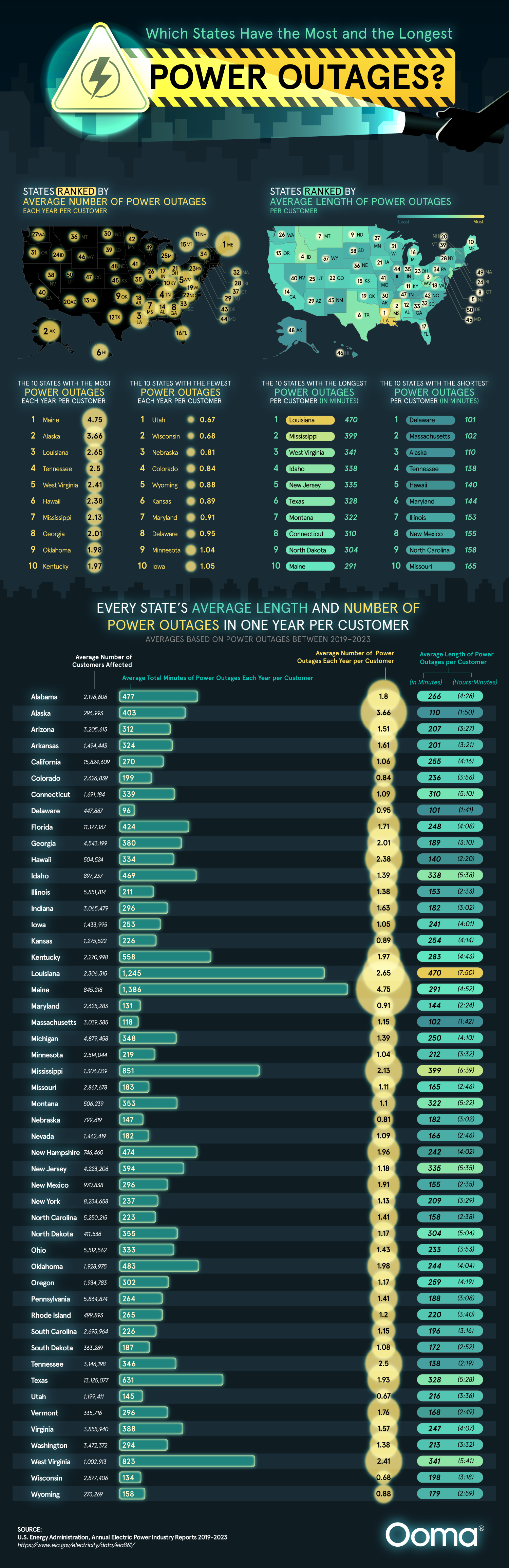
Power Outages by State Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the frequency and duration of power outages experienced by customers across various U.S. states. By visualizing this data, we can better understand how different regions of the country face challenges related to electrical infrastructure and reliability. Power outages can be caused by a host of factors, including severe weather, aging infrastructure, and increased energy demand. The map effectively highlights which states endure the most power outages and how long those outages typically last, providing insight into the resilience of each state's power grid.
Deep Dive into Power Outages
Power outages are a significant concern for both residents and businesses alike. They can disrupt daily life, cause economic losses, and pose safety risks. Understanding the reasons behind these outages is crucial for improving infrastructure and preparing for future challenges.
Interestingly, the frequency of power outages varies widely across the United States. States like Texas and Florida frequently top the charts for the longest outages per customer. Why is that? One major factor is the climate. For instance, Florida's sub-tropical weather often brings hurricanes and thunderstorms, leading to downed power lines and widespread outages. Texas, known for its extreme weather patterns, also faces challenges with its unique power grid, which operates independently from the rest of the country. This independence can sometimes lead to vulnerabilities, especially during peak demand periods.
Moreover, the aging infrastructure in many states contributes to the problem. According to the American Society of Civil Engineers, much of the electrical grid in the U.S. is over 30 years old, and parts are in dire need of upgrades. States experiencing high outage durations often have older systems that are less efficient and more susceptible to failures. For example, states like West Virginia and Kentucky, known for their mountainous terrain, can face challenges in maintaining and upgrading power lines due to difficult access, further exacerbating outage durations.
Interestingly, socioeconomic factors also play a role in power reliability. Areas with higher incomes tend to have better infrastructure and quicker response times during outages. In contrast, lower-income regions may struggle with longer recovery times due to limited resources for maintenance and upgrades. This disparity is evident when comparing urban areas with well-funded utility companies to rural regions where services may be less reliable.
In addition, the increasing frequency of extreme weather events linked to climate change is reshaping the landscape of power outages. Storms, wildfires, and floods are becoming more common, and utility companies are scrambling to adapt. For instance, California has implemented proactive power shut-offs during high-risk fire seasons to mitigate the threat of wildfires, which can lead to significant outages for residents.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, it’s clear that the southeastern region of the U.S. experiences a higher frequency of outages. States like Louisiana and Mississippi are often affected by hurricanes, leading to prolonged outages. In contrast, the Pacific Northwest, particularly states like Washington and Oregon, tends to see fewer outages, thanks in part to the region's robust infrastructure and milder weather.
In the Northeast, states like New York and New Jersey have made significant investments in their power grids following major outages in recent years, such as those caused by Hurricane Sandy in 2012. These efforts have led to improved reliability, but the region still faces challenges, particularly during winter storms.
On the other hand, the Midwest presents a mixed picture. States like Illinois and Michigan have experienced severe storms that disrupt power more frequently, but they also benefit from a relatively modern grid. This contrast highlights the importance of regional strategies in addressing power reliability.
Significance and Impact
Understanding power outages and their duration is crucial not just for utility companies but for policymakers and residents as well. As climate change continues to impact weather patterns, we can expect more frequent and severe outages. This knowledge drives the need for investments in infrastructure, better emergency preparedness, and policies aimed at increasing resilience.
Moreover, as our reliance on technology grows, the implications of power outages become even more pronounced. From public health to economic stability, ensuring reliable electricity is more than just a convenience; it's a necessity. Looking ahead, states must prioritize modernizing their power grids to withstand the evolving challenges of our climate and society. Whether through renewable energy sources, smart grid technology, or enhanced maintenance protocols, the goal remains the same: to minimize the impact of power outages on daily life.
In conclusion, the topic of power outages is multifaceted, encompassing environmental, economic, and social dimensions. By analyzing this map, we can gain valuable insights into the states facing the most significant challenges and the steps that can be taken to improve the situation moving forward.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 24, 2025
- Views
- 176
Comments
Loading comments...