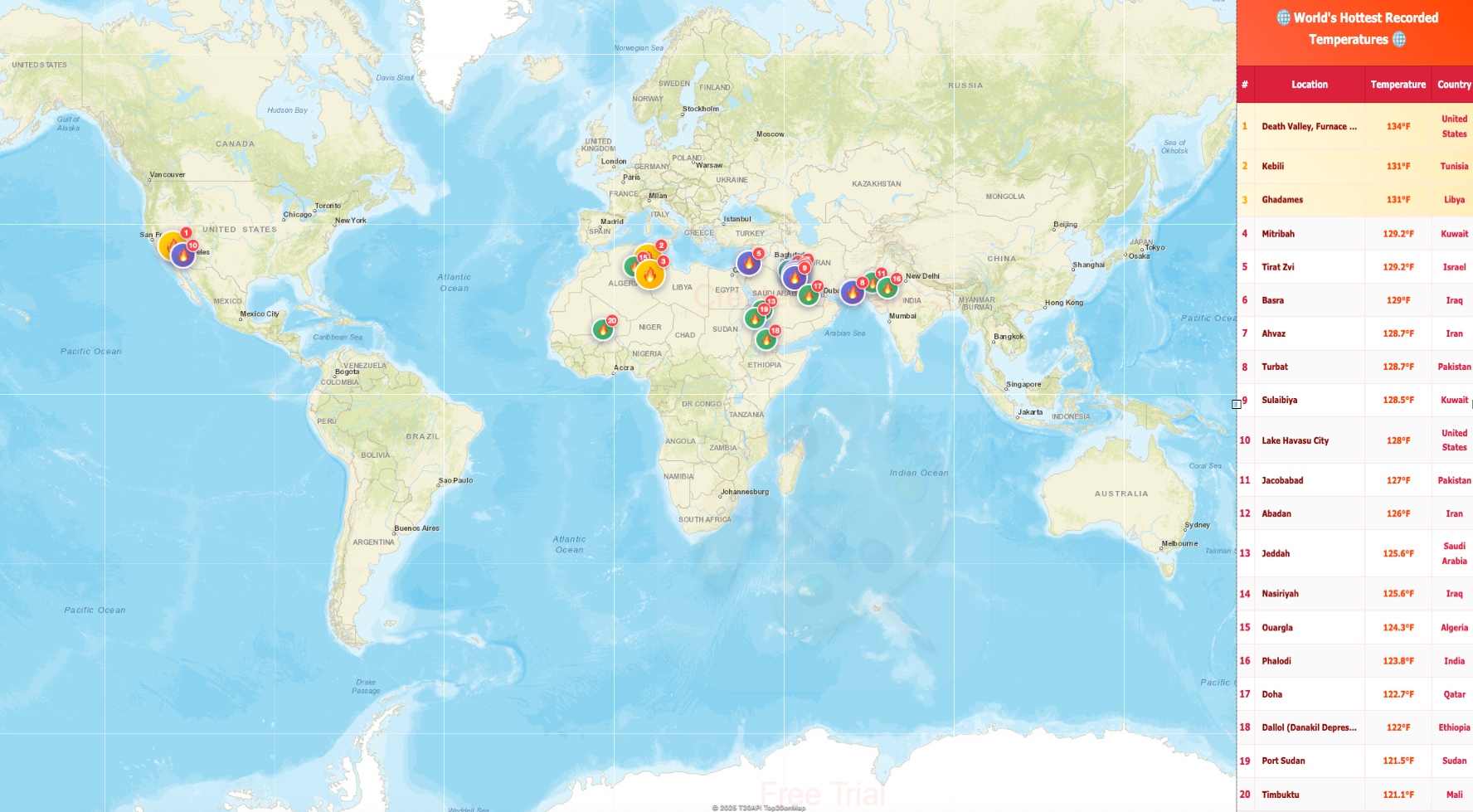
Map of World’s Hottest Recorded Locations

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "World’s Hottest Recorded Locations" highlights the extreme temperatures recorded across the globe, focusing on the hottest 20 locations known to humanity. What’s particularly striking about this map is that every single one of these record-setting temperatures is located in the Northern Hemisphere, showcasing a geographical phenomenon that underscores the relationship between latitude, climate, and geography.
Deep Dive into Extreme Heat
Let’s delve into the specifics of what contributes to these extreme temperatures. The Earth’s climate is influenced by a variety of factors, but when it comes to heat records, latitude plays a crucial role. Most of the hottest places on Earth are situated within a narrow band known as the subtropical desert belt, primarily between 20°N and 32°N latitude. This region is characterized by high-pressure systems that inhibit cloud formation and precipitation, enabling the sun's rays to heat the land to scorching levels.
Interestingly, the list of the hottest places is dominated by deserts. Death Valley in California, USA, holds the record for the highest air temperature ever recorded at 134°F (56.7°C) in 1913. This extreme heat is largely a result of Death Valley's unique topography, which is below sea level and surrounded by mountains that trap heat.
In addition to Death Valley, other notable high-temperature locations include Kebili in Tunisia, where temperatures reached 131°F (55°C), and the city of Ahvaz in Iran, which recorded a blistering 128°F (53.9°C). These areas share similar climatic features: dry air, minimal vegetation, and a high incidence of solar radiation.
Furthermore, the concentration of extreme heat records in the Northern Hemisphere is intriguing. With 13 out of the 20 hottest temperatures clustered between 20°N and 32°N, it raises the question of how geographical features, such as mountains and ocean currents, might influence weather patterns. The presence of large landmasses like Africa and Asia contributes to these high temperatures due to their extensive desert regions.
Regional Analysis
Breaking this down regionally, the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) emerge as hotbeds of extreme heat. Countries like Kuwait and Iraq have recorded some of the highest temperatures in recent years, underscoring the impact of climate change and urbanization on local climates. In 2016, Kuwait recorded temperatures that soared to 129°F (54°C), showcasing the increasing intensity of heat in these regions.
In contrast, while the southern hemisphere has its own hot spots, such as the Australian deserts, it hasn't managed to record temperatures that rival the extremes of the Northern Hemisphere. Notably, Australia’s hottest temperature was recorded at 123°F (50.7°C), significantly lower than those in the Northern Hemisphere, which prompts further inquiry into the climatic and geographical differences between these regions.
Moreover, the economic implications of these extreme temperatures cannot be ignored. Regions that experience such heat often face challenges related to water scarcity, agriculture, and health issues. For instance, the agricultural productivity in these hot regions is severely impacted by the lack of water and the need for irrigation, which can lead to food insecurity.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geographical distribution of the hottest recorded temperatures is essential for multiple reasons. First, it highlights the vulnerability of certain regions to climate change, as increasing temperatures may exacerbate existing challenges, such as droughts and heatwaves. As global temperatures rise, the patterns of extreme heat could shift, potentially creating new hotspots in regions that are currently more temperate.
Moreover, this concentrated heat phenomenon poses serious health risks, especially for vulnerable populations. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to heat-related illnesses and even fatalities. As such, cities and governments must prepare by developing heat action plans and improving infrastructure to mitigate the effects of extreme heat.
In conclusion, the map of the world's hottest recorded locations is not just a testament to the extremes of our planet but also a call to action for understanding and addressing the climatic challenges that come with it. As we move forward, the implications of these heat records will continue to resonate across various sectors, highlighting the necessity for adaptive strategies in our fight against climate change.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 22, 2025
- Views
- 54
Comments
Loading comments...