Agricultural Spread Across Europe Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
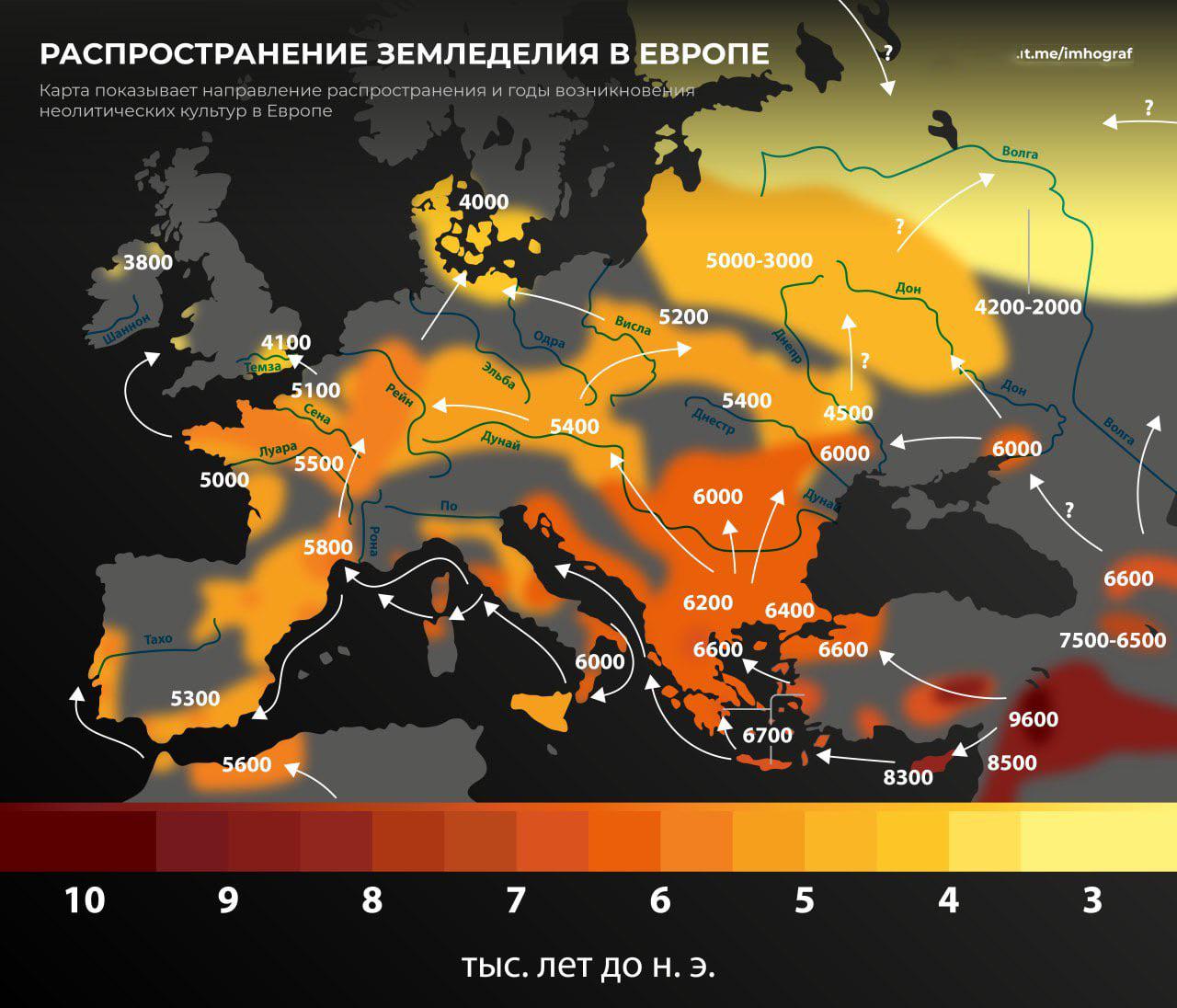
What This Map Shows
The "Spread of Agriculture Across Europe" map visualizes the distribution of agricultural practices and land use across various European regions. This map highlights how different types of agriculture—such as crop farming, livestock rearing, and mixed farming—are spread throughout the continent. By examining this visualization, we can gain insights into how geography, climate, and cultural practices influence agricultural development in Europe.
