Bean Consumption Per Capita in Europe Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
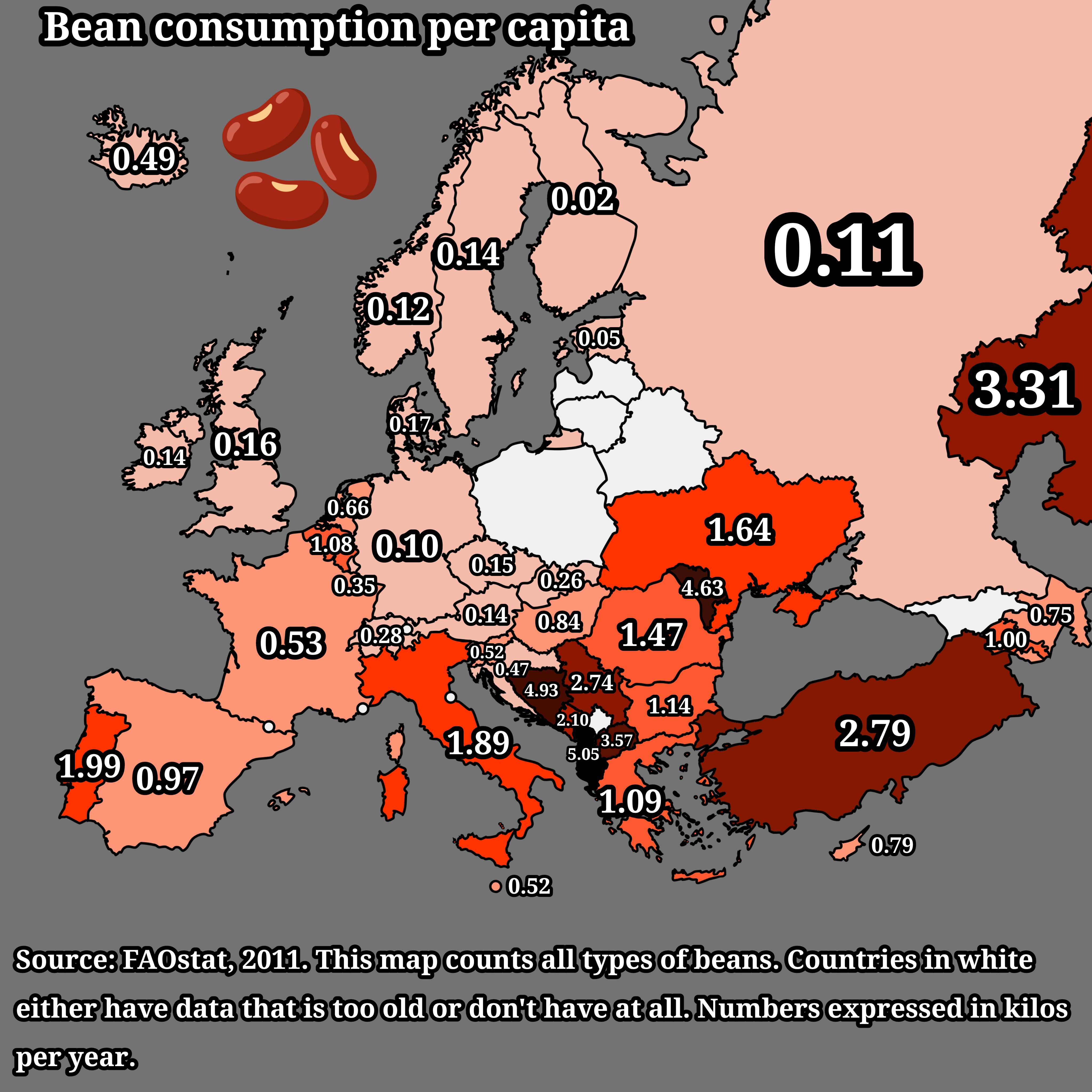
What This Map Shows
The "Bean Consumption Per Capita in Europe Map" provides a detailed visualization of the average bean consumption across various European countries. With vivid colors highlighting different levels of consumption, this map allows us to see at a glance which nations are leading in bean consumption and which ones lag behind. As we dive deeper into the topic, we’ll discover the cultural, economic, and dietary factors influencing these trends.
