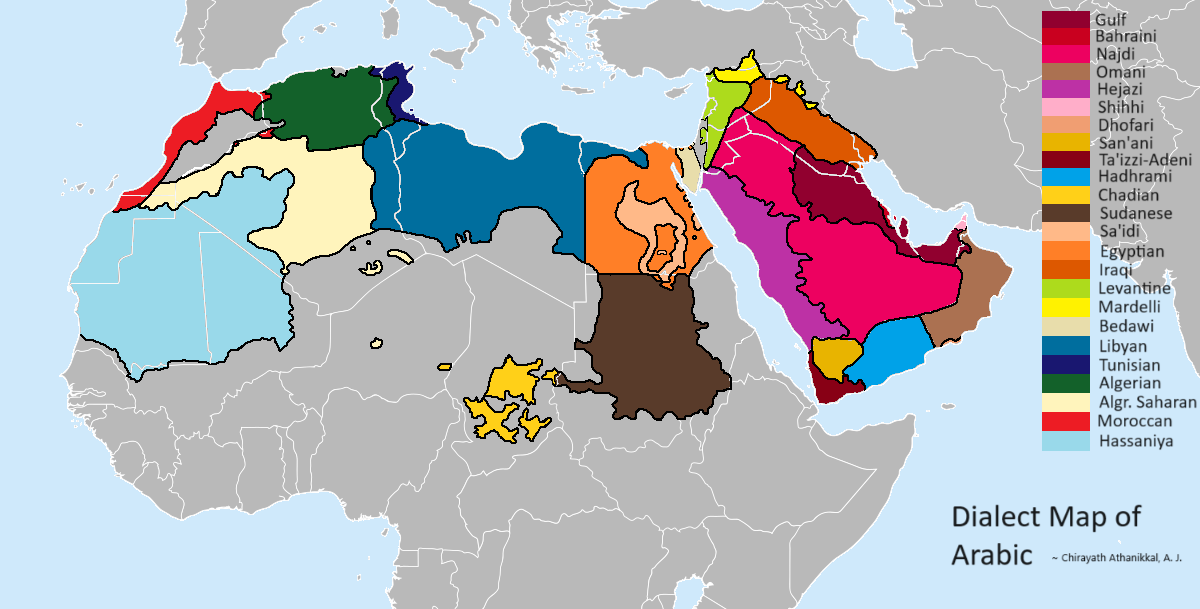
Dialect Map of Arabic

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Dialect Map of Arabic" provides a visual representation of the various dialects spoken across the Arab world. It highlights the rich tapestry of linguistic diversity within the Arabic language, illustrating how regional variations can significantly affect pronunciation, vocabulary, and even grammar. This map serves as a crucial tool for understanding not just the language itself but also the cultural and social nuances that come with it.
Deep Dive into Arabic Dialects
Arabic is a Semitic language with a multitude of dialects that vary widely across different regions. These dialects can be broadly categorized into several major groups: Maghrebi Arabic, Egyptian Arabic, Levantine Arabic, Gulf Arabic, and Sudanese Arabic, among others. Each of these groups reflects the unique historical influences, social structures, and cultural practices of their respective areas.
Interestingly, Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is the formal version of the language used in writing and formal speech across the Arab world. However, in everyday conversation, the dialects come into play, with speakers often using their local dialect at home or in casual settings. This leads to a fascinating linguistic phenomenon where a speaker from Egypt may struggle to understand a speaker from Morocco despite both being considered "Arabic" speakers.
For instance, Maghrebi Arabic, spoken in countries like Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, is heavily influenced by Berber languages and French due to historical colonization. Consequently, it includes many loanwords and unique pronunciations, making it quite distinct from Gulf Arabic, which has influences from Persian and has retained many Classical Arabic features.
Moreover, the dialects can change dramatically even within a single country. In Egypt, the dialect spoken in Cairo differs significantly from that spoken in Upper Egypt, showcasing variations in accent, vocabulary, and sometimes even grammar. This level of diversity is one of the reasons why Arabic is often considered a language family rather than a single language.
What’s fascinating is that these dialects not only reflect linguistic differences but also indicate cultural identities. For example, a person's dialect may reveal their regional background or social class. As such, language can be a powerful marker of identity within the Arab world, influencing everything from social interactions to political affiliations.
Regional Analysis
When examining the Dialect Map of Arabic, we can see how geography plays a critical role in shaping these dialects. In the Levant, consisting of countries like Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine, the dialects share similarities but vary in tone and pronunciation. For example, Lebanese Arabic is known for its melodious tone, influenced by the country’s diverse cultural heritage, whereas Syrian Arabic has a more guttural sound.
In the Gulf region, dialects such as Kuwaiti, Emirati, and Saudi Arabic often include vocabulary borrowed from English due to modern influences and globalization. Interestingly, despite these borrowings, the core grammatical structure remains rooted in Classical Arabic, showcasing a blend of tradition and modernity.
On the other hand, Sudanese Arabic stands out with its unique phonetic qualities and vocabulary influenced by indigenous African languages. This contributes to a rich linguistic landscape that demonstrates how language can evolve based on historical migrations and cultural exchanges.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the dialects of Arabic is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights the cultural identities of the Arab people, allowing for a deeper appreciation of their history and social structures. Language is a living entity, constantly evolving and adapting, and the variations we see are a testament to the dynamic nature of human communication.
Moreover, in today's globalized world, knowledge of these dialects can facilitate better communication and foster connections among Arabic speakers from different regions. It can also play a significant role in fields such as education, diplomacy, and international business, where understanding cultural nuances is key to successful interactions.
As we move forward, the growth of technology and social media continues to influence dialects, leading to new forms of communication that blend traditional dialects with modern slang and expressions. Keeping an eye on these trends can provide insights into the future of the Arabic language and its dialects.
In conclusion, the Dialect Map of Arabic is not just a representation of geographical language variations; it encapsulates the rich cultural identities and social dynamics of the Arab world. By exploring these dialects, we gain a better understanding of the complexities of language and the people who speak it.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 10, 2025
- Views
- 58
Comments
Loading comments...