World Internet Access Map by Population

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
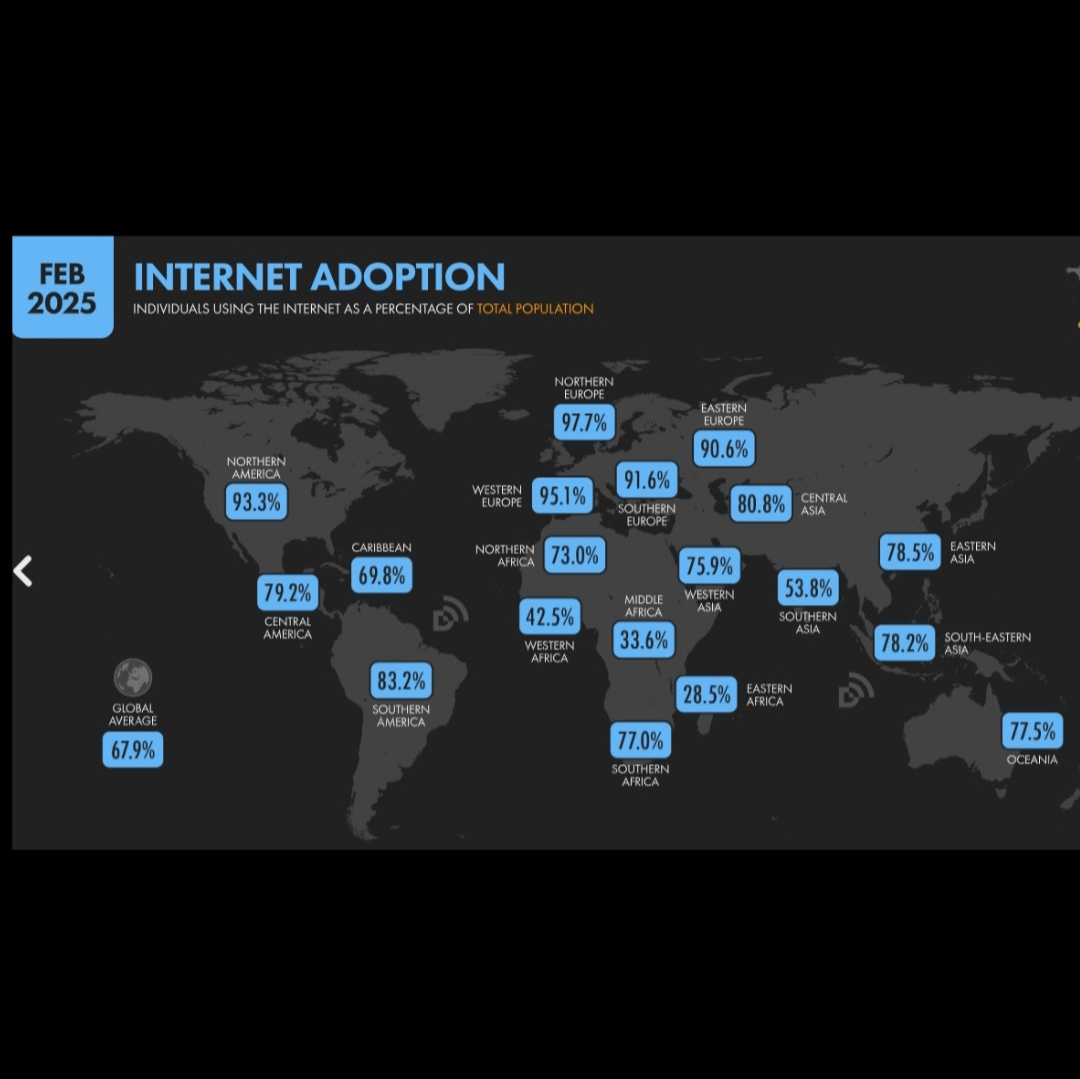
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Almost 70% of the World Population Has Internet Access" visually represents the global distribution of internet connectivity, showcasing countries and regions where access is prevalent. This visualization highlights areas where the majority of the population is connected to the internet and contrasts these with those where access remains limited. Understanding this landscape is crucial as it reflects not just technological advancement, but also the socio-economic dynamics at play in our increasingly digital world.
Deep Dive into Internet Access
Internet access has transformed societies, economies, and cultures. As of 2023, nearly 70% of the global population can connect to the internet, a remarkable achievement considering that just a few decades ago, this technology was in its infancy. This connectivity isn't just about browsing the web; it encompasses access to education, healthcare, economic opportunities, and civic engagement.
Interestingly, internet access is not uniform across the globe. Factors such as geography, income levels, and governmental policies play significant roles in determining connectivity. Urban areas typically enjoy better access compared to rural regions, where infrastructure may lag. For example, cities like Tokyo and New York boast near-universal connectivity, while rural areas in regions like Sub-Saharan Africa still face significant challenges.
Statistics reveal that as of late 2023, over 5 billion people are online, with the highest penetration rates found in North America and Europe. These regions have well-established infrastructure and high disposable incomes that facilitate access. In contrast, in areas like Africa and parts of Asia, internet penetration hovers around 30% to 50% in many countries, illustrating a digital divide that has serious implications for economic development and social inclusion.
The types of internet access also vary widely. While some regions rely heavily on mobile networks, others have robust fixed broadband services. Mobile internet has revolutionized access in many developing nations, allowing people to connect without the need for expensive infrastructure. However, the quality of service can vary greatly, affecting the user experience.
Regional Analysis
When we break down internet access by region, significant variations emerge. In North America, nearly 90% of the population is connected, thanks to widespread availability of high-speed internet and competitive service providers. Conversely, in regions like sub-Saharan Africa, internet access is significantly lower, with countries such as Chad and the Central African Republic recording rates below 20%. This disparity raises crucial questions about equity and economic opportunity.
In Asia, countries like South Korea and Japan lead with over 95% connectivity, driven by advanced technology and government initiatives promoting digital literacy. In contrast, nations like Afghanistan struggle with access due to ongoing conflict and lack of infrastructure.
Interestingly, even within countries, access can vary dramatically. The United States, for example, has urban centers with excellent internet speeds, while rural areas face challenges in connectivity. The digital divide is not just a global issue; it exists within nations, often mirroring existing socio-economic inequalities.
Significance and Impact
Understanding internet access is vital in today's world. Why does it matter? The implications are profound. Access to the internet influences education, economic growth, healthcare, and social justice. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the lack of internet access in certain regions highlighted the vulnerabilities in education systems, where students without connectivity fell behind their peers.
Additionally, as businesses increasingly move online, the digital divide could exacerbate economic inequalities. Countries with lower internet penetration may struggle to compete in a global market that values digital skills and online presence. Future projections suggest that if trends continue, the global community will need to focus on bridging this divide, ensuring that everyone can participate in the digital age.
In conclusion, the map illustrating that almost 70% of the world population has internet access serves as a powerful reminder of where we stand in the quest for global connectivity. It highlights successes but also underscores the critical work that remains to ensure that everyone, regardless of where they live, can benefit from the opportunities that the internet provides.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 17, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...