Historical Map of Turkey in Textbooks

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
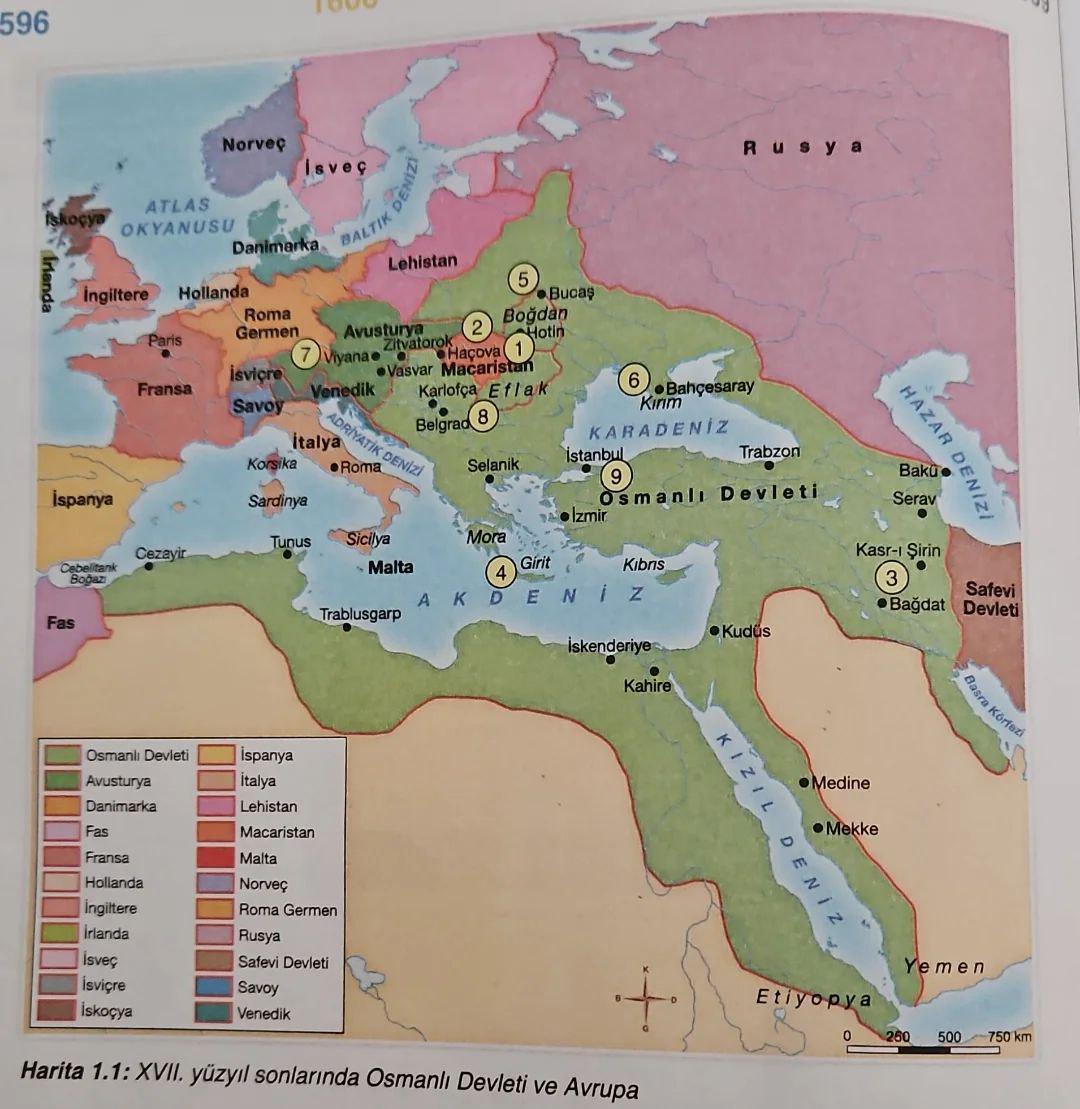
This map, derived from a Turkish history textbook, offers a detailed portrayal of significant historical events, territorial changes, and cultural landmarks throughout Turkey's rich past. It serves as a visual guide to understanding the geographical context of various empires that have influenced the region, including the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Republic of Turkey itself. By examining this map, we can better appreciate how geography played a pivotal role in shaping historical narratives and cultural identities in Turkey.
Deep Dive into Turkey's Historical Geography
Turkey's geographical position, straddling both Europe and Asia, has made it a crossroads of civilizations for centuries. Its unique location has not only influenced trade routes but also military strategies and cultural exchanges. Have you ever wondered why so many empires have sought to control this territory? The answer lies in its strategic importance.
The earliest known inhabitants of Turkey, such as the Hittites and Phrygians, capitalized on its fertile lands and proximity to trade routes. As we move through history, the rise of the Byzantine Empire showcased the significance of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) as a cultural and economic hub. This city, positioned on the Bosporus Strait, served as a bridge between East and West, making it a vital point for commerce and military endeavors.
What's fascinating is how the Ottoman Empire expanded across both continents, influencing various regions through a complex administrative system. The map likely highlights key cities, such as Edirne (Adrianople) and Bursa, which served as significant capitals at different times. The Ottomans were known for their architectural achievements, and many of their grand mosques and palaces are located in these historically rich areas.
The Republic of Turkey emerged from the ashes of the Ottoman Empire in the early 20th century, bringing about profound changes in national borders and cultural identity. The map may depict the territorial shifts that occurred during the Turkish War of Independence, leading to the establishment of modern Turkey in 1923. This transition was not just political; it was also geographical, as borders were redefined and communities were reorganized.
In contemporary times, Turkey’s geographical features—ranging from mountains to coastal plains—continue to influence its cultural and economic landscapes. The Anatolian plateau, for example, is a crucial agricultural area, while the coastal regions are significant for tourism. Understanding these geographical contexts is essential for interpreting Turkey's historical evolution.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map by region, it’s important to recognize the distinct historical narratives that different areas of Turkey possess. For instance, the Aegean region, known for its ancient ruins like Ephesus, offers insights into Hellenistic influences. The Mediterranean region, with cities like Antalya, showcases the blend of ancient and modern cultures that attract millions of tourists annually.
In contrast, Eastern Turkey, with its rugged mountains and diverse ethnic groups, tells a different story. The Kurdish population, for example, has a rich history that is often underrepresented in mainstream narratives. This regional analysis highlights the complexities of Turkey’s demographic landscape, where cultural identities are intricately tied to geography. Interestingly, each region's unique history is often reflected in local traditions, cuisine, and dialects.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Turkey’s historical geography is not merely an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for contemporary politics and cultural relations. The legacy of past empires continues to shape modern Turkey's interactions with neighboring countries, particularly in matters of trade, security, and cultural diplomacy.
Current trends, such as the rise of nationalism and debates over cultural heritage, underscore the importance of historical geography in shaping national identity. As Turkey navigates its place in a rapidly changing world, the lessons from its past, as illustrated in this map, remain relevant in discussions about unity and diversity within its borders.
As we reflect on this map, it becomes clear that Turkey's geography is not just a backdrop; it is a central character in its historical narrative. The interplay of land, culture, and history continues to influence the Turkish identity and its relationship with the world today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 20, 2025
- Views
- 178
Comments
Loading comments...