Map of Visigothic Kingdom and Early al-Andalus

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
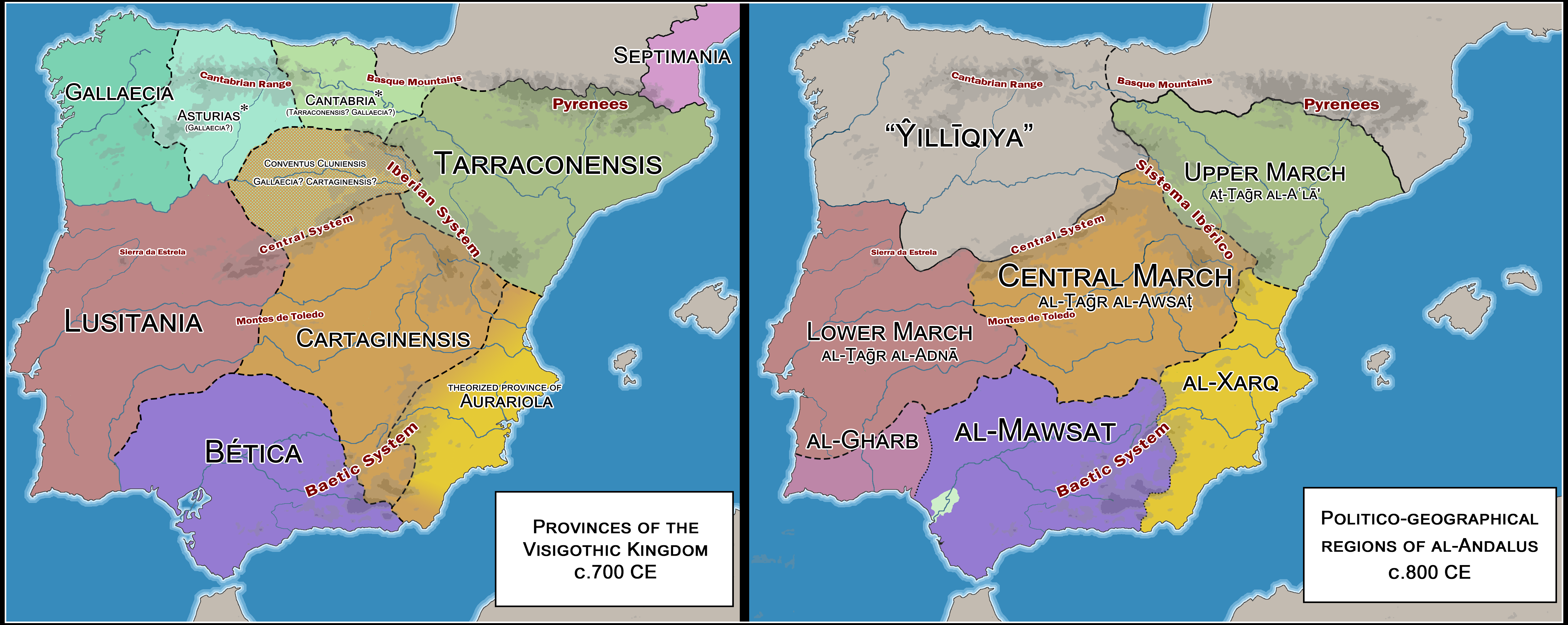
What This Map Shows
This map presents a detailed comparison between the provinces of the latter Visigothic Kingdom and the territorial divisions of early al-Andalus. It visually delineates the shifts in power and territory as the Iberian Peninsula transitioned from Visigothic rule to Islamic governance following the Umayyad conquest in the early 8th century. The provinces outlined on this map help us understand the historical and cultural changes that occurred during this transformative period.
Deep Dive into the Historical Context
To truly appreciate the significance of this map, it’s essential to delve into the historical context of both the Visigothic Kingdom and early al-Andalus. The Visigothic Kingdom emerged in the early 5th century as a result of the migration of the Visigoths into the Roman Empire's territories. At its peak, the kingdom covered much of modern-day Spain and Portugal, divided into provinces like Hispania Tarraconensis, Baetica, and Lusitania.
Interestingly, the Visigoths were known for their unique blend of Roman and Germanic influences, which shaped their societal structure, legal codes, and religious practices. However, by the early 8th century, the kingdom faced internal strife, including power struggles among noble families and the rise of regional governors, which weakened centralized authority.
In 711 AD, the Umayyad Caliphate launched a successful invasion, leading to the swift conquest of much of the Iberian Peninsula. Al-Andalus, as the Islamic territory was known, was marked by its own unique administrative divisions, which were significantly different from those of the Visigothic era. The map illustrates these divisions, including the major provinces such as Algeciras, Córdoba, and Toledo, showcasing a shift from the former Christian governance to a complex Islamic administrative system.
What's fascinating is the way the Islamic rulers integrated local populations and traditions into their governance. Al-Andalus became a cultural and intellectual hub during this period, known for advancements in science, philosophy, and the arts, contrasting with the declining cultural atmosphere of the Visigothic Kingdom. This transformation is not only reflected in political boundaries but also in the cultural landscape of the region.
Regional Analysis
The map's regional analysis reveals a stark contrast between the provinces of the Visigothic Kingdom and those of early al-Andalus. For instance, Hispania Tarraconensis, which once served as a crucial administrative center under the Visigoths, was transformed into the province of Tarragona in al-Andalus, reflecting the Islamic influence on governance and urban development. Similarly, Baetica, known for its agricultural wealth, became the province of Córdoba, which later emerged as the capital and a center for learning and trade.
In the northern regions, the remnants of Visigothic control persisted longer, as the mountainous terrain provided natural defenses against the invading forces. Areas like Asturias remained relatively isolated, allowing for the preservation of Visigothic traditions and the eventual rise of the Reconquista movement. This juxtaposition between the cultural richness of al-Andalus and the more provincial aspects of the Visigothic territories highlights the dynamic nature of political and cultural evolution in the region.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the shifts from the Visigothic Kingdom to early al-Andalus is crucial for grasping the broader historical narrative of the Iberian Peninsula. This transition not only altered the political landscape but also paved the way for significant cultural exchanges that would shape Europe’s future.
Have you noticed how the architectural influences from this period can still be seen today? The mosques, palaces, and gardens of al-Andalus have left a lasting legacy, showcasing the region’s rich history and diverse cultural influences. Moreover, the intellectual advancements made during this time contributed to the European Renaissance, emphasizing the importance of cross-cultural interactions.
Current trends in historical geography continue to explore these themes, examining how past territorial divisions impact modern cultural identities and national borders. As scholars and enthusiasts alike delve deeper into this fascinating history, the map serves as a crucial tool for visualizing and understanding these complex dynamics. The implications of these historical shifts resonate today, reminding us that geography is not merely about land but also about the stories and legacies that shape our world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 12, 2025
- Views
- 292
Comments
Loading comments...