Foreign Remittance as Percentage of GDP Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
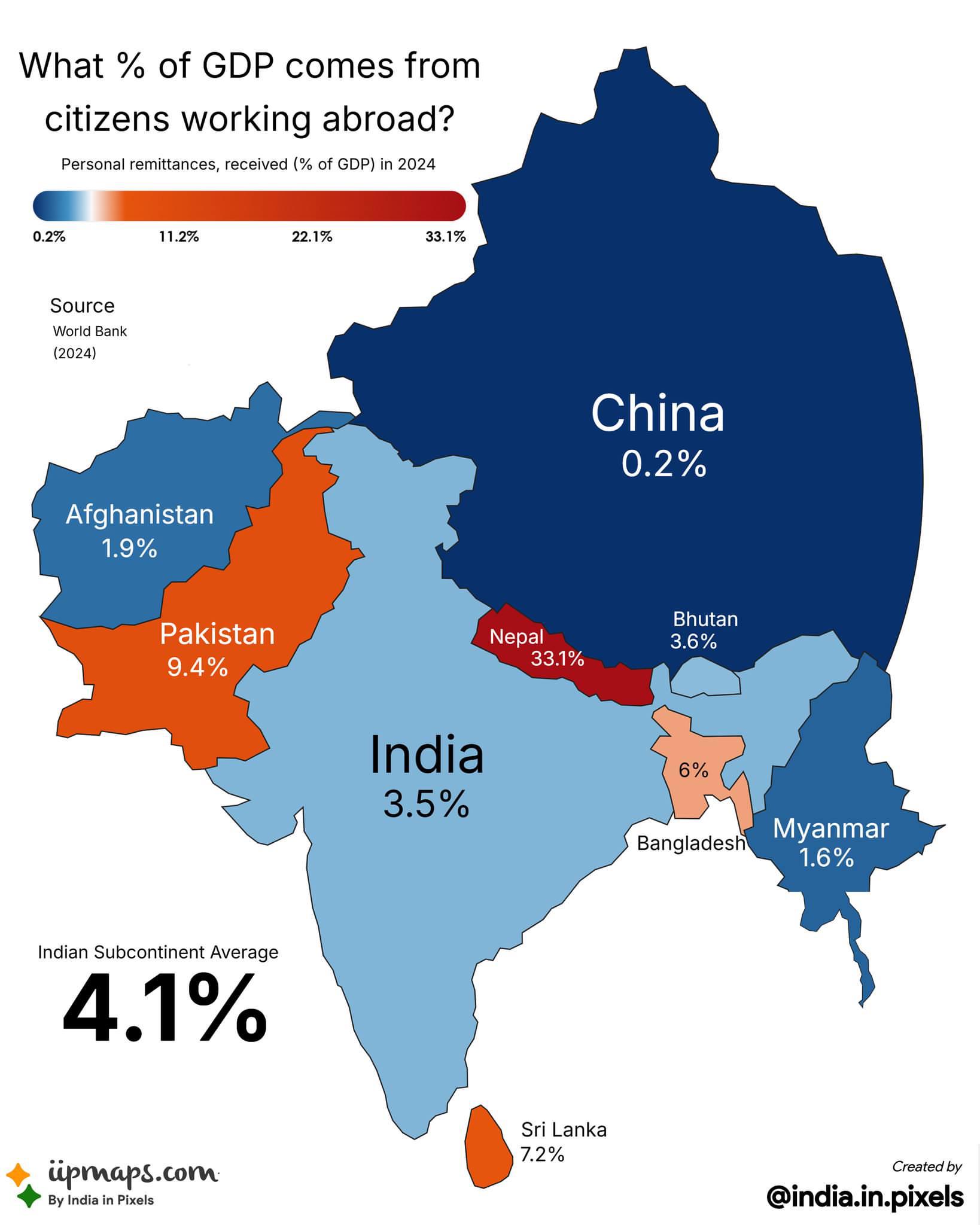
What This Map Shows\nThis map visualizes the percentage of a country's GDP that comes from foreign remittances, highlighting the vital role that money sent home by expatriates plays in national economies. Remittances, typically sent by migrant workers to their families, can significantly influence economic stability and growth in many nations. Each country is color-coded to represent how much of its GDP is bolstered by these funds, providing a clear overview of the global landscape of remittance dependency.
Deep Dive into Foreign Remittances\nForeign remittances are a critical component of the global economy, with billions of dollars flowing from developed to developing nations each year. According to the World Bank, remittances reached an estimated $702 billion in 2020, demonstrating their importance as a financial lifeline for families across the globe. Interestingly, these funds often surpass foreign direct investment and official development assistance in many countries, especially in lower-income regions.
The dynamics of remittance flows are influenced by various factors, including labor market conditions, immigration policies, and the economic situations in both sending and receiving countries. For instance, countries like India and China are the top recipients of remittances, largely due to their large diaspora populations. In India, remittances constituted approximately 3% of its GDP in recent years, significantly impacting rural development and poverty alleviation initiatives.
What's fascinating is that remittances can also have multiplier effects on local economies. For example, when families receive money from abroad, they often spend it on education, healthcare, and local businesses, stimulating economic growth. However, dependency on remittances can also create vulnerabilities. Countries that rely heavily on these funds may find themselves at risk during global economic downturns, as migrant workers may lose jobs or face reduced wages.
The impact of remittances is not uniform; it varies significantly depending on the economic structure, social systems, and migration patterns of each country. In some nations, such as Nepal and Haiti, remittances can account for a staggering proportion of GDP—sometimes exceeding 25%! This reality underscores the critical nature of remittances in sustaining household livelihoods and national economies.
Regional Analysis\nWhen examining the map, we can see distinct patterns emerging across different regions. In South Asia, for instance, countries like Afghanistan and Bangladesh have remarkably high percentages of GDP derived from remittances, often exceeding 10%. This is indicative of the substantial number of individuals working abroad, particularly in the Middle East and Southeast Asia, sending money back home to support their families.
In contrast, countries in Eastern Europe, such as Ukraine and Moldova, also show significant reliance on remittances, though they often represent a smaller percentage of GDP than in South Asian countries. This difference can be attributed to various factors, including the size of the diaspora and the economic conditions in the host countries. In Latin America, nations like El Salvador and Honduras are similarly dependent on remittances, which often make up more than 20% of their GDP, illustrating the ongoing trends of migration and economic necessity in the region.
Interestingly, some countries have begun to actively encourage remittances through policy measures, such as reducing transaction fees for money transfers. For example, the Philippines has taken steps to facilitate the flow of remittances through financial literacy campaigns and improved banking services, recognizing the important role these funds play in the national economy.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the significance of remittances is essential for grasping contemporary economic dynamics. In many developing countries, remittances serve as a buffer against economic shocks, providing households with the means to navigate financial hardships. However, the reliance on external funds can lead to issues of economic vulnerability, particularly during global crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, which saw many migrants losing jobs and, consequently, sending less money home.
As we look to the future, trends in migration and remittance flows are likely to evolve. Factors such as changing immigration policies, economic opportunities in both home and host countries, and global economic conditions will all play a role in shaping the landscape of remittances. For countries heavily reliant on these funds, adapting to these changes will be crucial for ensuring economic stability and growth.
In conclusion, this map serves as a vital tool for understanding the role of foreign remittances in national economies, illustrating not just numbers, but the intricate web of human connections that underpin them. As we move forward, recognizing and addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by remittances will be key to fostering resilient economies worldwide.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 10, 2025
- Views
- 76
Comments
Loading comments...