State of Palestine Recognition Status Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
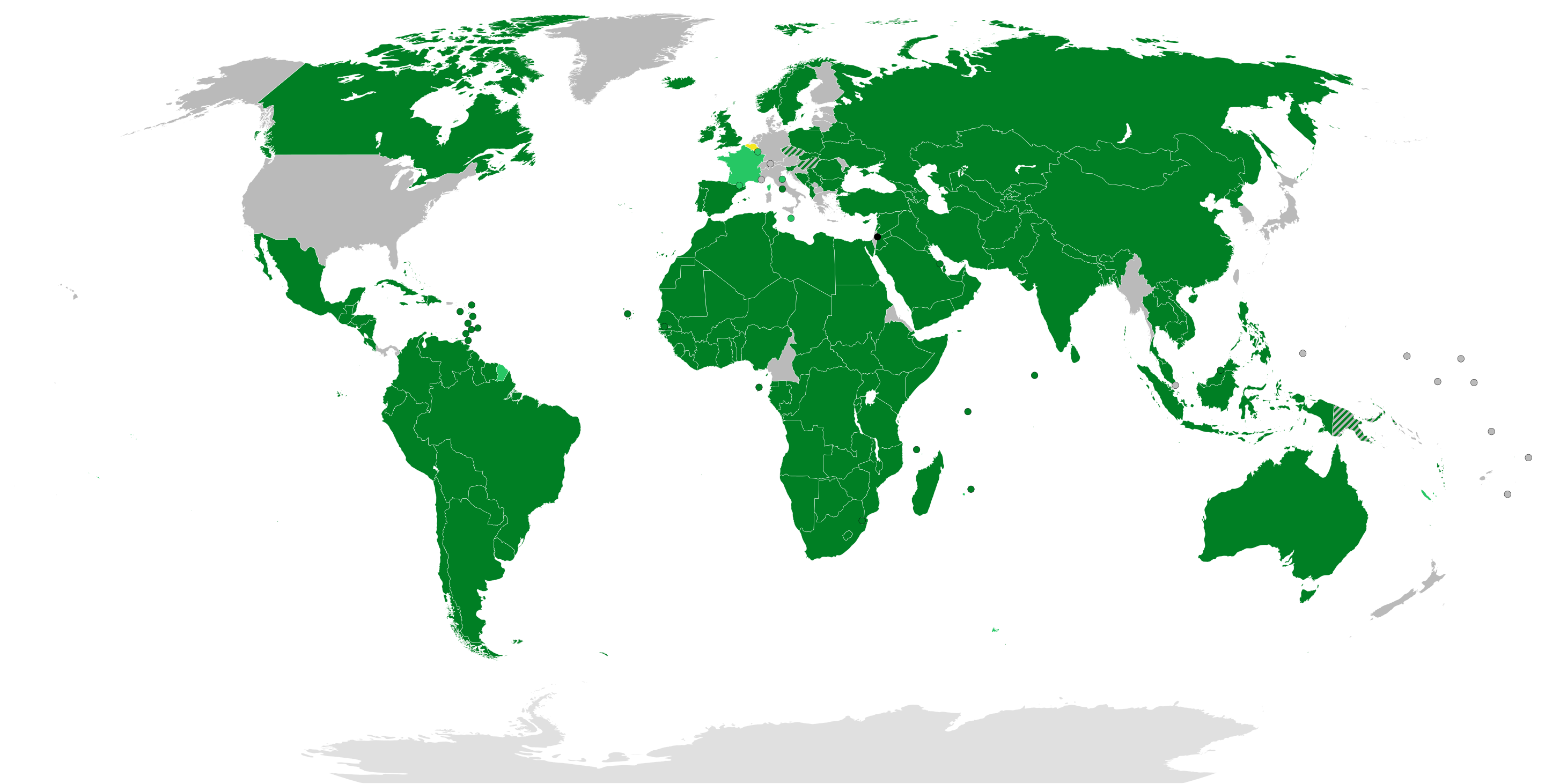
What This Map Shows
The "State of Palestine Recognition Status (21st September 2025)" map visually illustrates the global recognition of Palestine as a sovereign state as of the specified date. It delineates which countries and organizations recognize Palestine as a state, which do not, and those that maintain a neutral or ambiguous stance on the issue. With a focus on political geography, this map provides essential insights into international relations, diplomacy, and the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Deep Dive into Palestine Recognition
Recognition of Palestine as a state is not merely a political gesture; it encompasses a complex array of historical, cultural, and diplomatic factors. The Palestinian Authority (PA) declared independence in 1988, and since then, the quest for statehood has been at the forefront of Palestinian aspirations. As of 2025, over 130 UN member states recognize Palestine as a sovereign state, allowing it to participate in various international organizations, including UNESCO and the International Criminal Court.
