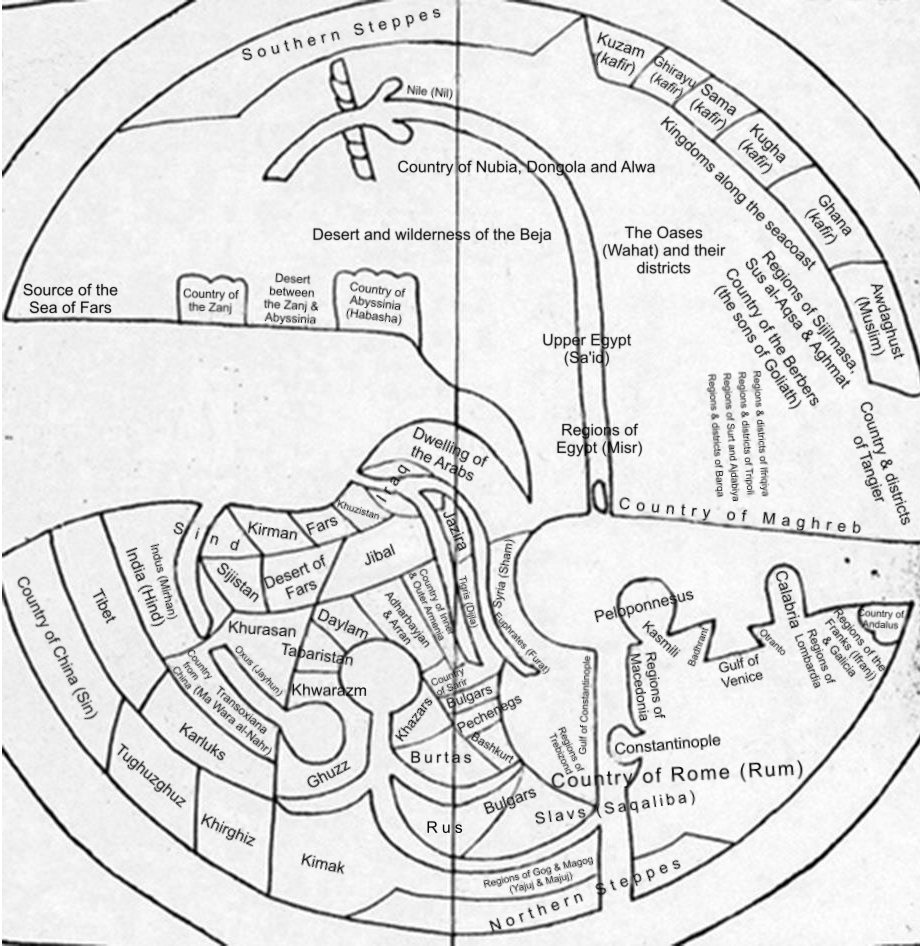
Ibn Howqal 10th Century World Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The Ibn Howqal World Map, dating back to the 10th century, is a remarkable historical cartographic representation that provides insights into the geographical understanding of the medieval Islamic world. This map is not merely a visual depiction of the Earth; it serves as a window into the cultural, political, and economic landscapes of the time. The map illustrates a world that was interconnected through trade routes, cultural exchanges, and the spread of knowledge. It captures regions such as Africa, Europe, and parts of Asia, outlining key cities, rivers, and landmarks that were significant to the societies of the era.
Deep Dive into Medieval Geography
One of the captivating aspects of the Ibn Howqal map is how it reflects the geographical knowledge of the 10th century, a period characterized by extensive exploration and trade. During this time, the Islamic Golden Age flourished, allowing scholars to compile and share knowledge about distant lands. Ibn Howqal, a geographer and explorer, documented not only the physical features of the regions he observed but also the cultural and commercial interactions that shaped them.
The map indicates various trade routes that were vital for economic exchanges. For example, the trans-Saharan trade routes connecting North Africa to sub-Saharan regions facilitated the movement of gold, salt, and other commodities. Interestingly, the depiction of the Mediterranean Sea highlights how crucial it was for maritime trade, linking Europe with the Middle East and North Africa.
What's fascinating is that Ibn Howqal’s observations included descriptions of the climate and agriculture in different regions. He noted the fertile lands of the Nile Delta, which supported agriculture, while also mentioning the arid landscapes of the Arabian Peninsula. This attention to environmental factors indicates an early understanding of how geography influences human activity, a topic that is still relevant today.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing the map reveals distinct geographical features and cultural characteristics across various regions. For instance, in Europe, the map highlights significant cities like Constantinople, a major hub for trade and cultural exchange between the East and West. Comparatively, in Africa, cities like Cairo are prominently featured, indicating their importance in trade networks.
Furthermore, the map illustrates how the regions were interconnected. The areas surrounding the Mediterranean were not only politically significant but also rich in cultural exchanges, as they were home to diverse societies. Meanwhile, in regions like Persia (modern-day Iran), the map emphasizes the influence of the Islamic culture, showcasing a different yet equally important aspect of the medieval world.
In Central Asia, the map captures the nomadic lifestyle prevalent among various tribes and their interactions with settled societies. This contrast between sedentary and nomadic communities is crucial for understanding historical dynamics and migration patterns.
Significance and Impact
The Ibn Howqal map is significant not only as a historical artifact but also as a testament to the interconnectedness of civilizations during the medieval period. It allows us to understand how geography affected trade, migration, and cultural interactions. Moreover, it raises questions about how our current maps and geographic understanding are shaped by historical perspectives.
In contemporary discussions about globalization, the map serves as a reminder of the long-standing human inclination to explore and connect with distant lands. The reverberations of the trade routes depicted by Ibn Howqal continue to influence our world today, as modern trade networks still echo these ancient pathways.
As we look to the future, studying such historical maps can offer valuable insights into the environmental and political challenges we face. For instance, understanding how geography influences human behavior can inform current discussions on climate change, resource distribution, and urban planning. Have you ever thought about how much our past shapes our present geographical understanding? The legacy of Ibn Howqal’s map is an invitation to explore those connections further.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 13, 2025
- Views
- 132
Comments
Loading comments...