Landlocked Countries with a Navy Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
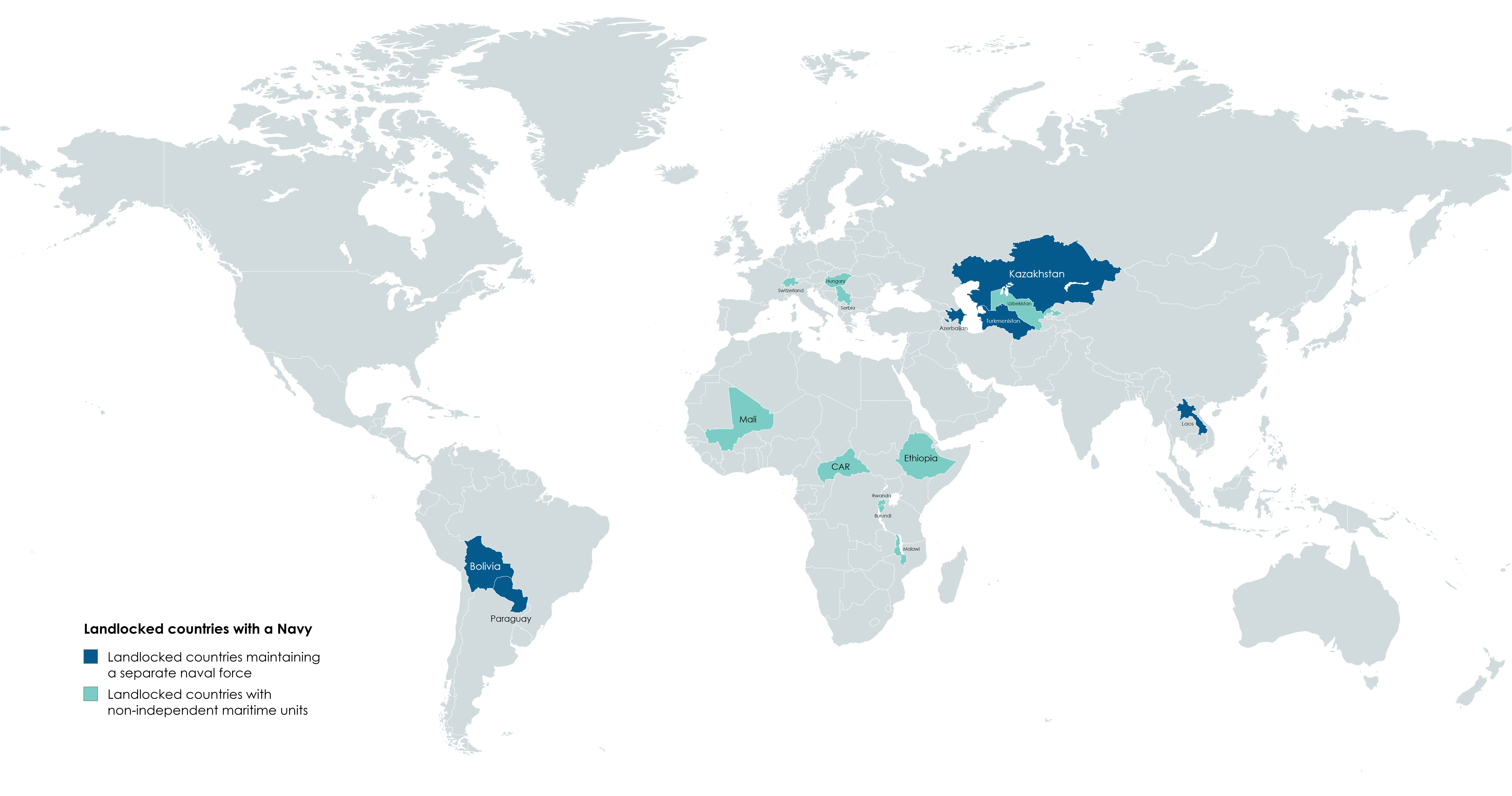
The "Landlocked Countries with a Navy Map" provides a unique perspective on a seemingly contradictory concept: nations without direct access to the ocean that maintain naval forces. This visualization highlights countries that, despite their geographical limitations, have established naval capabilities. At first glance, one might wonder how a landlocked nation can possess a navy. Yet, this map reveals the interesting complexities of global military strategy and national security.
Deep Dive into Landlocked Navies
Let’s unpack the intriguing idea of landlocked countries possessing naval forces. The term "navy" typically conjures images of ships patrolling oceans and engaging in maritime operations. However, landlocked countries have adapted military strategies that include the development of naval capabilities, albeit often focused on riverine and lake operations.
For instance, countries like Bolivia and Paraguay maintain small naval forces, not for oceanic warfare but for patrol and transportation on their respective rivers. Bolivia has a navy that operates on Lake Titicaca and the Paraguay River, which have historical significance for trade and transport. Interestingly, Bolivia's naval presence stems from its loss of coastline to Chile in the 19th century, making its naval ambitions a matter of national pride and identity.
In Europe, countries like Hungary and Switzerland utilize their naval forces on inland waterways like the Danube River and Lake Geneva, respectively. The Hungarian navy operates primarily for patrol and support of civilian shipping, showcasing how landlocked nations strategically use their limited maritime access to bolster national security and foster economic activity.
Moreover, some landlocked nations have developed their naval capabilities to assist in humanitarian missions or environmental monitoring. For example, landlocked countries may engage in joint naval exercises with neighboring coastal states to enhance cooperative security efforts. This cooperation can be crucial in addressing transboundary issues such as piracy, illegal fishing, and environmental protection in shared water bodies.
The development of naval forces in landlocked countries also raises questions about military expenditure and resource allocation. With limited budgets, these nations must balance naval investments against other pressing needs like education, infrastructure, and health. This balancing act is essential for maintaining a functional military while ensuring the overall well-being of the populace.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals significant regional variations in how landlocked countries engage with naval capabilities. In South America, Bolivia and Paraguay lead the way, using their naval forces to assert sovereignty over their river systems. Both countries have developed their navies with a focus on patrolling and protecting important trade routes, which are vital for their economies.
In contrast, European landlocked nations such as Hungary and Switzerland exhibit a different approach to their naval capabilities. Their focus is less on traditional military engagements and more on domestic security, environmental monitoring, and international cooperation. For instance, Hungary's naval operations on the Danube are often aligned with European Union initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable development and regional stability.
In Africa, countries like Mali and Niger, while landlocked, face unique challenges. They do not maintain formal naval forces but have developed riverine units for security operations on the Niger River. This adaptation highlights the necessity of securing water resources while combating threats such as smuggling and terrorism along vital waterways.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the dynamics of landlocked countries with navies is crucial for grasping contemporary security issues. This topic matters because it highlights the adaptability of nations in addressing their unique geographical challenges. As global trade increasingly relies on waterways for transportation, even landlocked countries must ensure their interests are protected.
Current trends indicate that landlocked nations are becoming more engaged in international maritime security discussions, often through partnerships with coastal nations. As climate change continues to impact global sea levels and weather patterns, these nations may find their naval capabilities even more relevant for addressing humanitarian crises and environmental challenges.
In conclusion, the existence of navies in landlocked countries underscores a fascinating intersection of geography, military strategy, and national identity. It provokes further questions about how countries navigate their limitations while asserting their interests on the global stage. As we look to the future, the role of these unique naval forces will likely evolve, reflecting the ever-changing dynamics of international relations and environmental stewardship.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 6, 2025
- Views
- 114
Comments
Loading comments...