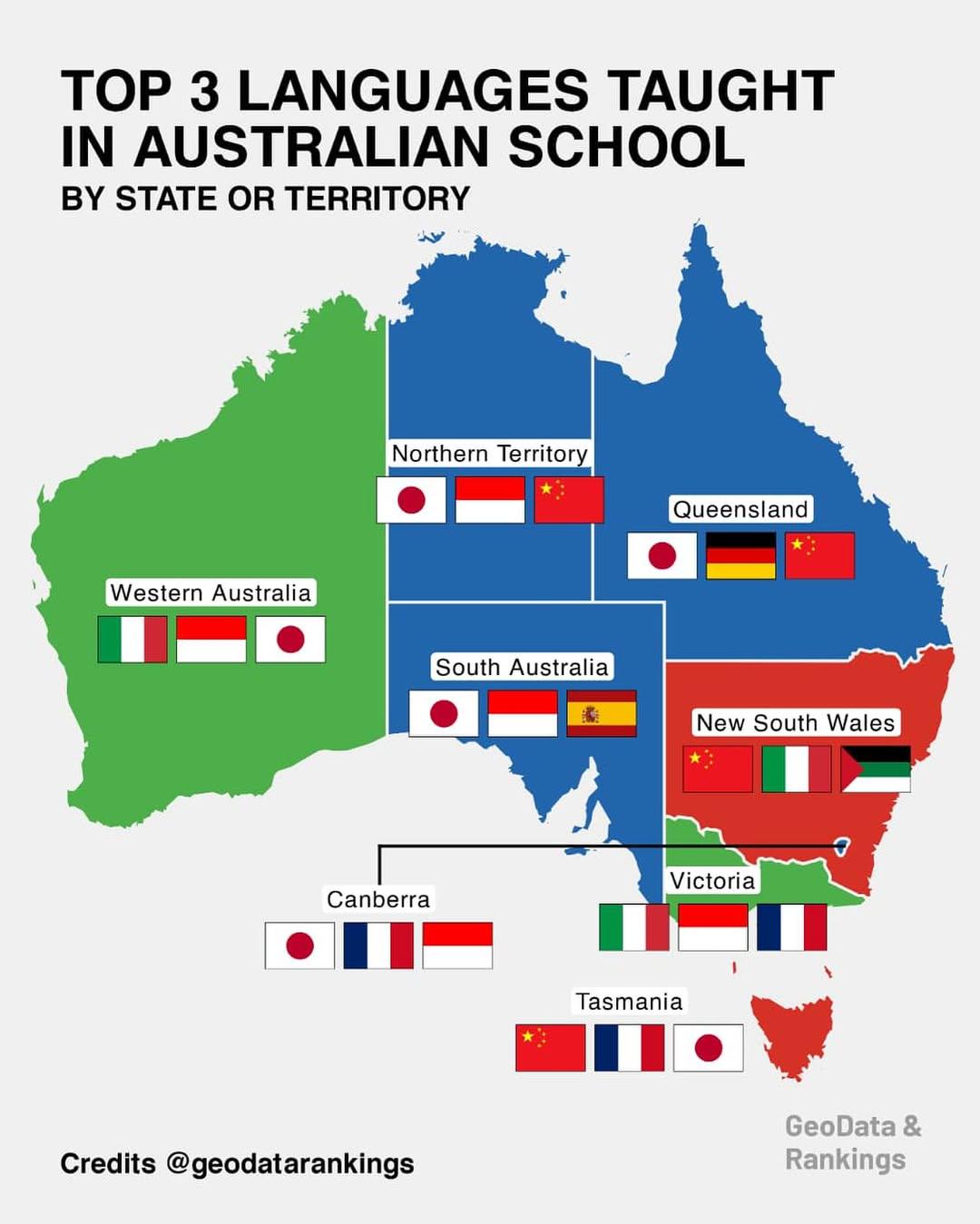
Top 3 Languages Taught in Australian Schools Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map provides a comprehensive overview of the top three languages taught in schools across various states and territories in Australia. By visualizing language education distribution, we can glean insights into cultural influences, migration patterns, and educational priorities in different regions. The prominence of certain languages may reflect historical ties, economic partnerships, and community demographics. With Australia being a multicultural nation, language instruction is not just about communication—it's about understanding diverse cultures.
