Male to Female Ratio in Europe Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
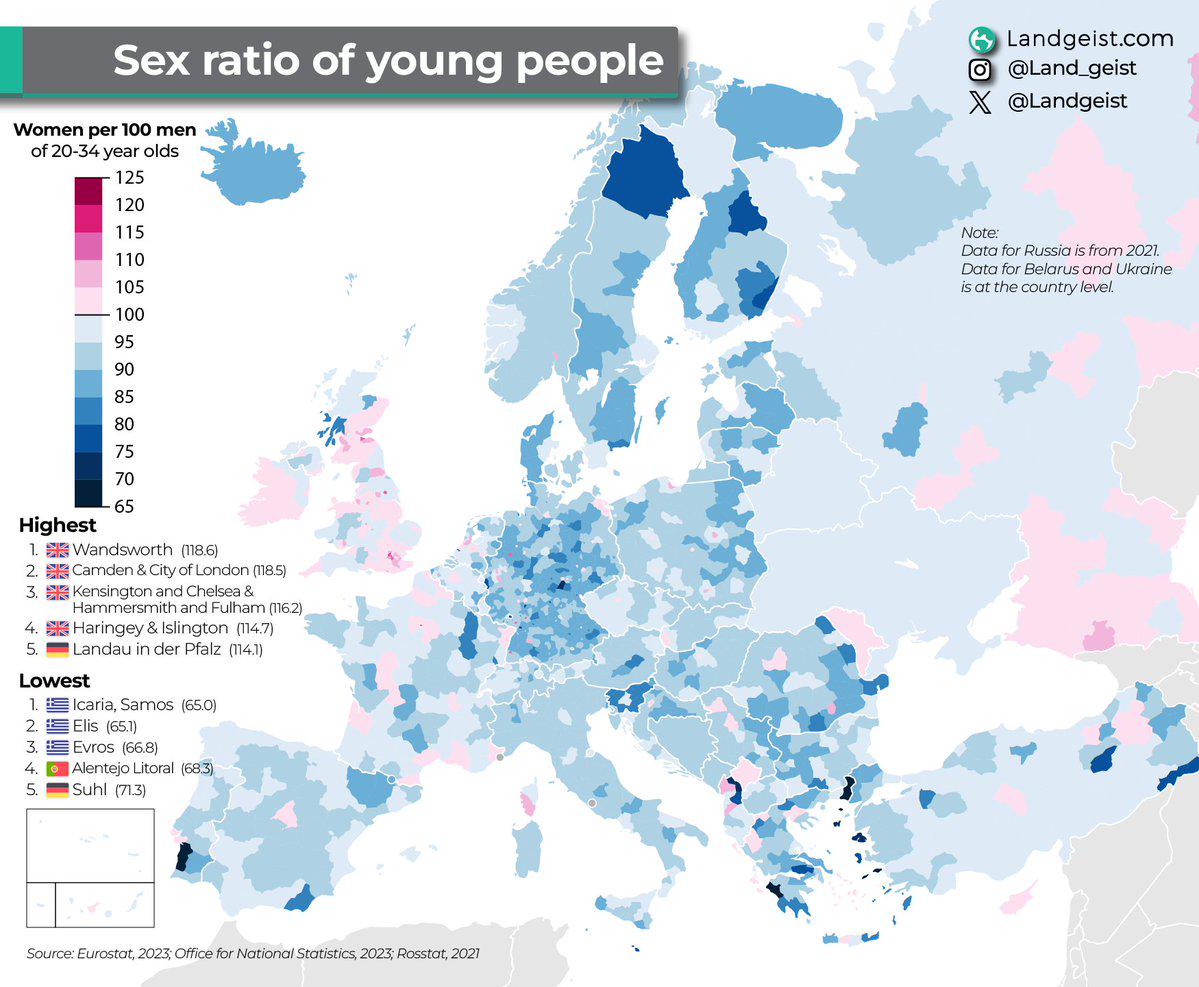
What This Map Shows
The "Male to Female Ratio in Europe Map" for 2023 provides a compelling visual representation of the gender distribution across various European countries. This map highlights the male-to-female ratio, indicating the number of males per 100 females in different regions. Understanding this ratio is crucial for analyzing demographic trends, social structures, and even economic factors in Europe.
Deep Dive into Gender Ratios
The male-to-female ratio is an essential demographic indicator that reveals much about a population's structure. Globally, the natural sex ratio at birth tends to favor males, typically around 105 boys for every 100 girls. However, as populations age, various factors, including life expectancy and migration trends, often lead to significant disparities in the overall gender ratio.
In Europe, the average male-to-female ratio is approximately 94 men for every 100 women, with notable variations across countries. For instance, countries like Luxembourg and Malta exhibit a balanced ratio, while nations such as Latvia and Lithuania display a higher number of females compared to males, influenced by higher male mortality rates and a history of emigration.
Interestingly, the reasons behind these disparities extend beyond mere biological factors. Historical events, such as the World Wars, significantly impacted gender ratios, leading to a surplus of women in many European nations. Additionally, contemporary issues like labor migration continue to shape these demographics. Many men migrate for work, particularly in sectors such as construction and agriculture, leaving behind a female-dominated population in several rural areas.
Moreover, the aging population in Europe also plays a critical role. Women, on average, live longer than men, resulting in higher female populations in older age brackets. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in countries with older populations, such as Italy and Germany, where the ratio can skew heavily towards females in senior demographics.
Regional Analysis
When examining regional differences, it's fascinating to see the variations in gender ratios across Europe. For example, in Scandinavia, particularly in Norway and Sweden, the male-to-female ratio is relatively balanced, reflecting progressive social policies and high levels of gender equality. In contrast, Eastern European countries, such as Belarus and Ukraine, often report a significant surplus of women due to the aforementioned historical and economic factors.
Southern Europe presents another intriguing picture. Countries like Spain and Portugal show a similar trend with more females than males, influenced by both lifestyle choices and migration patterns. In urban areas, the gender ratio can fluctuate due to young women moving to cities for education and employment, while men may migrate abroad for job opportunities, further skewing local ratios.
Interestingly, in some regions, the male-to-female ratio can also impact social dynamics. For instance, a higher female population may lead to changes in relationship patterns, marriage rates, and fertility rates. In areas with a surplus of women, we often see increased competition for partners, which can lead to shifts in societal norms and expectations.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the male-to-female ratio in Europe is vital for various reasons. It helps policymakers address issues related to healthcare, education, and social services. For example, a predominantly elderly female population in certain regions may necessitate additional healthcare resources tailored to the needs of aging women.
Moreover, the implications extend into the workforce and economic stability. As countries strive for gender equality and seek to empower women in the workplace, knowing the demographics can guide initiatives to promote female participation in various sectors. The ongoing trends of gender migration, with many females increasingly entering the workforce, can also reshape economic landscapes.
As we look to the future, monitoring these gender ratios will be crucial. Changes in immigration policies, economic conditions, and social attitudes towards gender will undoubtedly influence these figures. By analyzing trends and understanding the implications of gender distribution, we can better prepare for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in Europe.
In summary, the male-to-female ratio map of Europe is not just a static representation of numbers; it tells a story of demographic shifts, cultural changes, and the evolving landscape of gender in society.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 8, 2025
- Views
- 262
Comments
Loading comments...