Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Seaway Map Over Europe

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
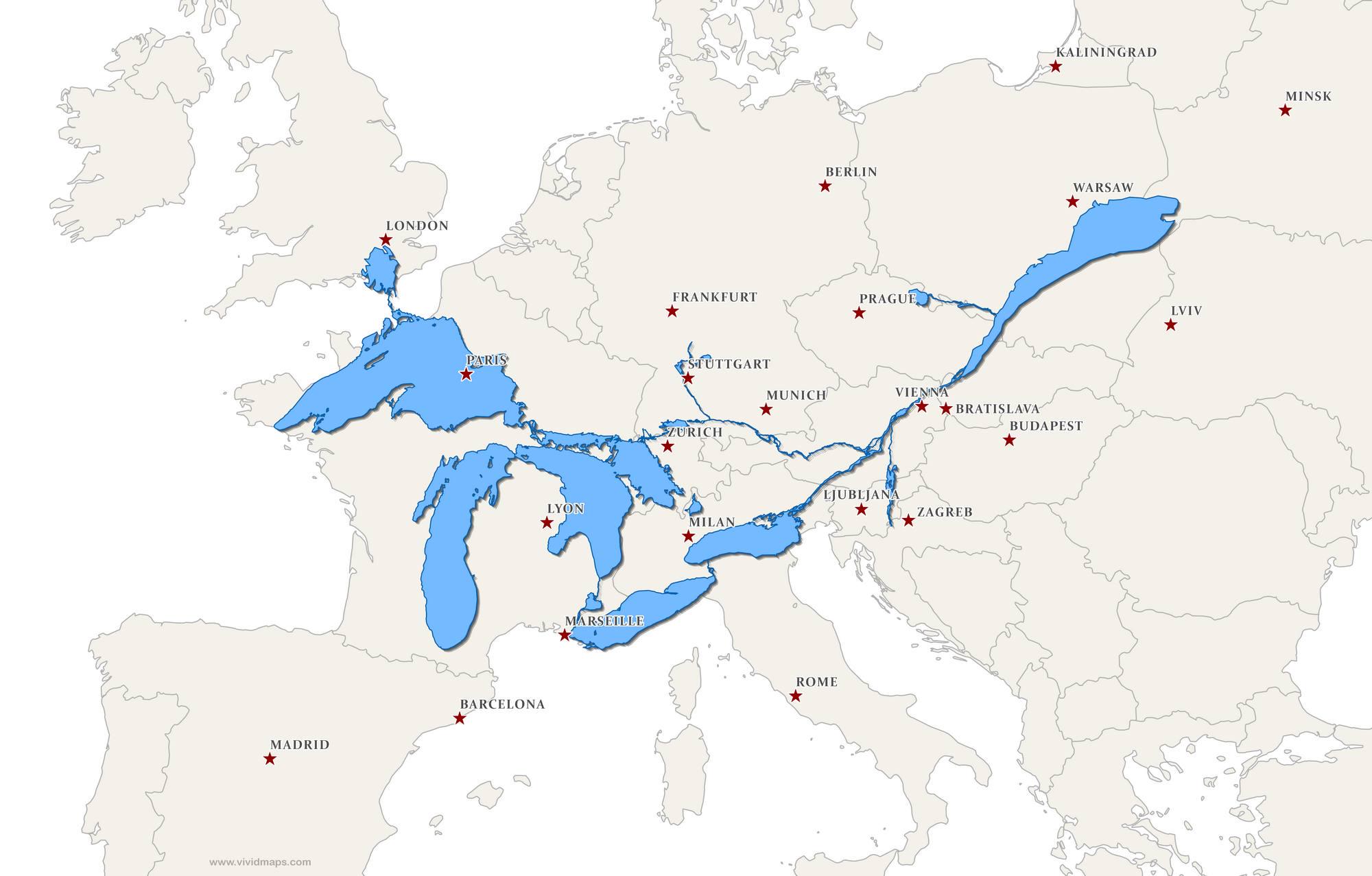
What This Map Shows
This fascinating map superimposes the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence Seaway over Europe, providing a unique perspective on these significant North American water bodies by comparing their size and geographic context to familiar European landmarks. It highlights how vast the Great Lakes are, showcasing their immense freshwater system and the critical role the St. Lawrence Seaway plays in trade and transport. This visualization invites viewers to draw parallels between these two regions, igniting a curiosity about water systems and their influence on geography.
Deep Dive into the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence Seaway
The Great Lakes, consisting of Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, Lake Erie, and Lake Ontario, form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area. Together, they cover approximately 94,250 square miles (244,106 square kilometers) and hold about 20% of the world's surface freshwater. This impressive statistic alone emphasizes the critical role these lakes play in both ecology and human activity.
Interestingly, the Great Lakes were formed during the last Ice Age, around 14,000 years ago, as glaciers receded and carved out their basins. Today, they are not just natural wonders; they function as a vital resource for millions of people. The lakes support shipping, recreation, and fishing industries, with the shipping industry alone moving over 160 million tons of cargo each year.
The St. Lawrence Seaway, completed in 1959, is a crucial waterway that connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean. Spanning over 2,300 miles, it allows for the navigation of large vessels, facilitating trade between Canada and the United States and beyond. The seaway comprises a series of locks, canals, and channels that overcome the elevation difference between the lakes and the ocean, making it one of the engineering marvels of the modern era.
This waterway is particularly important for the transportation of bulk commodities, such as grain, iron ore, and coal. It helps sustain the economies of several states and provinces, contributing significantly to local and national economies. The Seaway has a profound impact on industrial development, fostering urban growth in cities such as Chicago, Detroit, and Toronto.
Regional Analysis
When we examine the regional implications of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence Seaway, it becomes evident that their influence extends far beyond just the immediate areas they touch. For instance, the Great Lakes region is one of the most densely populated areas in North America. Cities like Chicago and Detroit thrive on the lakes' resources, showcasing a rich history of industrialization fueled by their proximity to this freshwater source.
In contrast, looking at Europe, we might compare the Great Lakes to major European rivers like the Rhine or the Danube. While these rivers are vital for transport and trade, they are not as expansive in surface area as the Great Lakes. The Rhine, one of Europe's busiest waterways, spans about 765 miles and is crucial for commerce, yet it pales in comparison to the sheer volume of freshwater held in the Great Lakes.
Interestingly, the environmental challenges faced by both regions also mirror each other. In North America, issues such as pollution, invasive species, and the impacts of climate change pose significant threats to the Great Lakes. Similarly, European waterways grapple with pollution from industrial runoff and agricultural practices, highlighting that despite geographical differences, the concerns about maintaining water quality and ecosystems are universally critical.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence Seaway is vital for recognizing their importance in global geography. These water bodies are not just local resources; they are essential components of international trade and environmental health. As climate change continues to shape weather patterns, the Great Lakes will likely face fluctuations in water levels, impacting ecosystems, local economies, and communities.
Moreover, the lessons learned from managing the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence Seaway can offer insights into global water management strategies. As populations grow and freshwater resources become scarcer, the experiences from these North American water systems could inform sustainable practices worldwide. Ever wondered why freshwater conservation is becoming increasingly critical? The reality is that as our planet's climate changes, the management of such vital resources will determine the sustainability of communities and ecosystems for generations to come.
In conclusion, the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence Seaway are more than just geographical features; they are lifelines that shape economies, cultures, and ecosystems. Understanding their significance provides valuable insights into our interconnected world and the ongoing need for responsible stewardship of our natural resources.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 3, 2025
- Views
- 60
Comments
Loading comments...