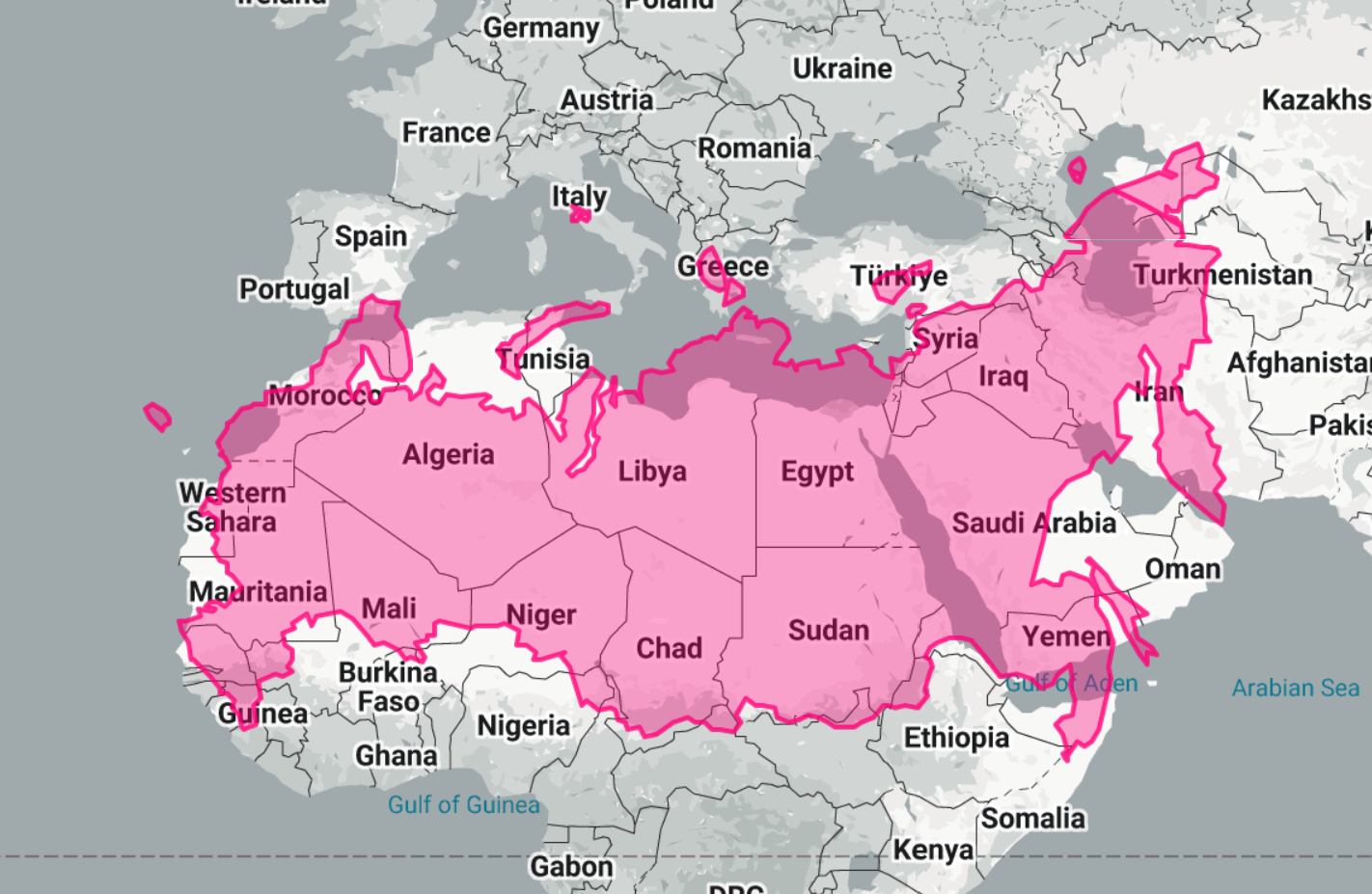
Sahara and Arabian Deserts Size Comparison Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Sahara and Arabian Deserts Size Comparison Map" provides a striking visual representation of the immense scale of two of the world's largest deserts. It highlights the sheer expanse of the Sahara Desert, which stretches across North Africa, and the Arabian Desert, located on the Arabian Peninsula. This map serves not only as an eye-opener to the vastness of these arid regions but also sets the stage for a deeper exploration into the characteristics that define these deserts, their climates, and their ecological significance.
