Male Circumcision Rates by Country Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
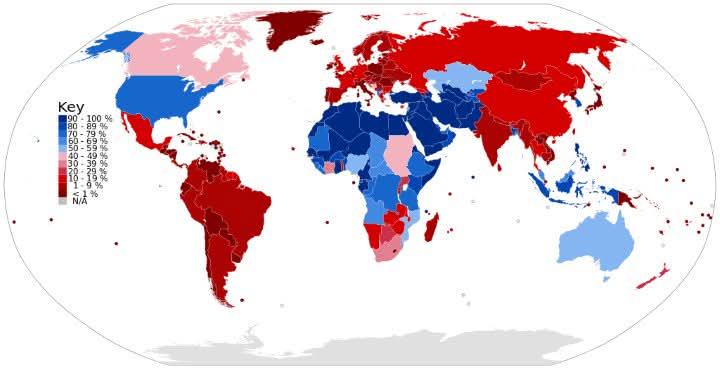
What This Map Shows
The "Male Circumcision Rates by Country Map" provides a comprehensive overview of the prevalence of male circumcision across various nations. This visualization highlights the percentage of males who have undergone circumcision, revealing significant geographical differences and cultural practices surrounding this procedure.
As we delve deeper into this topic, it’s essential to understand that male circumcision is not merely a medical procedure but is steeped in social, cultural, and religious significance in many societies.
Deep Dive into Male Circumcision
Male circumcision, the surgical removal of the foreskin from the penis, is a practice that has been carried out for thousands of years. It often varies in prevalence based on cultural, religious, and health perspectives. In many countries, particularly in Africa and the Middle East, circumcision is a common practice, often linked to religious beliefs – such as Islam and Judaism – where it is seen as a rite of passage or a covenant with God.
Interestingly, in regions like sub-Saharan Africa, circumcision is not only a cultural or religious practice but also a public health measure. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized male circumcision as an effective means of reducing the risk of HIV transmission. Countries like Kenya, Uganda, and South Africa have implemented national campaigns promoting circumcision as a way to combat the HIV epidemic, which has contributed to high circumcision rates in these areas.
However, the practice is not universally accepted. In many Western countries, such as the United States, circumcision is performed for various reasons, including hygiene and parental preference. The rates can be quite high, with estimates suggesting that about 70-80% of newborn males in the U.S. undergo the procedure. Yet, in parts of Europe, circumcision rates are significantly lower, often below 10%, as it is less commonly practiced and often viewed with skepticism.
Statistics show that the global prevalence of male circumcision varies widely. In countries like Somalia, virtually all men are circumcised, while in countries like Japan and South Korea, the numbers can be as low as 1-2%. This disparity can be attributed to cultural norms, religious practices, and the influence of modern medicine.
In addition, the debate surrounding circumcision is ongoing. Proponents argue that it has potential health benefits, including reduced risks of sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections. In contrast, opponents raise ethical concerns about bodily autonomy and the risks associated with the procedure itself, including complications and the psychological impact on individuals.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing this map regionally, we can see distinct patterns emerge. In North America, circumcision rates remain high, influenced by cultural practices, though recent years have seen a decline as more parents opt for non-circumcision due to the growing debate on its necessity. In contrast, in Europe, particularly in countries like Germany and the UK, circumcision is often performed for religious reasons, leading to a mixed landscape of prevalence.
In Africa, the map reveals a striking pattern; countries such as Egypt, Sudan, and Mali show almost universal circumcision, deeply rooted in cultural and religious practices. On the other hand, in Southern Africa, the rates can vary significantly. For example, in Zambia and Zimbabwe, circumcision campaigns have increased rates to around 50%, while in Botswana, it is lower due to different cultural perceptions.
In Asia, the practice appears more sporadic. Countries like Turkey, where Islam is prevalent, show higher circumcision rates, while in places like Thailand and Vietnam, it remains quite rare. The cultural context here is crucial; in many Asian cultures, circumcision is not traditionally practiced and is often associated with Western influence.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the global landscape of male circumcision is essential not only for cultural awareness but also for public health initiatives. The implications of circumcision extend beyond individual choice; they touch on public health, cultural identity, and ethical considerations. As the WHO continues to promote circumcision as a preventive health measure against HIV, it raises questions about cultural sensitivity and the balance between health and personal beliefs.
Interestingly, as we see shifting attitudes towards circumcision in various regions, it raises future projections about its prevalence. Will countries where circumcision is historically low begin to adopt the practice in the face of health campaigns? Or will cultural beliefs continue to drive the narrative?
In conclusion, the map of male circumcision rates around the world serves as a lens through which we can examine cultural practices, health policies, and the evolution of societal norms regarding this age-old procedure. As discussions continue, it remains vital to approach this topic with respect for the diverse beliefs and practices that shape the lives of many individuals globally.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 18, 2025
- Views
- 1,392
Comments
Loading comments...