
Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
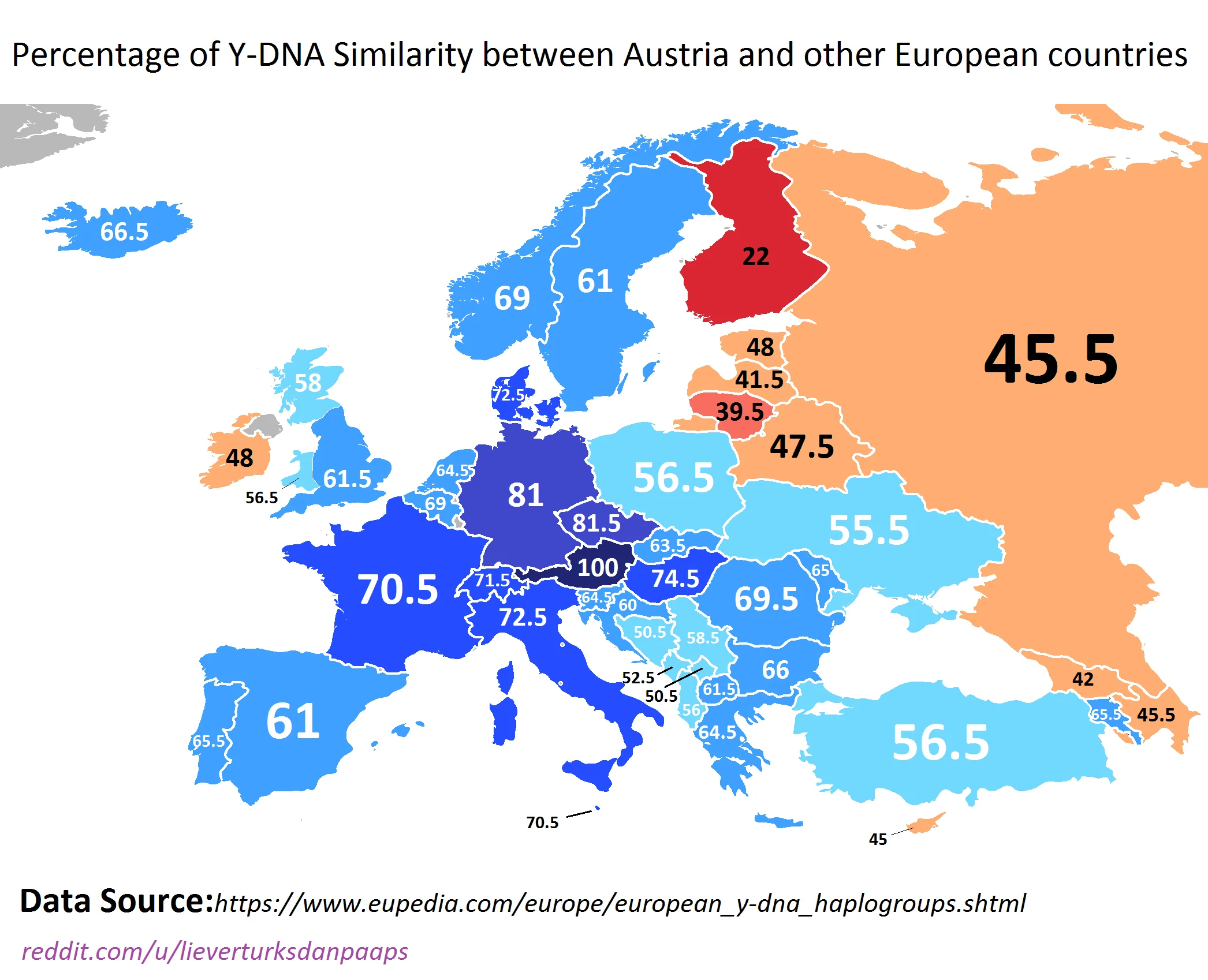
The visualization titled "Percentage of Y-DNA Similarity between Austria and other European countries" illustrates the genetic connections that exist between Austria and various European nations based on Y-DNA analysis. This type of genetic study involves examining the Y chromosome, which is passed from father to son, making it a vital tool for tracing paternal lineage. The map highlights the percentage of genetic similarity, revealing how closely related the male populations of Austria are to those in neighboring countries and beyond.
Deep Dive into Y-DNA Similarity
Y-DNA testing has gained popularity in recent years, not just among genealogists but also among researchers looking to understand human migration and ancestry. What’s fascinating is how these genetic similarities can often tell a story of shared history, migration patterns, and cultural exchanges that have shaped modern Europe.
Austria, located in the heart of Europe, has a rich tapestry of genetic influences due to its historical ties with various cultures and nations. The Y-DNA similarities represented in the map can be attributed to several factors, including historical migrations, trade routes, and even conflicts that brought populations closer together.
For example, a high percentage of Y-DNA similarity with neighboring countries, such as Germany and the Czech Republic, can be anticipated due to shared borders and the movement of people over centuries. Historically, the Austro-Hungarian Empire influenced migration patterns, with people moving freely across the region. This is reflected in the genetic data, showing a strong correlation with nearby populations.
Interestingly, as you look further afield to countries like Italy or Slovenia, the genetic similarities may vary. Italy has had a complex influence on Austria, especially in regions like Tyrol and Carinthia, where there has been significant intermarriage and cultural exchange over the years. Conversely, with countries farther from Austria, like the UK or Ireland, you might see lower genetic similarity percentages. This can be attributed to a lack of historical migration between these regions and Austria's population.
Furthermore, genetic studies have revealed fascinating insights into the impact of the Roman Empire on the genetic makeup of Europe. The empire’s reach extended into Austria, leading to a mingling of populations and thus a lasting genetic footprint that can still be traced today.
Regional Analysis
When breaking down the Y-DNA similarity percentages, it’s important to consider the geographical and cultural context of each area represented on the map. For instance, let’s examine Austria’s similarity with its immediate neighbors:
- **Germany:** Often shows high Y-DNA similarity, reflecting not only geographical proximity but also centuries of shared history, intermarriage, and migration. - **Czech Republic:** Similarity levels here are also high, attributable to the historical ties and movements of populations during the Austro-Hungarian Empire. - **Hungary:** Shares a significant percentage due to their intertwined histories; many Austrians and Hungarians share common ancestors from the region. - **Slovenia:** The map indicates a moderate to high similarity, which can be explained by cultural and economic exchanges across the borders.
As we move away from these neighboring countries, the percentages tend to decline. For example, Austria’s similarity with Scandinavian countries like Sweden and Norway is markedly lower. This decline can be attributed to the distinct migration histories and the geographic barriers that have historically separated these populations.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Y-DNA similarity is not merely an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for genealogy, anthropology, and even public health. For those interested in their ancestry, knowing how closely they are related to populations in other countries can provide insights into family history and heritage. This can foster a sense of identity and connection to one's roots.
Moreover, in the context of modern society, these genetic links can impact migratory policies, health initiatives, and even cultural exchanges. As globalization continues to blur national boundaries, recognizing these genetic similarities can help bridge cultural divides and enhance cooperation among European nations.
Looking ahead, the trends in genetic research suggest a growing interest in how DNA can inform our understanding of history and identity. As technology improves, we may see even clearer pictures of migration patterns and genetic connections, allowing us to appreciate the rich tapestry of human ancestry even more deeply. How will these insights shape our future interactions and relationships across Europe? Only time will tell, but it’s clear that our genetic past continues to influence our present.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 9, 2025
- Views
- 108
Comments
Loading comments...