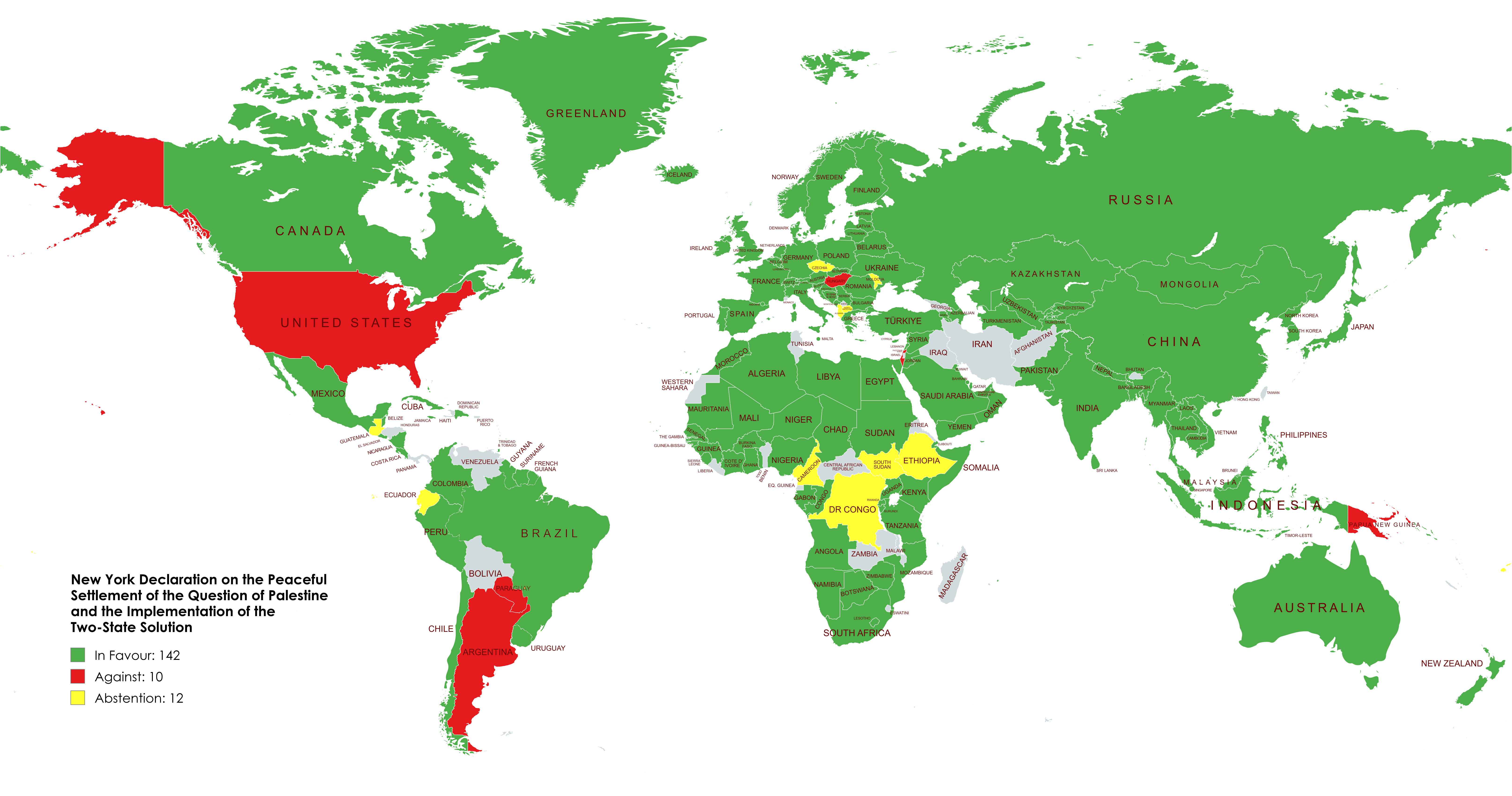
UN Vote Map on New York Declaration for Two-State Solution

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map visualizes the voting patterns of UN member states regarding the New York Declaration for a two-state solution between Israel and Palestine. It highlights how various countries voted—either in favor, against, or abstained from the resolution. The New York Declaration, adopted in 2016, aimed to revitalize the peace process and establish a framework for negotiations towards a two-state solution, which envisions independent Israeli and Palestinian states coexisting peacefully.
This visualization serves as a crucial tool for understanding global perspectives on one of the most contentious issues in international relations and geopolitics. By examining this map, we can gain insights into the political alliances, historical ties, and diplomatic stances of different nations with respect to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Deep Dive into the Two-State Solution
The two-state solution has long been proposed as a viable pathway to peace in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. This concept is rooted in the desire to resolve a dispute that has persisted for over seven decades, marked by violence, territorial disputes, and significant humanitarian concerns. The New York Declaration aimed to renew commitments from the international community to support a negotiated agreement that would establish two sovereign states.
Interestingly, the international community is divided in its views on this solution. Countries that voted in favor of the New York Declaration typically advocate for a peaceful resolution and recognize the right of both Israelis and Palestinians to self-determination. For instance, nations in the European Union, along with many from Latin America and Africa, have historically supported the two-state framework, seeing it as essential for regional stability and justice.
On the other hand, states that voted against the declaration often have strategic alliances with Israel or have different geopolitical interests in the region. The United States, for example, has historically supported Israel and often finds itself at odds with resolutions seen as unfavorable to its ally. The abstentions, meanwhile, reflect a more cautious approach, where countries may recognize the complexity of the situation but are hesitant to take a definitive stance due to various political or economic dependencies.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals some intriguing regional patterns. For instance, many Middle Eastern countries, despite their proximity to Israel and Palestine, have varying responses to the two-state solution. Countries like Jordan and Egypt, which have peace treaties with Israel, often endorse the two-state framework, seeing it as a way to ensure their own national security and regional stability. Conversely, countries with more hostile relations with Israel may oppose the resolution or abstain from voting, reflecting their internal political narratives.
In contrast, nations in Europe largely support the two-state solution, viewing it as a moral imperative that respects human rights and international law. The support from the European Union signals a collective stance that prioritizes diplomatic engagement over conflict. What's fascinating is how historical ties play a role; for example, many European nations have longstanding relationships with both Israelis and Palestinians, which influences their diplomatic positions.
Conversely, countries in Asia and Africa show varied responses as well, shaped by historical ties to colonialism, nationalism, and contemporary political alliances. Countries such as South Africa, with its own history of apartheid, often advocate for Palestinian rights, seeing parallels between their struggle and that of Palestinians.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the voting patterns on the New York Declaration is crucial, as it reflects the broader geopolitical dynamics at play in the Middle East and beyond. The implications of these votes extend far beyond the immediate issue of land and sovereignty; they influence diplomatic relations, international aid, and peacekeeping efforts. As global attitudes toward the Israeli-Palestinian conflict evolve, so too does the landscape of international diplomacy.
Moreover, the two-state solution remains a focal point for peace negotiations, despite the challenges it faces. Current trends indicate that while there are significant obstacles to achieving this goal—such as settlement expansions, security concerns, and political divisions within both Israeli and Palestinian communities—there remains a persistent push from various international actors to revive the dialogue.
As the situation continues to develop, the map provides a snapshot of where countries align on this critical issue, serving as a valuable resource for analysts, policymakers, and anyone interested in the intricate dynamics of global politics. The future of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict will likely hinge on these international attitudes and the willingness of the global community to engage in meaningful dialogue.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 13, 2025
- Views
- 72
Comments
Loading comments...