Literacy Skills Map of U.S. Adults

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
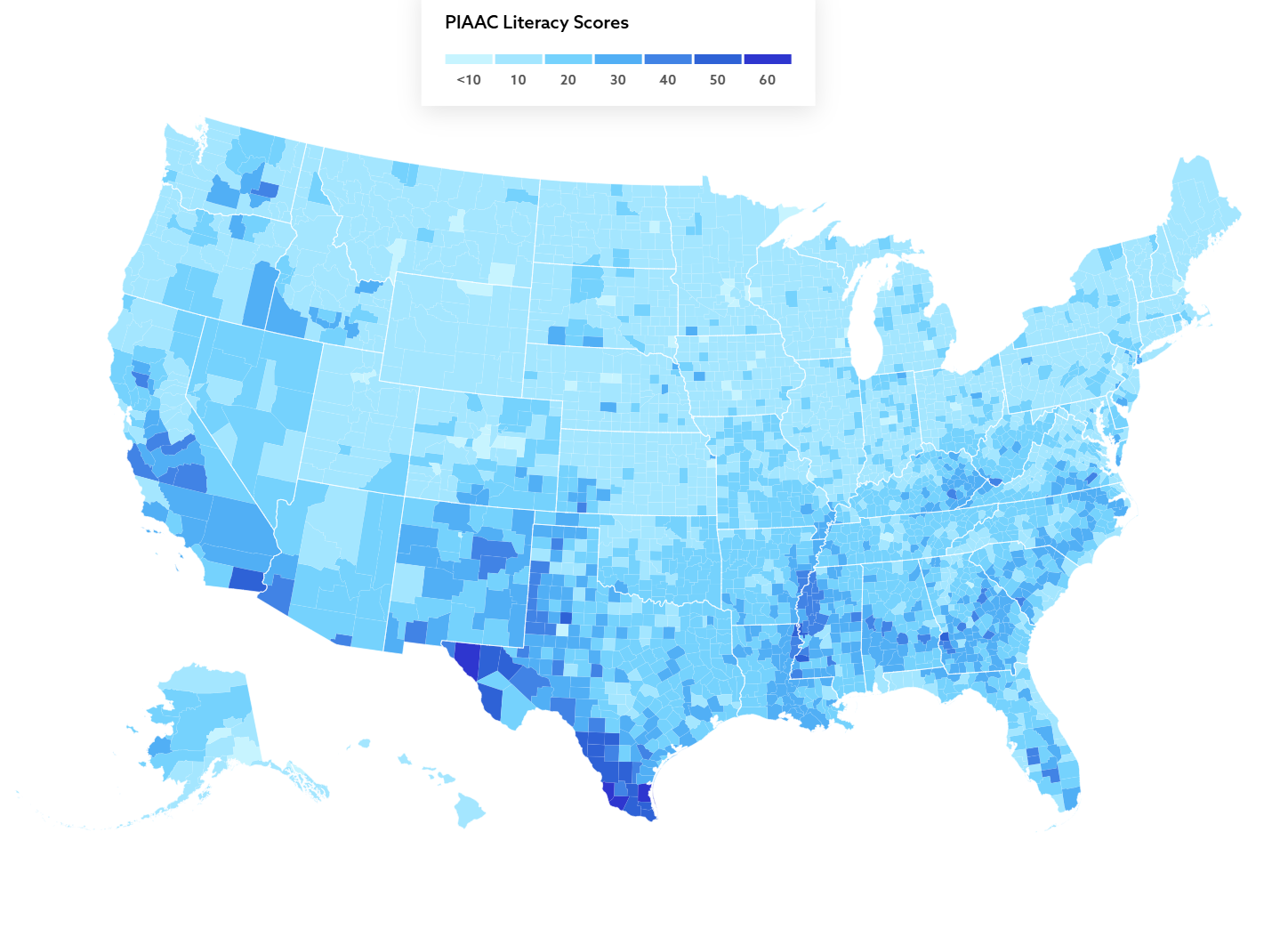
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Over 36 million adults in the U.S. lack basic literacy skills" provides a visual representation of adult literacy rates across various states in the United States. It highlights the staggering number of individuals who struggle with fundamental reading and writing skills, a crucial aspect of personal and professional development. This visualization is not just a collection of data points; it represents real lives and the challenges many Americans face in an increasingly complex world.