Deep Dive into Deserts
Deserts, by definition, are regions that receive less than 250 millimeters of precipitation annually, making them some of the driest places on Earth. The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, spans approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, covering much of Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, Chad, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, and Morocco. Interestingly, the Sahara has a diverse geography that includes sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and salt flats, making it a unique ecological zone.
On the other hand, the Arabian Desert, while smaller at about 2.33 million square kilometers, features its own remarkable characteristics. It encompasses countries such as Saudi Arabia, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, and parts of Jordan and Iraq. The Arabian Desert is known for its vast empty quarter, or Rub' al Khali, which is one of the largest sand deserts in the world. What’s fascinating is that despite their arid conditions, both deserts host a variety of flora and fauna that have adapted to survive in extreme environments.
Climatically, both deserts experience extreme temperature variations. The Sahara sees daytime temperatures soar above 50°C (122°F) during the summer months, while winter nights can plummet to near freezing. The Arabian Desert shares similar temperature extremes, with some areas recording temperatures as high as 56°C (132.8°F). However, it is important to note that the Arabian Desert also experiences more humidity due to its proximity to the Persian Gulf, which can influence local weather patterns.
Moreover, the unique geographical features of these deserts contribute to their ecological diversity. The Sahara, for instance, is home to the endemic Saharan silver antelope and the critically endangered addax antelope, both of which have adapted to the harsh conditions. In contrast, the Arabian Desert is known for the Arabian oryx, which has successfully been reintroduced into the wild after being on the brink of extinction due to hunting and habitat loss. These adaptations showcase the resilience of life in some of the planet's harshest climates.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing these deserts regionally, it’s imperative to recognize the differences not only in size but also in ecological and cultural significance. For instance, the Saharan region is often characterized by nomadic cultures that have thrived for centuries, relying on traditional practices such as herding and trade. The Tuareg people, known for their vibrant blue attire, have a rich history intertwined with the desert landscape, navigating its challenges with remarkable skill.
Conversely, the Arabian Peninsula has seen rapid urbanization and development, particularly in countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia. Cities such as Dubai and Riyadh serve as economic hubs, leveraging their desert landscapes for tourism and commerce. Interestingly, despite the harsh desert environment, these cities have transformed into symbols of modernity, showcasing the paradox of thriving life amidst desolation.
Furthermore, the impact of climate change is increasingly relevant to both deserts. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns threaten the delicate ecosystems that exist within these arid environments. As desertification spreads, it poses a challenge not just to local wildlife but also to human populations that depend on these lands for their livelihoods.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the size and dynamics of the Sahara and Arabian Deserts is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, these deserts play a significant role in influencing global weather patterns, particularly in the context of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which affects rainfall distribution across Africa and the Middle East. Moreover, they harbor unique ecosystems that need protection in the face of climate change and human encroachment.
Furthermore, the cultural heritage linked to these deserts is invaluable. The stories, traditions, and ways of life of the people who inhabit these regions offer insights into human resilience and adaptability. As we continue to delve into the challenges posed by climate change, recognizing the importance of sustainable practices and conservation efforts is more critical than ever.
In conclusion, while the map illustrates the astounding sizes of the Sahara and Arabian Deserts, it also invites us to explore the complexities and significance of these vast landscapes. The interplay between environment, culture, and modern challenges makes the study of these deserts not only intriguing but essential to understanding our planet's future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 26, 2025
- Views
- 160
Comments
Loading comments...