interestingly, the canals serve not only as thoroughfares but also as essential components of the city’s infrastructure, influencing its urban development.
One of the map's most notable features is the Grand Canal, which snakes through the heart of Venice and acts as the main waterway. Did you know that this canal is approximately 3.8 kilometers long and has an average width of 30 meters? The Grand Canal is lined with over 170 buildings, many of which are historical palaces that date back to the 13th century. These structures reflect a blend of Gothic, Renaissance, and Baroque architectural styles, showcasing Venice’s rich cultural tapestry.
The 1729 map also demonstrates the city’s strategic importance in trade, as Venice was a significant maritime power in the Mediterranean. At that time, the city was a hub for commerce, connecting Europe to the East, particularly through trade routes that brought spices, silk, and other goods from Asia. The waterways depicted in the map indicate how commerce flowed through the city, with canals acting as the arteries of Venetian life.
Moreover, the map provides insight into the city’s environmental challenges. The lagoon is a delicate ecosystem that has faced threats from rising sea levels and pollution, issues that are increasingly relevant today. Historically, Venice has dealt with flooding, a phenomenon known as 'acqua alta', which has been exacerbated by climate change. The 1729 map serves as a historical reference point for understanding how urban planning has evolved in response to these environmental challenges.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map more closely, you can see distinct districts within Venice, each with its own character and function. The area known as San Marco is prominently featured, home to the famous St. Mark’s Basilica and the Doge’s Palace. This district was the political and religious heart of Venice, attracting both locals and tourists, which contrasts sharply with the quieter, residential areas like Cannaregio.
Interestingly, the contrast between the bustling streets of San Marco and the serene canals of Dorsoduro illustrates the diverse urban dynamics of Venice. While San Marco thrives on tourism, Dorsoduro features art galleries and local residences, giving it a different atmosphere. The map allows viewers to appreciate these variances and understand the social fabric of Venetian society.
Furthermore, the 1729 map reveals the expansion efforts of the city during this period. The development of new islands and the reclamation of land for building projects are evident, showcasing how Venice has continually adapted to its needs. The areas indicated for future development reflect the city’s ambition to grow and modernize while maintaining its historical identity.
Significance and Impact
The 1729 map of Venice is not just a historical document; it holds immense significance for understanding the evolution of urban environments. The accuracy and detail represented in this map provide critical insights into the socio-economic conditions of the time. It prompts us to consider questions about how geography influences urban planning and community life.
Today, as Venice grapples with modern challenges such as tourism overload and environmental sustainability, the lessons drawn from this historical map remain relevant. Observing how Venice has navigated its geographical constraints can inform current urban planning efforts in other cities facing similar issues. The interplay between water and land in Venice teaches us about adaptation and resilience, illustrating the importance of historical references in crafting future solutions.
Moreover, the ongoing preservation efforts aimed at protecting Venice's unique architectural heritage and addressing climate change showcase the enduring impact of this map. As we reflect on the 1729 map, we are reminded of the complex relationship between geography, history, and culture, and how it shapes our understanding of urban environments in a contemporary context.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 26, 2025
- Views
- 56
Comments
Loading comments...