Deep Dive into Bean Consumption in Europe
Beans are an essential part of the human diet, providing not only protein but also fiber, vitamins, and minerals. In many cultures, they are a staple food, celebrated for their versatility and nutritional value. In Europe, the consumption of beans varies widely from one country to another.
Beans have been cultivated for thousands of years, and their significance in European diets can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Interestingly, beans are often categorized into various types, including kidney beans, black beans, chickpeas, and lentils, each with unique flavors and culinary uses. In Europe, the most popular types of beans include white beans, broad beans, and chickpeas.
As of the most recent data, countries like Portugal and Spain rank high in per capita bean consumption, often incorporating them into traditional dishes such as "feijoada" and "pisto" respectively. For example, a typical Portuguese feijoada is a hearty stew made with black beans and various meats, showcasing how beans play a central role in Mediterranean diets. On the other hand, Scandinavian countries tend to have lower bean consumption rates, primarily due to different dietary customs and the prevalence of other protein sources like fish and meat.
Interestingly, the rise of vegetarianism and veganism across Europe has led to an increase in bean consumption in recent years. Plant-based diets have gained traction, with beans being heralded as a vital component due to their high protein content and health benefits. In countries like Germany and the Netherlands, the trend towards more plant-based eating has significantly increased the demand for legumes, including beans. Furthermore, the European Union has recognized the importance of legumes in achieving sustainability targets, promoting their cultivation and consumption as a way to reduce carbon footprints.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map, we see distinct patterns emerging across different European regions. Southern European countries, such as Italy, Greece, and the Iberian Peninsula, exhibit higher per capita bean consumption. This can be attributed to their rich culinary traditions that celebrate beans as a fundamental ingredient in many local dishes. For instance, in Italy, beans are often used in soups and salads, while in Greece, they are featured in dishes like "fava" and "gigantes plaki."
Conversely, Central and Eastern European countries like Poland and Hungary show moderate to low bean consumption rates compared to their southern counterparts. In these regions, legumes are often overshadowed by other staple foods, such as potatoes and bread. However, there is a growing interest in incorporating beans into local diets, particularly as awareness of their health benefits increases.
Notably, the United Kingdom presents a unique case. While historically low in bean consumption, the rise of multicultural cuisine and health-conscious eating has led to a new appreciation for beans among British consumers. Dishes such as chili con carne and baked beans on toast are now staples in many households, reflecting a shift towards incorporating more legumes into daily meals.
Significance and Impact
Understanding bean consumption patterns in Europe is significant for several reasons. First, beans are not only a source of nutrition but also play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture. They have a unique ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, enhancing soil health and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. This makes them an environmentally friendly crop, essential for sustainable farming practices.
Moreover, as Europe grapples with dietary-related health issues, promoting bean consumption could contribute to improved public health outcomes. Beans are linked to various health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Encouraging their consumption aligns with the European Union's nutritional guidelines, which advocate for a balanced diet rich in plant-based foods.
Current trends indicate that as the population becomes more health-conscious, the demand for beans is likely to rise. Future projections suggest that with ongoing awareness campaigns and the promotion of plant-based diets, Europe could see a significant increase in bean consumption across all member states. This shift would not only benefit individual health but also support environmental sustainability efforts across the continent.
In conclusion, the "Bean Consumption Per Capita in Europe Map" serves as a window into the dietary habits of Europeans, revealing cultural preferences and health trends that shape our understanding of food consumption. Beans are more than just a dietary staple; they are a crucial component of a sustainable future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 25, 2025
- Views
- 82
Comments
Loading comments...