Interestingly, the recognition landscape is not static; it evolves with geopolitical shifts. For example, in recent years, nations like the United States have maintained a controversial stance, promoting negotiations between Israel and Palestine rather than outright recognition. This approach has implications for peace processes and the viability of a two-state solution, which remains a focal point of discussion in international diplomacy.
The map also highlights regions where recognition is polarized. Countries in the Middle East, such as Egypt and Jordan, recognize Palestine and have diplomatic relations with the PA, while others, like Israel and the United States, do not recognize Palestinian statehood. The European Union presents a mixed picture, as individual member states have varying policies; several have recognized Palestine, while others advocate for a negotiated two-state solution.
It's essential to consider the implications of this recognition status. Countries that recognize Palestine often support Palestinian self-determination, which can lead to increased international support for Palestinian rights. Conversely, lack of recognition may perpetuate the status quo, hindering peace efforts and reinforcing divisions.
Regional Analysis
The recognition of Palestine varies significantly across regions. In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), a majority of countries recognize Palestine, reflecting historical ties and solidarity movements. Nations like Turkey and Iran have vocally supported Palestinian statehood, often positioning themselves as champions of the Palestinian cause. In contrast, Gulf states have been more cautious, balancing their relations with Israel and the United States while advocating for Palestinian rights.
In Europe, recognition is more fragmented. Countries like Sweden and Ireland have formally recognized Palestine, while others, such as Germany and the UK, have taken a more hesitant approach, often citing the need for negotiations. This divergence highlights the geopolitical tensions and historical contexts that shape the recognition status.
Interestingly, in Latin America, many countries have recognized Palestine, reflecting a broader trend of solidarity with anti-colonial movements. Brazil, Argentina, and Bolivia have all formally recognized Palestine, often as part of a broader critique of U.S. foreign policy in the region.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the recognition status of Palestine is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it sheds light on the dynamics of international relations and how national interests shape foreign policy. Countries that recognize Palestine often do so as a statement against perceived injustices, while those that do not may prioritize strategic alliances over human rights considerations.
Moreover, the recognition status impacts the lives of Palestinians. International recognition can lead to increased foreign aid, diplomatic support, and a stronger voice in international forums. However, it can also provoke backlash from nations opposed to Palestinian statehood, leading to diplomatic isolation or economic sanctions.
Looking ahead, current trends suggest that recognition may continue to expand, particularly in regions with strong anti-colonial sentiments. However, ongoing conflicts, particularly surrounding the Gaza Strip and West Bank, complicate the situation. The future of Palestinian recognition will likely hinge on developments in the peace process, regional stability, and the evolving geopolitical landscape as nations navigate their relationships with both Israel and Palestine.
In conclusion, the map of Palestine's recognition status serves as a critical tool for understanding the broader context of international diplomacy. It illustrates not just where Palestine is recognized, but also the shifting sands of global politics that influence these decisions.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 22, 2025
- Views
- 60
Comments
Loading comments...