Deep Dive into Language Education in Australia
Language education in Australia is influenced by a myriad of factors, including immigration trends, globalization, and national policy. According to the Australian Curriculum, languages are a fundamental part of the educational experience, aimed at promoting communication skills and intercultural understanding.
Interestingly, the Australian Bureau of Statistics indicates that more than 300 languages are spoken across the nation, reflecting a rich tapestry of cultures. However, only a select few dominate the education landscape, particularly in primary and secondary schools.
The top three languages typically taught in schools are Mandarin, Spanish, and French. Let's break these down:
1. **Mandarin**: With Australia’s close ties to China, Mandarin has surged in popularity over the last two decades. As China continues to grow as a global economic powerhouse, learning Mandarin is seen as a valuable asset in the job market. In states like New South Wales and Victoria, Mandarin is often the leading language taught, aligning with the high population of Chinese speakers within these regions.
2. **Spanish**: Following Mandarin, Spanish has also gained traction as a widely taught language in Australia. The increasing Hispanic population and the cultural influence of Spanish-speaking countries have contributed to this trend. In regions such as Queensland and Western Australia, Spanish is frequently chosen by students due to its perceived ease of learning and relevance in global affairs.
3. **French**: French has a long-standing presence in Australian education, often seen as a traditional second language. It is particularly popular in states like South Australia, where historical connections with France have fostered interest in the language. French cultural institutions and events also support its teaching, making it an attractive option for many students.
The choice of language instruction often reflects not only personal interest but also strategic considerations regarding future employment opportunities and cultural connections. Moreover, the Australian Curriculum emphasizes the importance of languages in developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, providing a well-rounded educational experience.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals intriguing regional differences in language education. In New South Wales, for example, Mandarin is taught in about 40% of schools, reflecting the state’s significant Chinese community. Conversely, in Tasmania, there is a notable emphasis on French, which may be attributed to the state's historical ties with French explorers and the presence of French cultural institutions.
In Victoria, the diversity of its population is mirrored in the variety of languages taught, with a strong focus on both Mandarin and Spanish. Meanwhile, in the Northern Territory, Indigenous languages also play a critical role in education, showcasing the importance of cultural heritage alongside foreign languages.
Interestingly, the growing trend of language learning in Australian schools is not just about classroom instruction; it reflects a society increasingly aware of the importance of global citizenship and cultural competency. This growing emphasis can lead to shifts in teaching priorities, demonstrating how language education adapts to societal needs.
Significance and Impact
The significance of language education in Australia goes beyond mere communication; it cultivates an understanding of global cultures and enhances social cohesion. In today's interconnected world, being multilingual can lead to better job prospects, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic relations. As Australia continues to engage in international trade, fluency in languages like Mandarin and Spanish becomes increasingly valuable.
Moreover, the importance of learning a second language has been backed by research that suggests cognitive benefits, including improved problem-solving abilities and increased creativity. The trend toward bilingualism in Australia reflects a broader commitment to fostering an inclusive and diverse society.
Looking ahead, we can anticipate shifts in language instruction in response to geopolitical changes and evolving demographics. With the Australian education system already adapting to new challenges, the future of language education will likely continue to evolve, fostering a generation of students equipped to thrive in a globalized world.
In conclusion, the map of the top three languages taught in Australian schools provides a valuable insight into not just educational trends, but the broader social and cultural dynamics at play in this vibrant country. As students navigate their language learning journeys, they are not just acquiring skills; they are also building bridges across cultures, shaping a more interconnected future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 11, 2025
- Views
- 92
Comments
Loading comments...