Ethnic Groups of Central Europe Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
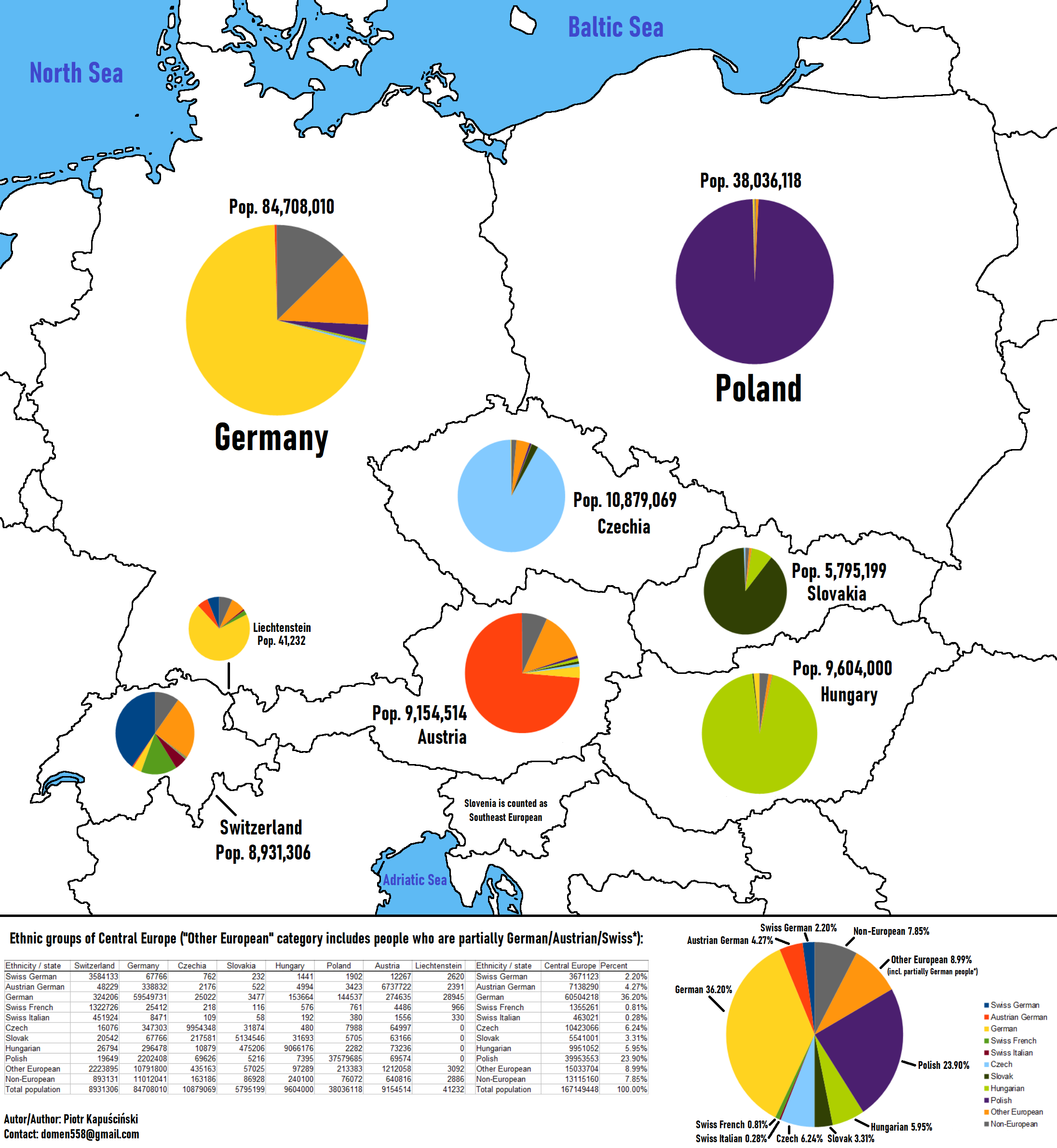
What This Map Shows
This updated map of Central Europe provides a detailed visualization of the various ethnic groups within the region, showcasing how the diverse cultures and histories shape the identity of countries like Germany, Austria, Switzerland, the Czech Republic, and Hungary. By dividing Swiss people into German, French, and Italian ethnicities, this map offers a more nuanced perspective, reflecting ethnicity rather than mere nationality. This approach allows us to better understand the rich tapestry of cultural identities that make up Central Europe.
