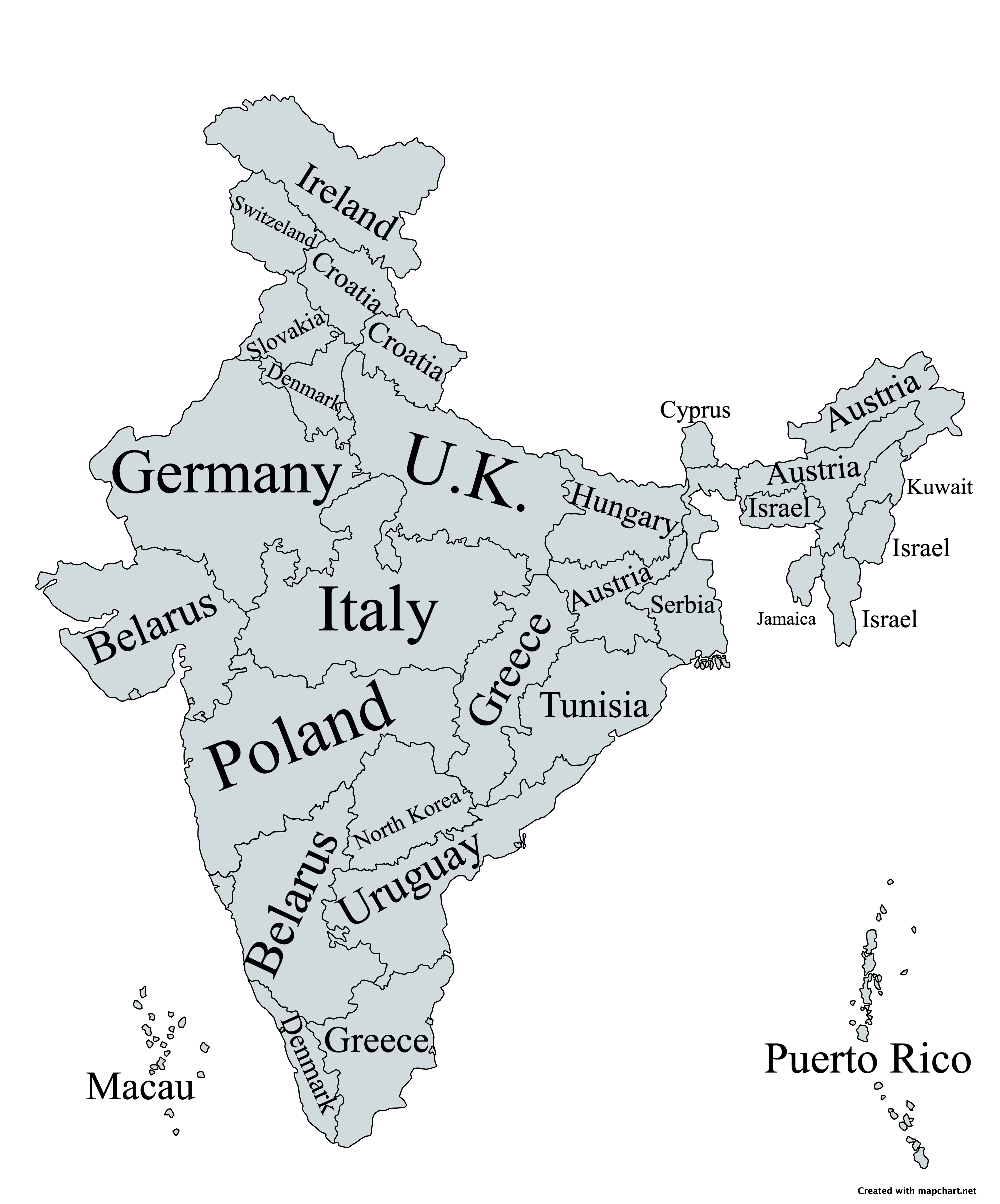
Indian States Compared to Countries by Land Area Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map offers a compelling comparison between the land area of Indian states and various countries around the world. Unlike many visualizations that focus on population density or GDP, this representation emphasizes how vast or compact each state is when juxtaposed with entire nations. As you delve into this visual, you might find yourself surprised at how some Indian states measure up against countries such as Belgium, Brazil, or even Canada. This perspective can shift our understanding of both regional importance and geographical scale.
Deep Dive into Land Area
Land area is a fundamental aspect of geography that plays a crucial role in numerous factors, including resource distribution, population density, and economic potential. The total land area of India is approximately 3.287 million square kilometers, making it the seventh-largest country in the world. Interestingly, when we compare Indian states to countries based on land area, we uncover a fascinating narrative that reflects the diversity and vastness of India.
For instance, Rajasthan is not only the largest state in India, covering an area of about 342,239 square kilometers, but it also rivals the land area of countries like Afghanistan and Italy. This fact highlights not just the size of Rajasthan but also the variety of landscapes it encompasses, from the Thar Desert to the Aravalli mountain range. On the other end of the spectrum, states like Goa, which is roughly 3,702 square kilometers, can be compared to countries like Luxembourg, showcasing how some Indian states might fit into much smaller nations.
Land area affects agricultural practices, urban planning, and infrastructure development. States with larger areas, like Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, have the potential for diverse agricultural outputs, while smaller states may focus on specific industries or tourism, as is the case with Goa's thriving hospitality sector. Furthermore, geographical features such as rivers, mountains, and climate also significantly influence how land is utilized within these states.
Regional Analysis
When we analyze the map regionally, we notice distinct patterns that emerge. Northern states like Uttar Pradesh and Punjab hold vast agricultural lands, contributing to India's food security. Uttar Pradesh, for instance, with an area of about 243,286 square kilometers, is comparable to the size of Italy, emphasizing its agricultural significance in the country.
Conversely, the northeastern states, despite their relatively smaller land areas, such as Tripura (10,491 square kilometers) and Nagaland (16,579 square kilometers), are rich in biodiversity and cultural heritage. This region's unique geographical advantages, including abundant rainfall and rich soil, allow for specialized farming practices, particularly in horticulture and organic farming.
In the southern part of India, states like Karnataka and Tamil Nadu showcase a contrast between urbanization and rural landscapes. Karnataka, with an area of 191,791 square kilometers, can be compared to the size of Greece, while Tamil Nadu (130,058 square kilometers) shares similarities with the land area of North Korea. These comparisons underline how land area plays a role in balancing urban growth with agricultural sustainability.
Interestingly, in western India, Gujarat's land area of about 196,024 square kilometers makes it comparable to the size of the United Kingdom. This highlights not only the state's economic prowess but also its diverse ecosystems, from coastal regions to arid deserts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding land area in the context of Indian states compared to countries has broader implications. As India continues to develop, these comparisons reveal insights into resource allocation, regional development, and economic planning. For instance, states with larger land areas often have access to more natural resources, which can lead to higher economic outputs. However, it can also lead to challenges related to governance and infrastructure development.
Moreover, as urbanization increases, smaller states may face pressure to expand their infrastructure and services to accommodate growing populations. This phenomenon raises questions about sustainability and land use planning. Have you noticed how some states are investing in smart cities to manage their resources better? The implications of land area comparisons extend beyond mere numbers; they resonate with real-world challenges and opportunities.
In conclusion, this map serves as a reminder of the diverse landscapes and vastness of India, inviting us to appreciate not just the numbers but the stories behind them. As we think about the future, understanding these geographical dynamics will be crucial for informed decision-making and sustainable development across the subcontinent.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 30, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...