Mountains as Share of Land in EU Countries Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
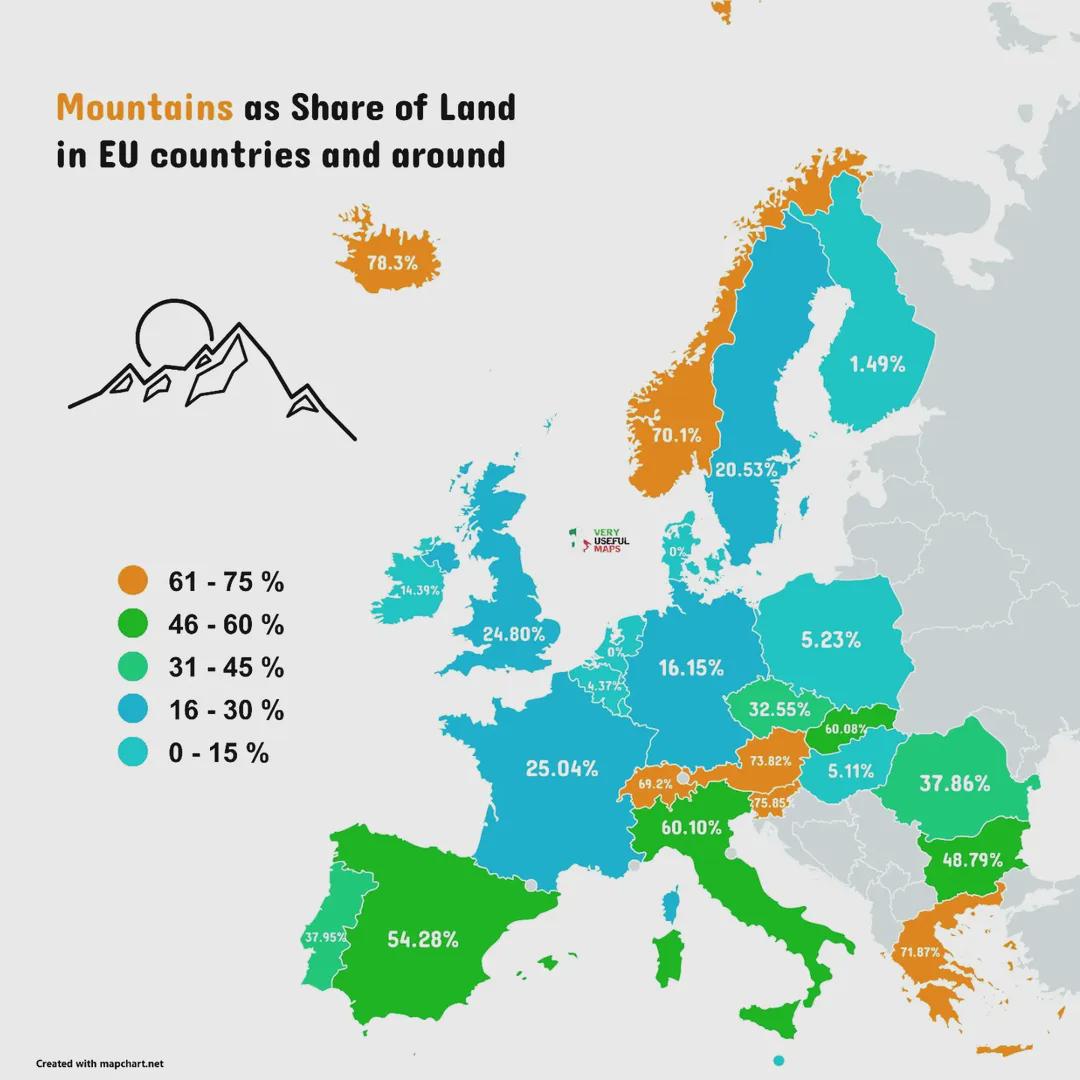
What This Map Shows
The 'Mountains as Share of Land in EU Countries and Around' map visually represents the proportion of mountainous terrain in various countries across Europe. By highlighting the percentage of land that is classified as mountainous, this visualization allows us to understand the geographical diversity within the European Union and its neighboring countries. Mountains are not just visually striking; they significantly influence climate, biodiversity, and human activity.
Deep Dive into Mountains in Europe
Mountains play a crucial role in shaping the physical geography of Europe. Ranging from the towering Alps, which stretch across eight countries, to the rugged Carpathians and the ancient Apennines, these landforms are vital to both the environment and the economy. Interestingly, mountainous areas cover about 25% of the European land area, and this figure can vary dramatically from one country to another.
Mountains are more than just peaks; they are ecosystems teeming with life. For instance, the Alps are home to a rich tapestry of flora and fauna, including endemic species like the Alpine ibex and edelweiss. Moreover, these regions often act as water towers, feeding rivers and lakes that are essential for agriculture and drinking water. The presence of mountains also influences local weather patterns, leading to unique microclimates that support various agricultural practices.
However, the significance of mountains goes beyond their ecological contributions. They are crucial for tourism and recreation, attracting millions of visitors annually. Ski resorts in the Alps, mountain hiking trails in the Pyrenees, and picturesque villages nestled in valleys offer economic benefits to these regions. For example, in countries like Switzerland and Austria, tourism related to mountainous landscapes contributes significantly to GDP.
Yet, while mountains can be seen as assets, they also present challenges. The rugged terrain can limit infrastructure development, making transportation and accessibility difficult. This is particularly evident in countries like Italy and Greece, where mountainous regions can isolate communities. Additionally, climate change poses a serious threat to these mountainous ecosystems, leading to glacial retreat and altered habitats.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals distinct patterns in the distribution of mountainous land across Europe. For instance, countries like Switzerland and Austria boast nearly 60-70% of their land designated as mountainous, showcasing their dramatic alpine landscapes. In contrast, flatter countries such as the Netherlands or Denmark have negligible mountainous areas, emphasizing the stark geographical differences within Europe.
Interestingly, the Balkan Peninsula presents a unique case. Nations like Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina are rich in mountainous terrain, contributing to their stunning natural beauty and biodiversity. However, despite their geographical advantages, these countries often face economic challenges, such as limited infrastructure and reliance on tourism, which can be volatile.
Furthermore, the Pyrenees delineate the border between Spain and France, contributing to the distinct cultural and climatic differences on either side. The Spanish side, with its rugged peaks and valleys, is known for its unique Basque culture, while the French side is characterized by a more alpine lifestyle. This interaction between geography and culture highlights the profound impact that mountains have on human history and societal development.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of mountainous regions in Europe is essential for several reasons. First, these areas are pivotal for biodiversity conservation, as they often host unique ecosystems. Protecting mountain regions is critical in the face of climate change, which threatens not only the flora and fauna but also the livelihoods of communities that depend on these ecosystems.
Moreover, as the global population grows, the pressure on mountainous areas will increase. Urbanization, agriculture, and tourism can lead to environmental degradation if not managed sustainably. Countries are beginning to recognize the importance of sustainable practices in mountainous regions to balance economic development with environmental conservation.
In conclusion, the map of mountains as a share of land in EU countries and around provides more than just geographical data. It opens a window into understanding the complex interplay between natural landscapes and human activities. As we look to the future, it is vital to consider how we can responsibly manage these precious resources for generations to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 2, 2025
- Views
- 86
Comments
Loading comments...