Raccoon Observations Per Capita Map Ontario

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
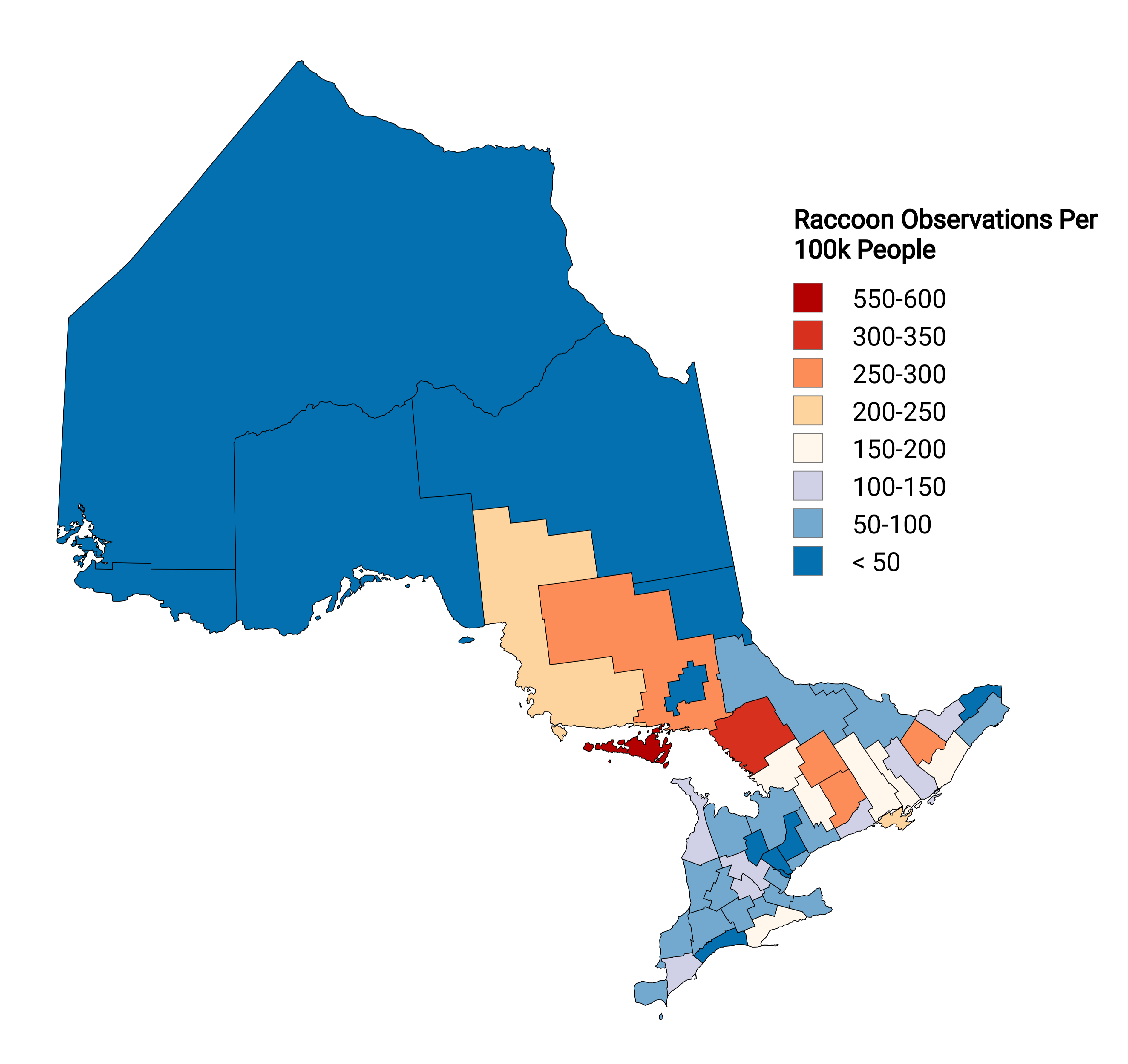
What This Map Shows
The "Raccoon Observations in Ontario Per Capita Map" visualizes the density of raccoon sightings across various regions of Ontario, highlighting where these adaptable creatures are most frequently observed. The data is sourced from iNaturalist, a platform that encourages citizen science and biodiversity monitoring. The map provides a clear snapshot of raccoon populations in relation to human density, offering valuable insights into their habitats and interactions with urban environments.