Deep Dive into Ethnic Diversity in Central Europe
Central Europe is a fascinating region, characterized by a mosaic of ethnic groups that contribute to its unique social fabric. Ethnic diversity here stems from a complex history of migrations, invasions, and intermingling cultures over centuries. For instance, Germany, the largest country in Central Europe, is predominantly German, but it also has significant Turkish, Polish, and Russian minorities, reflecting its history of labor migration and geopolitical proximity to Eastern Europe.
Interestingly, the German-speaking populations are not confined to Germany alone. Regions in Austria and parts of Switzerland, where German is the primary language, showcase the ethnic connection among these groups. The Swiss population, when divided into its respective ethnicities, reveals that around 62% identify as Swiss German, 23% as Swiss French, and 8% as Swiss Italian. This division highlights the cultural influences from neighboring countries and the internal dynamics within Switzerland itself.
Moving to the Czech Republic, about 94% of the population identifies as Czech, but the country is also home to Slovaks, Poles, and Romani people, each adding their own cultural flavors to the national identity. The historical relationship between Czechs and Slovaks is particularly notable, as they were once part of Czechoslovakia until its peaceful dissolution in 1993.
Hungary, too, exhibits a rich ethnic profile, predominantly Hungarian (around 90%), but with significant minority populations of Roma, Slovaks, and Serbs. The Roma, in particular, face significant social challenges, including discrimination and economic disadvantage, despite being an integral part of Hungarian history and culture.
As we look at the ethnic landscapes of each country, one cannot overlook the impact of historical events such as World War II and the subsequent changes in borders and populations. The forced migrations and resettlements that occurred during and after the war have left lasting impressions on the demographic makeup of these countries.
Regional Analysis
When breaking down the map regionally, we see distinct patterns emerge. In Germany, the northern regions, like Schleswig-Holstein, have a higher concentration of Danish minorities due to historical ties. Conversely, southern areas, such as Bavaria, reflect a blend of ethnicities, including a significant presence of immigrants from Eastern Europe and the Middle East.
In Austria, the urban areas like Vienna are melting pots of different ethnicities, with a substantial presence of people from the Balkans and the Middle East contributing to the city's vibrant culture. Interestingly, despite its smaller size, Austria's ethnic composition is quite diverse, with around 18% of the population being foreign-born.
Switzerland’s ethnic distribution is fascinating as well. The multilingual nature of the country often leads to unique cultural exchanges. For instance, the French-speaking parts, primarily in the west, are significantly influenced by their proximity to France, while the Italian-speaking regions in the south exhibit traits distinct from the German-speaking north.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the ethnic composition of Central Europe is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications. Ethnic diversity affects everything from political representation to social cohesion and economic development. For example, countries with significant ethnic minorities, like Hungary and Slovakia, often grapple with issues of integration and social justice. The rise of nationalism in recent years has also sparked debates about immigration and the rights of ethnic minorities, making this map particularly relevant today.
Moreover, as globalization continues to influence migration patterns, the ethnic landscapes of these countries are likely to evolve. Urban centers will increasingly reflect a blend of cultures, leading to rich, multicultural environments that challenge traditional notions of national identity. As we look to the future, the ethnic dynamics in Central Europe will continue to be shaped by both historical legacies and modern developments, making it a region to watch closely.
Ultimately, this map serves as a reminder of the complexity of identity in Central Europe. It encourages us to appreciate the rich cultural heritage that each ethnic group brings to the region, urging us to foster understanding and inclusivity in an increasingly interconnected world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 15, 2025
- Views
- 64
Comments
Loading comments...