Labor Force Participation Rate Female Ages 20-64 Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
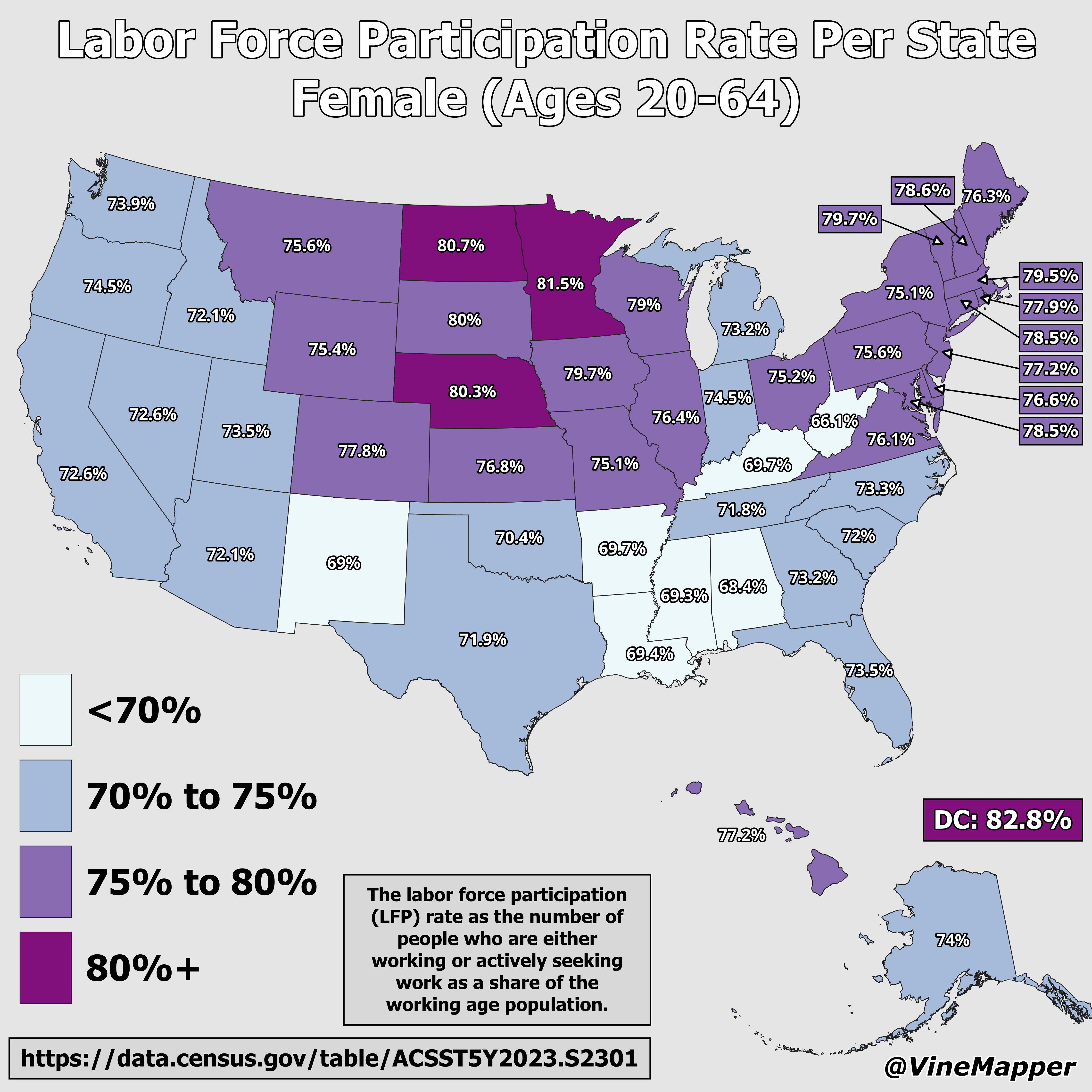
The "Labor Force Participation Rate Per State, Female (Ages 20-64) Map" presents a visual representation of the percentage of women aged 20 to 64 who are actively engaged in the labor force across various states in the U.S. This data is crucial for understanding gender dynamics in employment and the socio-economic factors that influence women's participation in the workforce. The map highlights disparities and trends that emerge on a state-by-state basis, offering insights into how different regions support or hinder female employment.
Deep Dive into Female Labor Force Participation
Labor force participation is a vital indicator of economic health and gender equality in the workplace. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the labor force participation rate reflects the percentage of the working-age population that is either employed or actively seeking employment. For women, this statistic is influenced by various factors, including education levels, family responsibilities, access to childcare, and cultural attitudes towards working women.
Interestingly, the labor force participation rate for women has seen significant fluctuations over the decades. In the 1950s, for instance, only about 34% of women were in the labor force. Fast forward to the present, and the rate has increased dramatically, peaking at about 60% in the early 2000s. However, recent years have shown a slight decline, raising questions about the influences affecting women’s work decisions today.
What's fascinating is how these rates vary across states. For example, states like Vermont and Massachusetts often report higher participation rates, attributed to robust educational systems and progressive workplace policies. In contrast, states in the South, such as Alabama and Louisiana, exhibit lower participation rates, which can often be linked to cultural and economic factors, including a higher prevalence of traditional gender roles and less access to affordable childcare.
Demographic trends also play a significant role. Women with higher education levels are more likely to participate in the labor market. This correlation suggests that as more women attain higher degrees, we can expect the labor force participation rates to rise. Moreover, the gig economy has opened new avenues for women, allowing for flexible work arrangements that cater to their diverse needs and responsibilities.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it becomes evident that regional differences significantly impact labor force participation rates among women. For instance, the Northeast and West Coast states, such as California and New York, tend to have higher participation rates. These states often benefit from more progressive labor laws, access to higher education, and urban job markets that attract a diverse workforce.
On the other hand, the Midwest and Southern regions show more variability. Midwestern states like Iowa and Minnesota reflect higher rates, possibly due to strong manufacturing sectors that employ many women. Meanwhile, Southern states such as Arkansas and Mississippi lag behind, which can be attributed to economic structures that predominantly favor male-dominated industries like agriculture and construction.
Interestingly, the map also reveals that changes in labor force participation rates can sometimes correlate with broader economic shifts. For example, states experiencing economic booms in technology or healthcare often see a rise in female participation as job opportunities expand. Conversely, states reliant on industries facing decline may witness stagnant or declining participation rates.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the labor force participation rate among women is not just about numbers; it reflects broader societal trends and the ongoing struggle for gender equality. High participation rates often indicate a more equitable society, where women have access to the same opportunities as men. Conversely, low rates can highlight systemic issues that need addressing, such as inadequate childcare support, wage gaps, and workplace discrimination.
As we look to the future, the importance of this data cannot be overstated. With ongoing discussions about work-life balance, paid family leave, and equitable pay, policymakers and advocates can use this information to push for changes that support women's participation in the labor force. As remote work becomes more normalized, we may see shifts in these rates as women find new ways to balance work and family life.
In conclusion, the "Labor Force Participation Rate Per State, Female (Ages 20-64) Map" serves as a critical tool for understanding the dynamics of female employment across the United States. By analyzing these rates, we can gain insights into the progress made and the work that still lies ahead in achieving gender equality in the workforce.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 12, 2025
- Views
- 78
Comments
Loading comments...