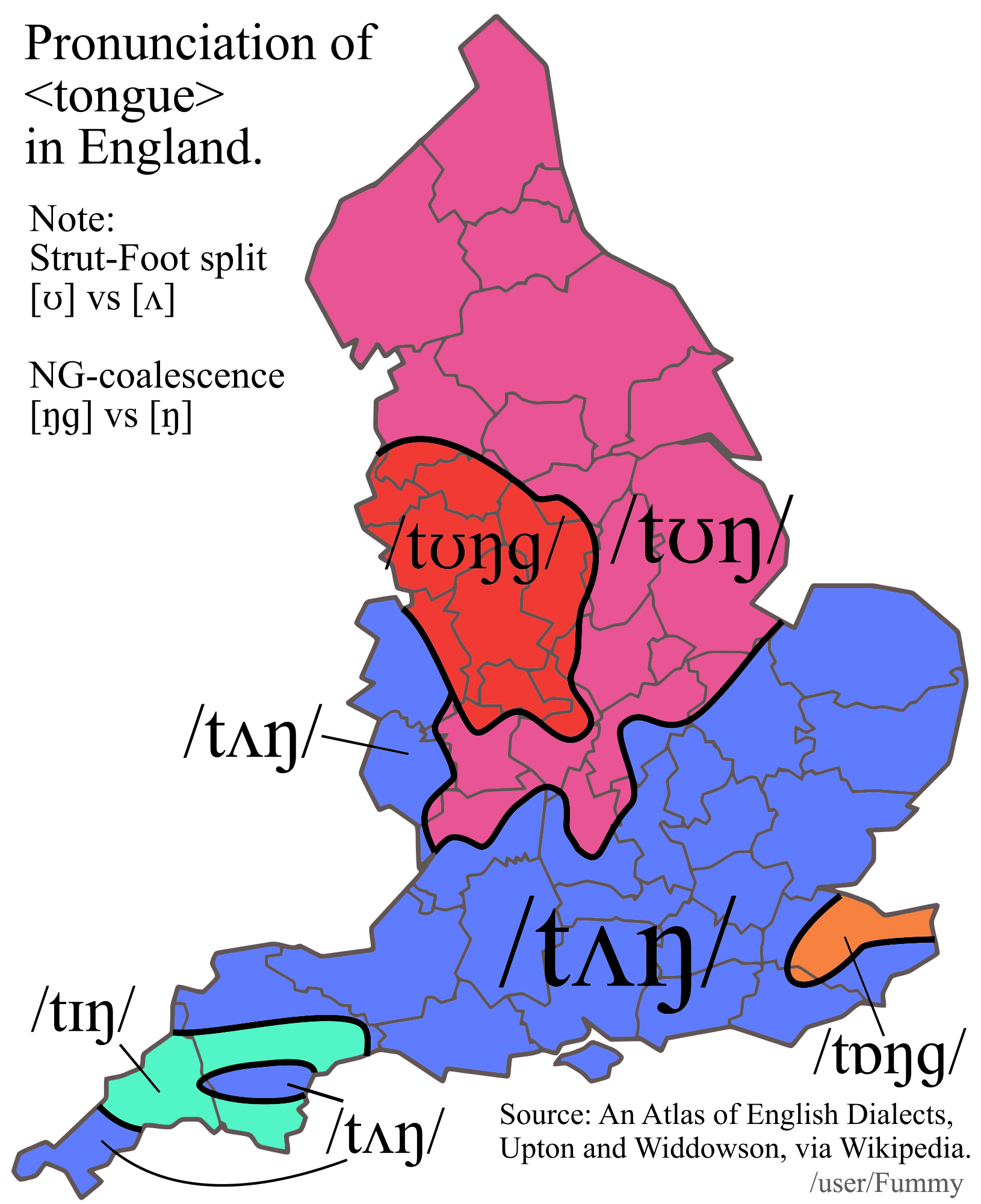
Map of Pronunciation Differences of 'Tongue' in England

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the regional variations in the pronunciation of the word "tongue" across different areas of England. As you look at the visualization, you'll notice that the way this common word is articulated can vary significantly from one region to another. These differences can be attributed to a blend of historical, social, and linguistic factors that have shaped the English language over centuries.
Deep Dive into Pronunciation Variations
Pronunciation is a fascinating aspect of language that can reveal much about cultural identity and social connections. The word "tongue," with its Old English roots, has undergone numerous transformations in pronunciation throughout history. Interestingly, how we pronounce this word can serve as a linguistic marker of regional identity.
In England, the differences in pronunciation can be broadly categorized into two main phonetic groups: those who pronounce the "ou" in "tongue" as a monophthong (like 'tuhn') and those who pronounce it as a diphthong (like 'tang'). This phonetic divide can be observed in various regional accents. For instance, in London and the Southeast, speakers often utilize the diphthong pronunciation, which is reflective of the wider influences of urban dialects and social mobility.
Conversely, in the North of England, particularly in regions such as Yorkshire and Lancashire, the monophthong pronunciation prevails. This reflects a more traditional linguistic heritage, often seen as a marker of local pride. Have you ever noticed how your own accent changes when you're with friends or family? That's a classic example of how closely tied our identities are to the way we speak.
The influence of social factors, including age, education, and socioeconomic status, also plays a crucial role in pronunciation. Younger generations in urban areas may adopt new pronunciations influenced by popular culture, while older generations may retain traditional pronunciations. This ongoing evolution makes the study of language and pronunciation a dynamic and continuously changing field.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can identify distinct clusters of pronunciation styles. For example, in the Midlands, particularly around Birmingham, speakers may exhibit a blend of both pronunciations, reflecting the diverse cultural influences in this urban center. On the other hand, speakers from the West Country, including areas like Cornwall and Devon, often lean towards a diphthong pronunciation, which aligns with their unique regional dialects.
Interestingly, the pronunciation of "tongue" can also reflect broader linguistic trends, such as the shift from non-rhotic to rhotic accents across England. Non-rhotic accents, prevalent in the South, often drop the 'r' sound in words, while rhotic accents found in parts of the West and North of England maintain this pronunciation. These distinctions are not just about pronunciation; they are woven into the fabric of local identity and heritage.
In urban areas, such as Manchester and Liverpool, the influence of multiculturalism has led to a fascinating hybridization of accents and pronunciations. Here, the pronunciation of "tongue" might combine elements from different dialects, showcasing the vibrant linguistic tapestry of modern England.
Significance and Impact
Understanding pronunciation differences is not merely an academic exercise; it carries real-world implications. Linguists and sociolinguists study these variations to better understand social dynamics, migration patterns, and cultural heritage. As language evolves, so too do the identities associated with it. This is particularly relevant in today's globalized society, where accents and pronunciations are often subject to change due to media influence and social interaction.
Moreover, this topic holds significance for educators and policymakers who work in linguistics and cultural preservation. Recognizing the value of regional dialects can foster a sense of pride in local heritage and may influence educational approaches to language teaching. As we move into the future, preserving these unique pronunciations could become essential for maintaining cultural diversity in an ever-homogenizing world.
So, the next time you hear someone pronounce "tongue" differently, remember that it's more than just a word; it's a reflection of history, identity, and the rich tapestry of the English language.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 14, 2025
- Views
- 110
Comments
Loading comments...