Deep Dive into Adult Literacy
Adult literacy is defined as the ability to read and write at a level necessary to function effectively in society. The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) defines literacy as the capacity to understand and use printed information, which includes everything from reading a bus schedule to understanding a job application. Interestingly, the statistics reveal that over 36 million adults in the U.S. fall below the basic proficiency level. This encompasses nearly 14% of the adult population—a significant figure that raises concerns about education, employment, and overall quality of life.
Literacy is more than just a personal skill; it is a vital contributor to economic stability and growth. Adults who lack basic literacy skills often find themselves at a disadvantage in the job market. In fact, studies indicate that individuals with low literacy are more likely to be unemployed or underemployed compared to their literate counterparts. This creates a cycle of poverty that is difficult to break, underscoring the importance of educational initiatives that target adult learners.
One of the most pressing issues regarding adult literacy is its correlation with socioeconomic status. Regions with higher poverty rates tend to have more individuals struggling with literacy. Likewise, education levels among parents significantly influence the literacy rates of their children. Have you noticed that communities with robust educational programs often report lower adult illiteracy rates? This connection highlights the need for comprehensive educational strategies that not only focus on children but also prioritize adult learning.
Furthermore, the digital age presents another layer of complexity. As technology continues to evolve, literacy now encompasses digital literacy—the ability to navigate online platforms and utilize digital tools effectively. Adults who lack basic literacy skills may also struggle with acquiring digital literacy, which is increasingly critical in today’s job market where many roles require at least a basic understanding of computers and the internet.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals significant disparities in literacy rates across the United States. For instance, states in the Southeast, such as Mississippi and Alabama, show particularly high percentages of adults lacking basic literacy skills. In contrast, states like Massachusetts and New Hampshire report much lower figures. This regional divide can be attributed to various factors including access to quality education, funding for adult education programs, and socioeconomic conditions.
Interestingly, urban areas often have more resources available for adult education and literacy programs compared to rural areas. However, even in urban settings, pockets of low literacy persist, particularly among marginalized communities. For example, cities like Detroit and Baltimore face unique challenges that contribute to lower literacy rates despite being in regions with otherwise ample educational resources.
Moreover, the impact of immigration should not be overlooked. Many immigrants arriving in the U.S. may not have had access to quality education in their home countries, leading to literacy challenges in their new environment. Programs tailored to support these individuals can make a significant difference in improving literacy rates.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the implications of low literacy rates is crucial for addressing broader societal issues. The ability to read and write is foundational for personal empowerment and community engagement. Individuals with low literacy skills are less likely to participate in civic activities, such as voting, which ultimately affects governance and policy-making.
Moreover, as we confront a rapidly changing job market, the demand for skilled workers continues to rise. Employers increasingly seek candidates who can adapt to new technologies and processes. As a result, businesses may struggle to find qualified employees if a significant portion of the population is unable to meet these demands. Recognizing this challenge, many organizations are advocating for increased investment in adult literacy programs, viewing them as essential for both economic development and social equity.
Current trends indicate a growing awareness of the importance of adult literacy, with various public and private initiatives emerging to address this crisis. Programs focusing on workplace literacy, digital skills training, and community education are gaining traction, offering hope for a future where every adult has the skills necessary to thrive. As we move forward, it is vital to continue advocating for policies that support adult education, ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to improve their literacy skills and, consequently, their lives.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 23, 2025
- Views
- 126
Comments
Loading comments...