Deep Dive into Raccoon Populations
Raccoons, scientifically known as Procyon lotor, are fascinating mammals that thrive in diverse environments, from dense forests to bustling urban areas. Their adaptability is one of the reasons they have become so prevalent across North America, including Ontario. These nocturnal creatures are known for their characteristic black facial markings and dexterous front paws, which they use to forage for food.
Interestingly, raccoons are omnivorous and have a varied diet that includes fruits, nuts, insects, and human refuse. This dietary flexibility allows them to inhabit areas with a wide range of food sources, which is particularly advantageous in urban settings where food waste is abundant. In Ontario, raccoons have adapted to life alongside humans, often seen rummaging through garbage or exploring backyards, leading to an increase in observations reported by residents.
The map shows that certain areas have dramatically higher per capita observations than others. For instance, urban centers such as Toronto and Ottawa have a high density of raccoon sightings. This is likely due to the availability of food and shelter, as cities provide ample opportunities for raccoons to thrive. In contrast, rural areas may show fewer observations, as these regions may not have the same density of human population or food sources, leading to fewer encounters.
Interestingly, raccoons are known carriers of certain diseases, such as rabies and raccoon roundworm, which raises public health concerns in areas with high observations. Understanding their distribution is crucial for wildlife management and public safety. Moreover, tracking changes in raccoon populations can also offer insights into broader ecological trends, including habitat loss and climate change impacts.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the observations by region, we see intriguing patterns that reflect both the environment and human behavior. For instance, the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) stands out on the map with an exceptionally high per capita observation rate. This is not surprising, considering the urban sprawl and the abundant food sources available. Residents often report seeing raccoons in parks and neighborhoods, especially during late evening hours.
In contrast, northern Ontario presents a different picture. Regions such as the Algoma District and the Cochrane District show significantly fewer raccoon observations. This could be attributed to a combination of factors, including lower human population density and less urban development, which limits the raccoons’ access to food and shelter. Furthermore, the harsher climate conditions in these northern areas may also discourage raccoon populations from establishing themselves as firmly as in the south.
What’s fascinating is the role of local initiatives in monitoring these populations. Community-driven efforts, such as the iNaturalist platform, allow citizens to contribute valuable data. This grassroots participation not only enhances biodiversity awareness but also helps in tracking changes in wildlife populations over time.
Significance and Impact
Understanding raccoon populations in Ontario is significant for several reasons. As urban areas expand, the interaction between wildlife and humans becomes more pronounced. Raccoons are often seen as a nuisance, particularly when they invade homes or cause property damage. However, they also play an essential role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations and dispersing seeds.
From a public health perspective, monitoring raccoon populations is crucial, especially in regions where rabies is a concern. Higher observation rates may indicate a need for increased public awareness campaigns about wildlife safety and disease prevention. Additionally, as climate change continues to alter habitats, understanding how raccoon populations adapt can offer insights into broader ecological shifts.
Looking ahead, the trends in raccoon observations can inform wildlife management strategies. For example, areas with rising observation rates might require more robust waste management policies to mitigate human-wildlife conflict. By understanding these dynamics, we can better coexist with these clever creatures and appreciate their role in our environment.
In conclusion, the "Raccoon Observations in Ontario Per Capita Map" serves not only as a fascinating look at where raccoons thrive but also as a reminder of the intricate relationship between humans and wildlife. By examining these observations, we can gain valuable insights into ecological health and the impact of urbanization on natural species.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 10, 2025
- Views
- 90
Comments
Loading comments...