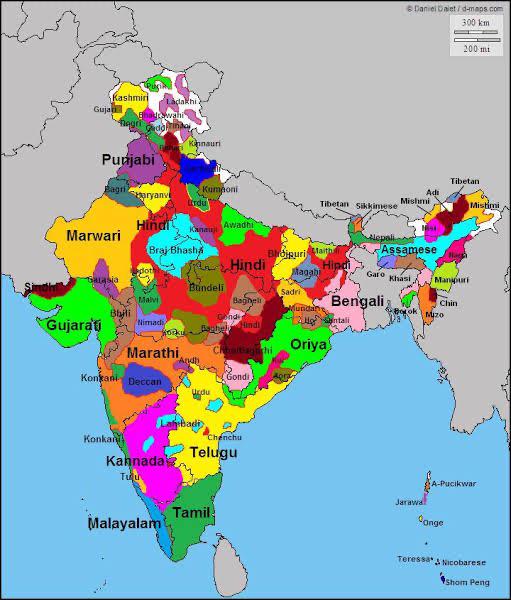
Linguistic Map of India

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The Linguistic Map of India visually represents the diverse tapestry of languages spoken across the subcontinent. With 22 officially recognized languages and thousands more spoken daily, this map provides a fascinating glimpse into the linguistic diversity that characterizes India. Each region showcases the predominant languages, offering insights into cultural identities and community ties that thrive within the country's vast geographic expanse.
Deep Dive into India's Linguistic Diversity
India is often referred to as a linguistic paradise, a place where language is not just a means of communication but a key component of cultural heritage. The map illustrates how languages are distributed across various states, highlighting not only the official languages but also regional dialects and minority languages that enrich the country's linguistic landscape.
For instance, Hindi, the most widely spoken language and one of the official languages, dominates the northern states such as Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh. However, it is essential to note that Hindi itself has many dialects, such as Awadhi and Bhojpuri, which vary significantly in terms of vocabulary and pronunciation.
In the southern states, languages like Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam take precedence. Tamil, one of the oldest classical languages in the world, is predominantly spoken in Tamil Nadu and parts of Sri Lanka, showcasing a rich literary tradition that dates back over 2,000 years. Interestingly, Tamil also has a significant diaspora, with speakers found across the globe, a testament to its cultural reach.
Meanwhile, in the northeastern region, languages such as Assamese, Manipuri, and various tribal languages like Bodo and Khasi reflect the rich ethnic diversity of the area. Each of these languages carries its own unique traditions and stories, often tied to the land and its history. What’s fascinating is how these languages often coexist, sometimes leading to the emergence of mixed languages and dialects unique to specific communities.
India's linguistic diversity is not merely a point of interest; it plays a crucial role in shaping social interactions, education, and politics. The Constitution of India recognizes 22 languages under the Eighth Schedule, ensuring that these languages receive official status and protection. This recognition is vital, as many languages face the threat of extinction due to globalization and urban migration.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the linguistic map region by region, one can observe distinct patterns. In the North, for example, states like Punjab and Haryana predominantly speak Punjabi and Haryanvi, respectively, reflecting the agricultural lifestyle of their populations. Contrast this with the western state of Gujarat, where Gujarati is spoken, a language rooted in business and commerce, illustrating the region's economic history.
In the central part of India, Maharashtra showcases Marathi as its primary language, while Madhya Pradesh is a mix of Hindi and regional dialects. This linguistic interplay offers a glimpse into the historical migrations and settlements that have shaped the area over centuries.
In the East, West Bengal is a bastion of Bengali culture, with the language seen as a source of pride and identity, especially during cultural festivals like Durga Puja. Interestingly, the presence of Bengali-speaking communities in neighboring states like Assam and Tripura indicates how languages can transcend state boundaries, leading to vibrant cultural exchanges.
The southern states, rich in classical languages, display an interesting phenomenon: the coexistence of languages with a historical significance alongside modern vernaculars. For example, while Kannada is spoken in Karnataka, the state also has a significant number of speakers of Urdu and English, reflecting the urbanization and globalization of the region.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the linguistic landscape of India is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it plays a role in fostering national unity while allowing for regional identities to flourish. However, the challenge of balancing linguistic diversity with national coherence is ongoing, especially in political and educational contexts.
Moreover, language preservation efforts are vital in combating the decline of many regional languages that are at risk of disappearing. Have you ever wondered why language revitalization initiatives are crucial? They not only preserve cultural heritage but also promote biodiversity, as many indigenous languages encapsulate local ecological knowledge.
Looking forward, the impact of technology on language use, such as the rise of digital communication, is shaping how languages evolve. With more people embracing regional dialects on social media platforms, there could be a renaissance of interest in local languages among younger generations.
In conclusion, the Linguistic Map of India is more than just a representation of languages; it is a lens through which we can study the country's complex cultural, social, and political fabric. The diverse languages spoken across India are not merely a means of communication but a celebration of the country's rich heritage and identity, weaving a colorful narrative of its past and present.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 5, 2025
- Views
- 8
Comments
Loading comments...