Deep Dive into Agriculture in Europe
Agriculture has been a cornerstone of European civilization for millennia. With its diverse climate zones and varied topography, Europe supports a wide range of agricultural systems. The map reveals that agriculture in Europe is not a monolithic entity; rather, it is a tapestry woven from different practices that reflect local conditions and traditions.
Interestingly, Western Europe, particularly countries like France, Germany, and the Netherlands, is well-known for its intensive agriculture. These regions benefit from fertile soil and favorable climates, allowing for the cultivation of various crops, such as wheat, barley, and sugar beets. In contrast, Southern Europe, which includes countries like Spain and Italy, showcases a different agricultural landscape characterized by Mediterranean crops such as olives, grapes, and citrus fruits. The warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters create ideal conditions for these types of agriculture.
In the east, countries like Poland and Hungary have a strong focus on cereal production, leveraging their rich black soil, known as Chernozem, which is among the most fertile in the world. The map illustrates how these regions are pivotal in supplying grain not only for domestic consumption but also for export to other parts of Europe and beyond.
What’s fascinating is the shift in agricultural practices due to socio-economic changes. For instance, the EU's Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) has significantly influenced farming practices since its inception in 1962, aiming to provide stable prices and secure food supplies. However, it also encouraged the intensification of farming, leading to environmental concerns. As a result, organic farming is gaining traction across the continent, with countries like Austria and Sweden leading the way in organic crop production, as depicted on the map.
Moreover, livestock farming remains a critical component of European agriculture. The northern regions, particularly in Scandinavia and the UK, are known for dairy and beef production. The map highlights the concentration of livestock farms in these areas, where the cooler climate and abundant pastureland support these industries well.
Regional Analysis
Let's take a closer look at how agriculture varies across Europe by region. In Northern Europe, particularly in Scandinavia, the agricultural landscape is shaped by a shorter growing season and harsher winters. As a result, farmers often focus on hardy crops and livestock that can withstand these conditions. For example, Iceland primarily relies on sheep farming and dairy production due to its unique climate.
Meanwhile, moving south to Central Europe, we find a region where agriculture is intensive and highly mechanized. Countries like Germany and France lead in the production of cereals and oilseeds, supported by advanced agricultural technology and research. The map reveals a high density of arable land in these areas, emphasizing their role as agricultural powerhouses.
In Southern Europe, the influence of traditional agricultural practices remains strong. The map shows a mosaic of small farms dedicated to olive and grape cultivation, reflecting centuries-old Mediterranean agricultural traditions. Countries like Italy and Greece are not only known for their agricultural output but also for their contributions to global culinary traditions, thanks to their unique crops.
Interestingly, Eastern Europe presents a transitional agricultural landscape. After the fall of the Soviet Union, many countries like Ukraine and Romania shifted from state-controlled farming to privatized agriculture. The map indicates a gradual increase in diverse crop production and a resurgence of small family farms, marking a significant transformation in agricultural practices in these nations.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the spread of agriculture across Europe is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights how agriculture shapes not only the economy but also the cultural identities of different regions. Have you noticed how local cuisine often reflects the agricultural products available in that area? This connection between agriculture and culture is profound and has implications for tourism, food security, and sustainability.
Moreover, current trends show a growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices as Europe grapples with climate change. The map serves as a reminder of the need for adaptive agricultural practices that can withstand environmental changes and ensure food security for future generations. For instance, the rise of permaculture and agroforestry practices is evident in many parts of Europe, aiming to restore the balance between agricultural productivity and ecological health.
As we look to the future, projections indicate that agricultural practices in Europe will continue to evolve. The integration of technology, such as precision farming and biotechnology, alongside traditional methods will likely shape the landscape of European agriculture in unprecedented ways. This evolution will be crucial not only for meeting the growing food demand but also for addressing environmental challenges.
In conclusion, the "Spread of Agriculture Across Europe" map provides a lens through which we can examine the diverse agricultural practices that define the continent. By understanding these patterns, we can appreciate the intricate relationship between geography, culture, and food production, ensuring that we remain informed about the significance of agriculture in our daily lives.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 23, 2025
- Views
- 122
Comments
Loading comments...