Viking Expansion Routes Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
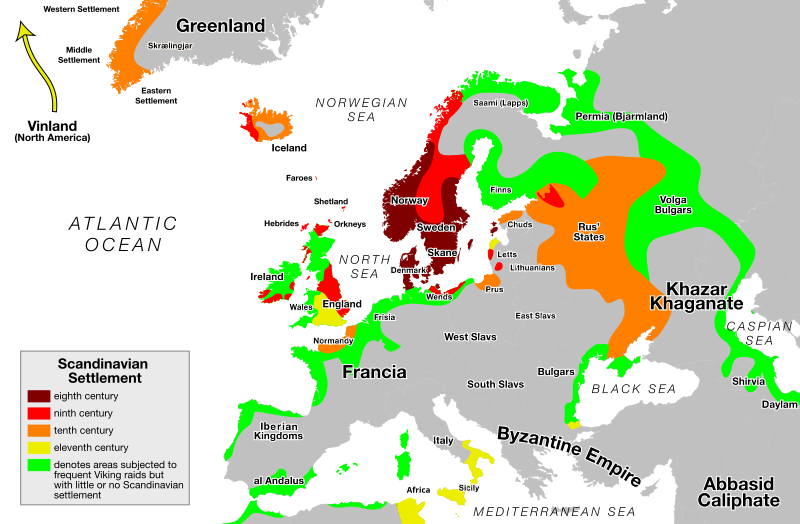
The "Viking Expansion Routes Map" visually represents the vast territories explored and settled by the Norsemen, commonly known as Vikings, during the late 8th to the early 11th centuries. This map highlights not only the geographic boundaries of their expeditions but also the intricate trade routes and settlement patterns that emerged during this dynamic period in history. It serves as a fascinating window into how these seafaring warriors and traders expanded their influence across Europe, Asia, and even parts of North America.
Deep Dive into Viking Expansion
The Viking Age, characterized by the raids, trade, and exploration of Norse seafarers, began around 793 AD with the attack on the Lindisfarne monastery in England. What's fascinating is that the Vikings were not just raiders; they were also explorers and settlers who established trade networks, cultural exchanges, and political alliances. Their longships were marvels of engineering, allowing them to navigate both open seas and shallow rivers, which played a crucial role in their ability to expand into diverse territories.
The map illustrates several key areas of Viking expansion. Starting from their homelands in Scandinavia, the Vikings ventured into the British Isles, where they established significant settlements in places like York and Dublin. Interestingly, they didn't just conquer; they integrated into local cultures, influencing the language and customs of the regions they inhabited.
Moving eastward, the Vikings navigated the rivers of Russia, reaching as far as the Black Sea and Byzantium. This expansion led to the establishment of trade routes known as the Varangian to the Greeks, connecting Northern Europe with the wealth of the East. You might wonder how they managed this: their trade included furs, amber, and slaves, while they imported silver, silk, and spices, enriching their culture and economy.
In the west, their most famous expedition led to the discovery of North America around 1000 AD, with Leif Erikson landing in what is now Newfoundland, Canada. This area, known as Vinland, was used for settlement, although it did not last long, primarily due to conflicts with the indigenous populations.
The Viking Age also saw the establishment of the Danelaw in England, where Norse law and customs governed large parts of eastern England. This area became a melting pot of cultures, contributing significantly to the development of medieval England.
Regional Analysis
The map allows us to break down Viking expansion into several distinct regions. In the British Isles, the impact of the Vikings was profound. In Scotland, the Norse settled in the Orkney and Shetland Islands, while in Ireland, they established coastal cities like Waterford and Wexford. These settlements were not merely military outposts; they became centers of trade and cultural exchange.
In Eastern Europe, the Vikings, known as the Varangians, played a crucial role in the formation of early Russian states. The city of Novgorod became a vital trade hub, linking Scandinavia with Byzantium and the East. The interactions between the Vikings and the Slavic peoples led to significant political and cultural developments, including the eventual establishment of the Kievan Rus.
In the North Atlantic, the settlement of Iceland and Greenland further illustrates the Vikings' adaptability and resourcefulness. These areas, though harsh, became important outposts for exploration and trade. The Norse established a thriving community in Greenland, which lasted for several centuries before environmental factors and dwindling resources led to its decline.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Viking expansions is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it reshaped the political landscape of Europe, leading to the formation of new kingdoms and trade networks that would lay the groundwork for modern European states. The cultural exchanges initiated by the Vikings influenced languages, governance, and societal structures across multiple regions.
Moreover, the legacy of the Vikings extends beyond their immediate geographical impacts. The maritime technologies and navigation skills developed during this period set the stage for future explorations, paving the way for the Age of Discovery centuries later. Current trends in archaeology continue to uncover new insights into Viking life, challenging previous notions about their society and enriching our understanding of this pivotal era in history.
In conclusion, the Viking Expansion Routes Map is not just a collection of lines and dots; it represents a transformative period that shaped much of Europe's medieval landscape. By studying these routes, we gain valuable insights into the interconnected world of the past, highlighting how exploration and trade can lead to profound cultural shifts that resonate to this day.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 1, 2025
- Views
- 58
Comments
Loading comments...