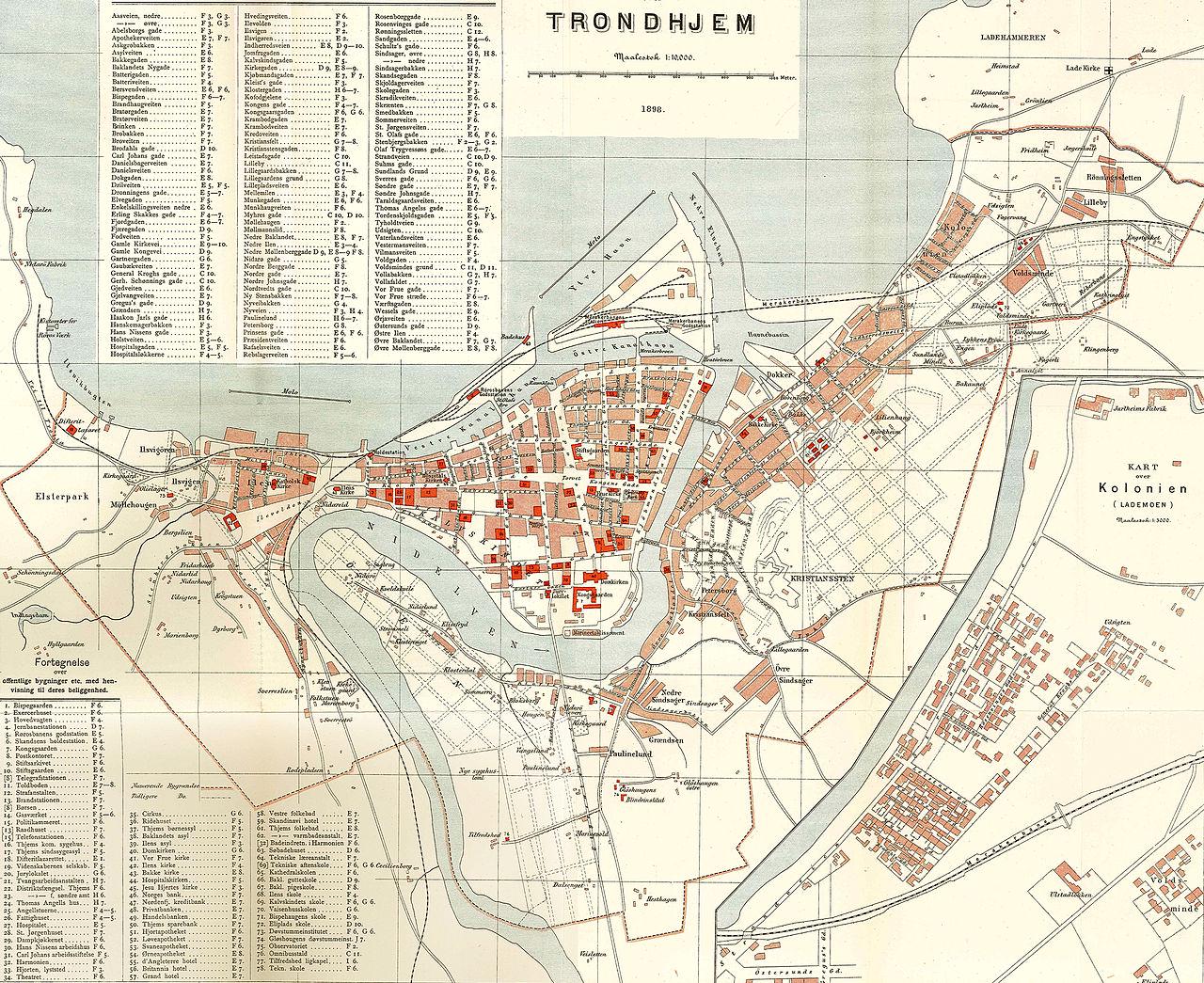
Map of Trondheim Norway from 1898

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows\nThe map of Trondheim from 1898 offers a fascinating glimpse into the urban layout and geographical features of one of Norway's oldest cities at the turn of the 20th century. This visualization captures the city's streets, notable buildings, and the surrounding topography, including the fjord that characterizes much of Trondheim's natural landscape. The map not only displays the city's infrastructure but also hints at the socio-economic landscape of the period, making it a valuable resource for understanding Trondheim's historical development.
Deep Dive into Trondheim’s Urban Development\nTrondheim, known for its rich history dating back to the Viking age, has witnessed significant transformations over the centuries. In 1898, the city was evolving from a small medieval settlement into a more structured urban center. The map reveals a grid-like street system that was developing, reflecting the city's growth and the increasing importance of urban planning during this era.
Interestingly, Trondheim’s location by the Trondheim Fjord had a profound impact on its development. The fjord provided a natural harbor, which facilitated trade and fishing, pivotal for the city's economy. The map indicates several docks along the waterfront, illustrating how maritime activities were central to Trondheim's livelihood. This coastal access not only influenced commerce but also attracted a growing population seeking opportunities in trade and industry.
As of 1898, Trondheim was also emerging as an educational hub, home to the Norwegian Institute of Technology, which opened its doors in 1910. The presence of such institutions began shaping the city's demographics, drawing students and professionals from various regions. The map hints at the layout of educational buildings that were beginning to sprout amidst more traditional residential and commercial structures.
Moreover, the architectural styles depicted in the map reflect the cultural influences of the time. The late 19th century was marked by a mix of neoclassical and national romantic styles, which can be observed in the buildings that line the streets. This era coincided with a wave of nationalism in Norway, which saw a revival of interest in Norwegian heritage and architecture, influencing how the city was built and perceived.
Regional Analysis\nWhile the map of Trondheim in 1898 provides a snapshot of the city, it's also essential to consider its surrounding regions. The broader Trøndelag region, where Trondheim is located, is characterized by its diverse geography. To the north, the mountainous terrain contrasts sharply with the coastal features of the fjord. This variation in geography has influenced economic activities, from agriculture in the fertile valleys to fishing and shipping along the coast.
Interestingly, comparing Trondheim to other urban centers in Norway, such as Oslo and Bergen, reveals distinct differences in urban planning and development. Oslo, as the capital, was experiencing rapid industrialization during this period, while Bergen maintained its strong fishing and trading roots. Trondheim, on the other hand, balanced both aspects, serving as a center for education, trade, and local governance, which is reflected in its infrastructure as shown on the 1898 map.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the historical context of Trondheim through the 1898 map is crucial for several reasons. It highlights the urban evolution of a city that laid the groundwork for modern Trondheim, which today is known for its vibrant culture and historical landmarks. Recognizing the urban planning strategies from over a century ago allows us to see the long-term impacts of those decisions on current city layouts and demographics.
Moreover, today’s urban planners can draw lessons from historical maps like this one. As cities face challenges such as population growth and climate change, understanding past urban development can guide future planning efforts. For Trondheim, the ongoing balance between preserving historical sites and accommodating modern infrastructure remains a pertinent issue.
In conclusion, the map of Trondheim from 1898 does more than just depict a city; it opens a window into the past, revealing the foundations upon which the modern city stands. As we continue to analyze such historical data, we gain valuable insights that inform our understanding of urban geography and its evolution over time.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 21, 2025
- Views
- 54
Comments
Loading comments...