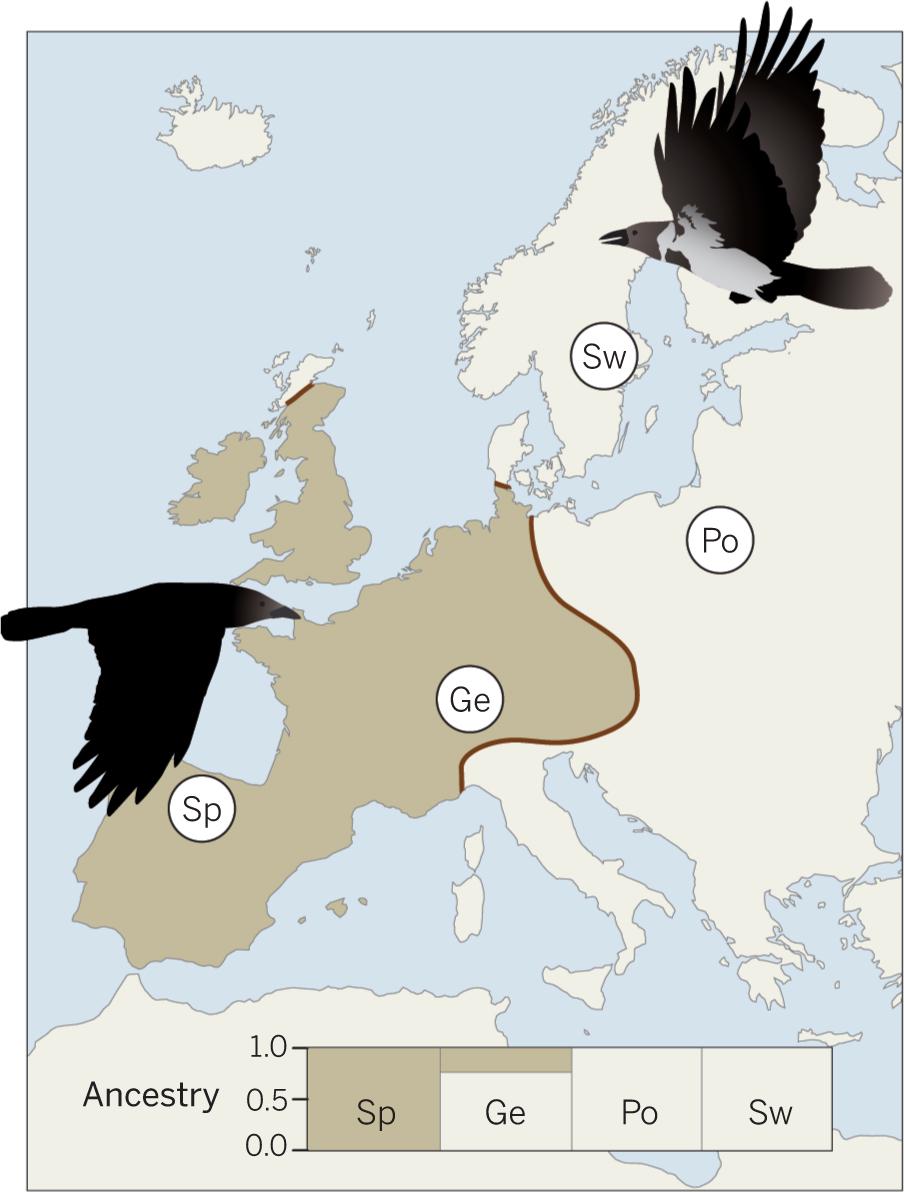
Carrion vs Hooded Crow Distribution Map in Europe

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Carrion vs Hooded Crow Distribution Map in Europe" provides a visual representation of the geographical ranges of two closely related crow species: the Carrion Crow (Corvus corone) and the Hooded Crow (Corvus cornix). This map highlights the distinct territories these birds occupy across various European regions, showcasing not only their overlaps but also their preferences for different habitats and climates.
Understanding the distribution of these crows is essential for ornithologists and bird enthusiasts alike, as it reflects broader environmental patterns and can indicate changes in ecosystems. So, what exactly do these crow species tell us about their habitats?
Deep Dive into Crow Species
Crows are part of the Corvidae family, known for their intelligence and adaptability. The Carrion Crow is predominantly found in western and central Europe, while the Hooded Crow occupies the northern and eastern parts. Interestingly, the Hooded Crow is often identified by its distinctive gray plumage contrasted with its black head and wings, while the Carrion Crow is entirely black.
Both species are scavengers, which means they play a vital role in the ecosystem by helping to clean up carrion. However, their preferred habitats differ slightly. The Carrion Crow favors open fields, woodlands, and urban areas, demonstrating remarkable adaptability to human environments. In contrast, the Hooded Crow is often found in coastal areas, marshes, and rural landscapes, showcasing a preference for more diverse habitats that include both land and water.
What's fascinating is how these birds have adapted their diets based on their environments. Carrion Crows will consume a wide range of food items, from insects to small mammals, and even human food waste, while Hooded Crows often rely on marine resources such as fish and crustaceans in addition to terrestrial prey. This dietary flexibility contributes to their success in various habitats.
Moreover, these species exhibit interesting social behaviors. Crows are known to be highly intelligent, often utilizing tools and displaying complex social interactions. For instance, they can recognize human faces and have been observed passing this information to other crows, which is essential for their survival. This intelligence is crucial for their survival, especially in areas where they encounter threats from both natural predators and human activities.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the distribution of these crows by region, significant variations emerge. In the UK and Ireland, the Carrion Crow dominates, often seen in urban centers and agricultural lands. Its adaptability to human presence is evident, as it thrives in cities where food sources are abundant. On the other hand, the Hooded Crow is prevalent in Scotland and Ireland's coastal areas, showcasing a remarkable ability to exploit marine environments.
In Eastern Europe, particularly in countries like Poland and the Baltic states, the distribution becomes more intricate. Here, both species can often be found overlapping, which raises interesting questions about competition and habitat preference. For instance, in urbanized regions, Carrion Crows tend to outnumber their Hooded counterparts, indicating a possible shift in the balance of their populations.
In Scandinavia, the Hooded Crow's preference for coastal habitats becomes more pronounced, while Carrion Crows are more common inland. This difference is likely due to the availability of food resources and environmental conditions that favor one species over the other.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of Carrion and Hooded Crows is more than just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. Changes in their distribution can indicate shifts in environmental health, such as habitat destruction or climate change impacts. For instance, an increase in Carrion Crow populations in urban areas may signal greater human-wildlife interactions, raising concerns about biodiversity and the health of urban ecosystems.
Moreover, conservation efforts can benefit from this knowledge. Recognizing the territories and behaviors of these crows can aid in developing strategies to protect their habitats, especially in areas where urbanization threatens their natural environments. Additionally, as climate patterns shift, monitoring these species can help predict how avian populations may respond to changing conditions.
In conclusion, the Carrion vs. Hooded Crow Distribution Map in Europe serves as a valuable tool for understanding these fascinating birds' ecological roles. By studying their distribution patterns, we gain insights into broader environmental trends and the interplay between wildlife and human activity, highlighting the importance of preserving natural habitats for future generations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 25, 2025
- Views
- 52
Comments
Loading comments...