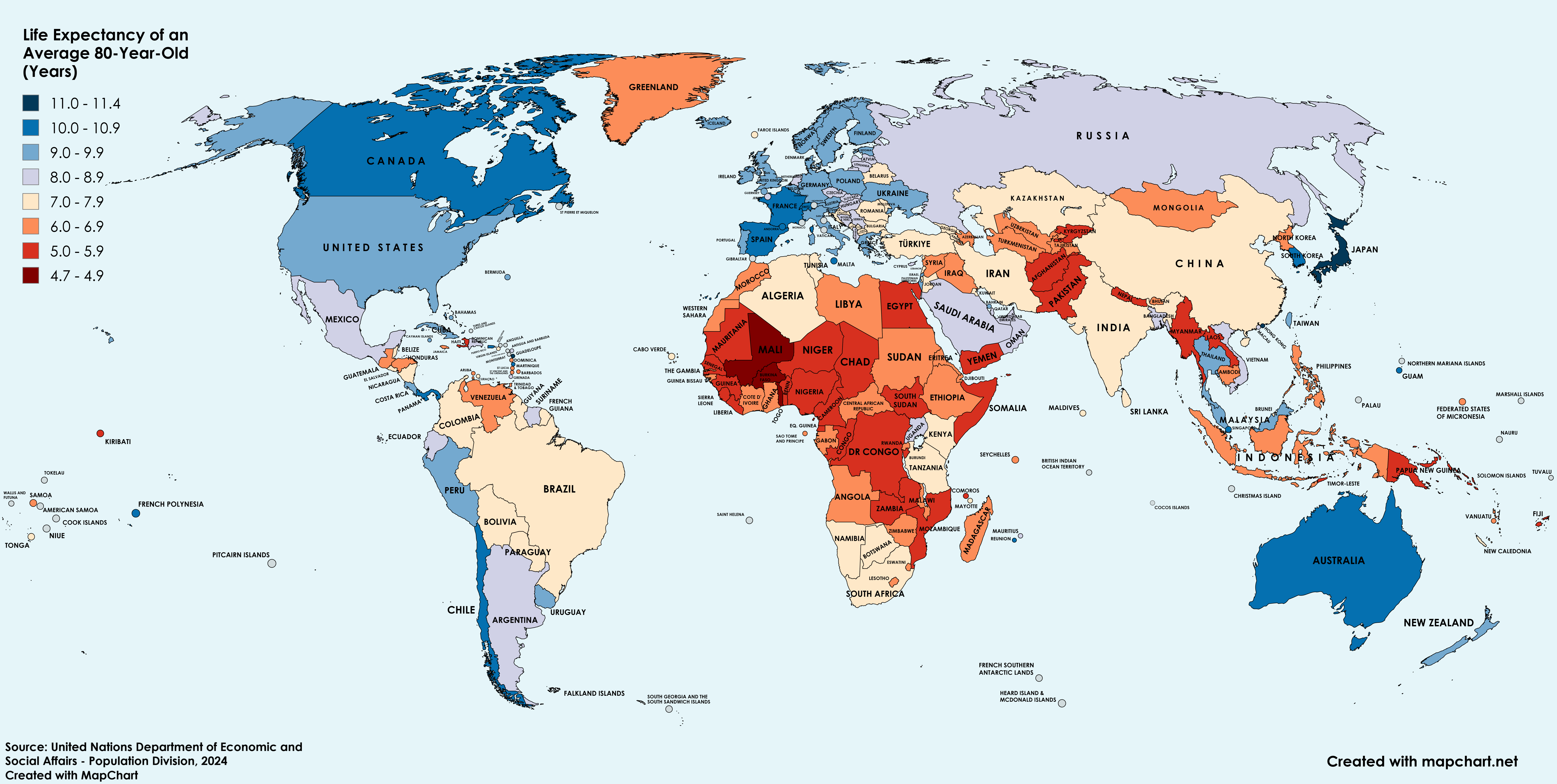
Life Expectancy of an 80-Year-Old Across the World Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Life Expectancy of an 80-Year-Old Across the World" offers an insightful visualization of how long individuals aged 80 can expect to live in various countries around the globe. This visualization highlights the disparities in longevity and health outcomes, portraying a world where factors such as healthcare quality, lifestyle, and socio-economic conditions play critical roles in determining life expectancy. What’s compelling about this map is that it doesn't just present numbers; it tells a story about aging populations and the quality of life experienced by the elderly in different regions.
Deep Dive into Life Expectancy
Life expectancy at age 80 is a significant demographic statistic, reflecting not only the average number of years that an individual can anticipate living beyond that age but also serving as a crucial indicator of the overall health of a population. This metric is particularly telling because it encapsulates the effectiveness of a country's healthcare system, lifestyle choices, and social support networks.
Interestingly, the variation in life expectancy for 80-year-olds is often influenced by numerous factors, including access to healthcare, nutrition, and social determinants of health. For instance, countries with well-developed healthcare systems, such as Japan and Switzerland, tend to show higher life expectancies for older adults. In Japan, a combination of a balanced diet, active lifestyle, and a strong community system contributes to some of the highest longevity rates in the world.
Conversely, in nations facing economic challenges and healthcare accessibility issues, such as some regions in sub-Saharan Africa, the life expectancy of an 80-year-old can be significantly lower. This disparity raises important questions about public health initiatives and the need for increased support for aging populations.
Moreover, the impact of lifestyle choices cannot be overstated. Factors like smoking rates, obesity, physical activity levels, and access to healthy foods all contribute to health outcomes in older adults. For example, Scandinavian countries often report higher life expectancy figures due to their high standards of living, social welfare programs, and emphasis on preventive healthcare.
In addition, it’s essential to consider the psychological aspect of aging. Social connections and mental health play pivotal roles in determining how well individuals live out their twilight years. Countries that foster community engagement and support networks for the elderly often see not just longer lives but also improved quality of life for their aging populations.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map, one can clearly see distinct patterns across continents. For instance, in North America, the life expectancy of an 80-year-old averages around 8 to 9 years more than in many parts of Africa. In the United States and Canada, the figures are bolstered by advanced medical technology and healthcare, yet disparities do exist based on socio-economic status and access to services.
In Europe, the life expectancy varies widely. Countries like Italy and Spain report higher figures, benefiting from Mediterranean diets and strong family structures. In contrast, Eastern European nations, which have faced economic struggles and health crises, often show lower life expectancies for older adults.
Asia presents a mixed picture, with countries such as South Korea and Japan showcasing impressive longevity, while regions with less access to healthcare lag behind. Interestingly, even within countries, urban areas often report higher life expectancy figures compared to rural areas due to better access to health services and healthier living conditions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding life expectancy for older adults is not just an academic exercise; it has profound implications for public policy, healthcare planning, and social services. As global populations age, countries must adapt to the needs of their elderly citizens. This includes not just extending life but enhancing the quality of those extra years.
The increasing number of 80-year-olds worldwide will challenge healthcare systems and social services, necessitating innovative solutions to support these populations. As we look to the future, trends indicate that longevity will continue to rise in many parts of the world, but this must be matched by efforts to improve health outcomes and living conditions.
Have you ever wondered how societies can better prepare for an aging population? These discussions are crucial as we strive to create environments where older adults can thrive. As the world shifts and evolves, the insights drawn from life expectancy data will play a vital role in shaping policies and societal attitudes toward aging, ultimately influencing how we perceive and support our elderly community members.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 16, 2025
- Views
- 54
Comments
Loading comments...