Maoist Insurgency Affected Areas Map in India

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
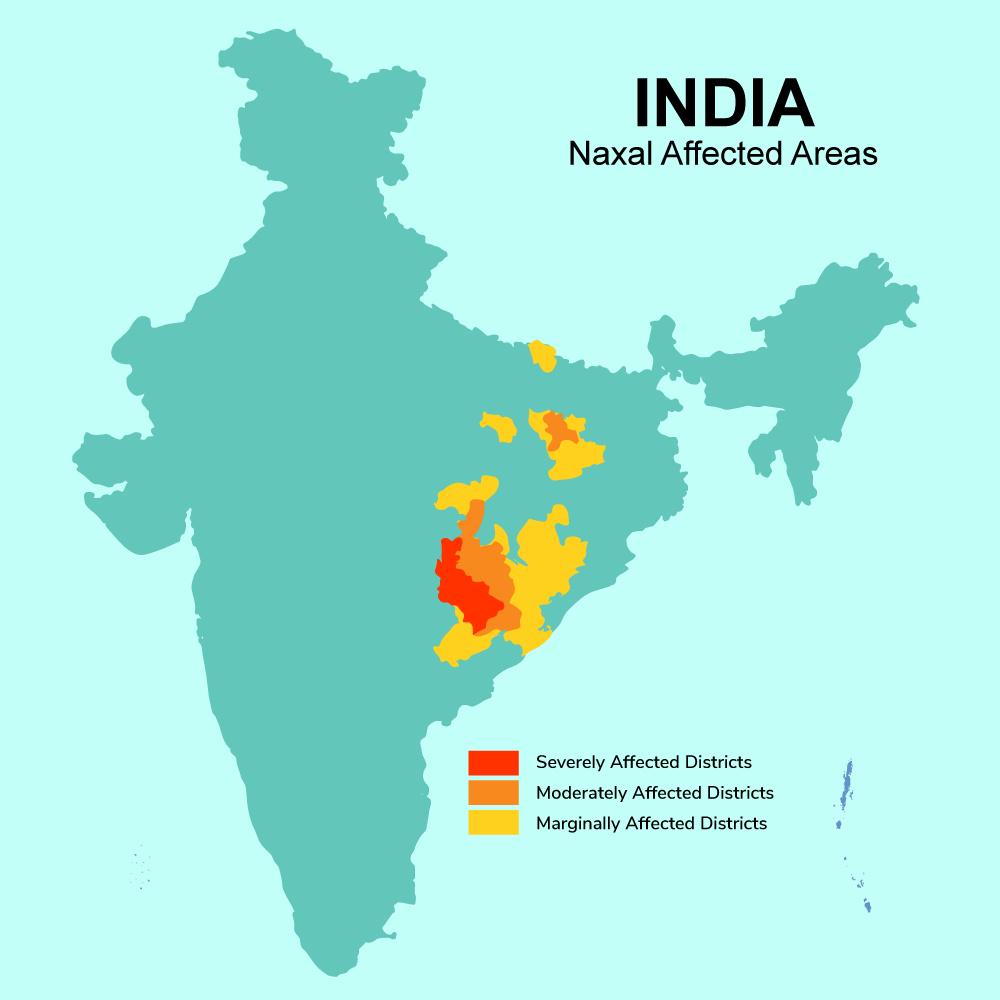
What This Map Shows
The map titled 'Maoist Insurgency Affected Areas in India' provides a stark visual representation of the districts most impacted by the ongoing conflict involving Maoist insurgents, commonly referred to as Naxalites. The districts shaded in red on this map indicate areas facing severe consequences from this insurgency, where daily life is marred by conflict, displacement, and a lack of basic services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure. This conflict, which has persisted for decades, primarily affects rural and tribal populations in India’s heartland, revealing the complex interplay of ideology, socio-economic challenges, and governance issues.
Deep Dive into Maoist Insurgency
The Maoist insurgency in India traces its roots back to the late 1960s, originating in West Bengal and subsequently spreading to various states, particularly in central and eastern India, such as Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Bihar, and Maharashtra. At its core, the insurgency is driven by a combination of socio-economic grievances, including poverty, land dispossession, and lack of access to basic services. The rebels advocate for the rights of marginalized communities, including Scheduled Tribes and Dalits, who often find themselves on the periphery of development.
Interestingly, the geographical landscape of these affected areas plays a significant role in the insurgency. Many of these districts are characterized by dense forests and rugged terrain, which provide natural cover for insurgent activities and make it challenging for security forces to operate. According to government estimates, the Maoist ideology has attracted thousands of recruits, capitalizing on the discontent stemming from socio-economic disparities.
Statistics reveal a grim picture: as of 2023, the insurgency has resulted in thousands of deaths, including those of civilians and security personnel. The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) notes that the conflict has displaced over 500,000 individuals, forcing them to flee their homes in search of safety. This displacement exacerbates existing vulnerabilities, especially among tribal populations who often rely on agriculture and natural resources for their livelihoods.
Moreover, the lack of basic services in these red-identified districts complicates the situation further. Health facilities are often non-existent or severely under-resourced, and educational institutions face high dropout rates due to insecurity and poverty. The insurgency perpetuates a cycle of violence and underdevelopment, making it difficult for these communities to escape their plight.
Regional Analysis
When we examine the map closely, we can identify distinct regions affected by the Maoist insurgency. For instance, in Chhattisgarh, districts like Bastar and Sukma are heavily impacted, where the dense forests not only provide refuge for insurgents but also complicate governmental efforts to establish law and order. The state has witnessed a significant number of encounters between Maoist fighters and security forces, leading to a volatile environment.
Moving towards Jharkhand, districts such as Latehar and Palamu show a similar pattern of conflict. Here, the presence of mineral wealth has exacerbated tensions, as local populations often feel sidelined in the benefits derived from resource extraction. In Odisha, the districts of Malkangiri and Koraput experience frequent clashes, illustrating how the insurgency is not just a law and order issue but also a struggle for social justice and rights.
Comparatively, the impact of the insurgency varies across states. For example, while Chhattisgarh has seen a significant military response, leading to temporary reductions in violence, the root causes, such as poverty and land rights, remain unaddressed. On the other hand, states like West Bengal have managed to contain the spread of Maoist influence through political engagement and developmental initiatives.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the Maoist insurgency and its geographical implications is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the ongoing socio-economic disparities in India, particularly in rural areas. The insurgency is not merely a security issue but a manifestation of long-standing grievances that require comprehensive strategies addressing poverty, land rights, and governance.
Furthermore, the conflict poses significant challenges for local and national governments. The need for effective policy measures that include development programs and community engagement cannot be overstated. Interestingly, various NGOs and civil society organizations are actively working in these regions, attempting to foster dialogue and deliver essential services, albeit amidst ongoing conflict.
Looking forward, projections suggest that without significant intervention, the cycle of violence and underdevelopment may persist. The government’s approach must evolve from a purely militaristic strategy to one that incorporates socio-economic development and peace-building initiatives. Only then can we hope to see a reduction in violence and a sustainable resolution to the conflicts plaguing these areas.
In conclusion, the 'Maoist Insurgency Affected Areas Map in India' not only serves as a tool for understanding where this conflict is most severe but also sheds light on the underlying issues that fuel it. By addressing these root causes, there is potential for healing and progress in these afflicted regions.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 20, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...