Lighthouses of Europe Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
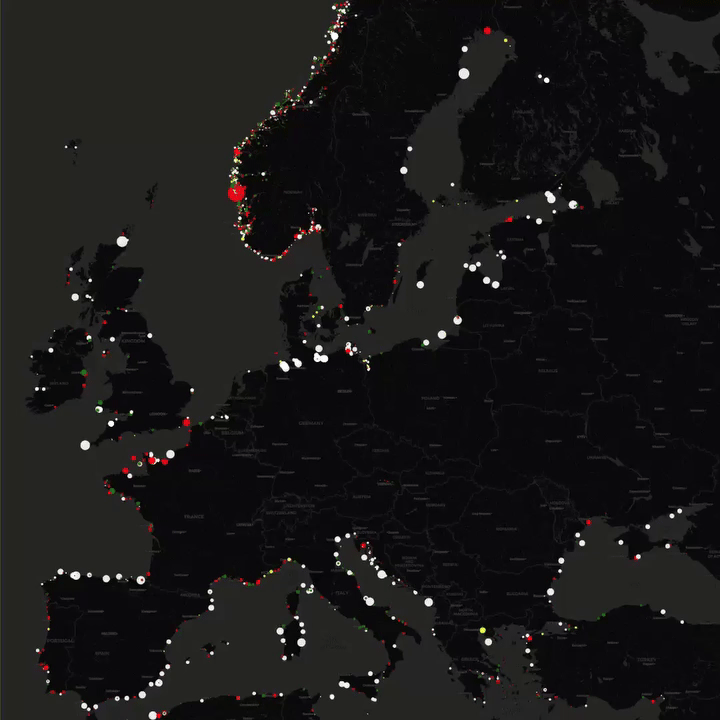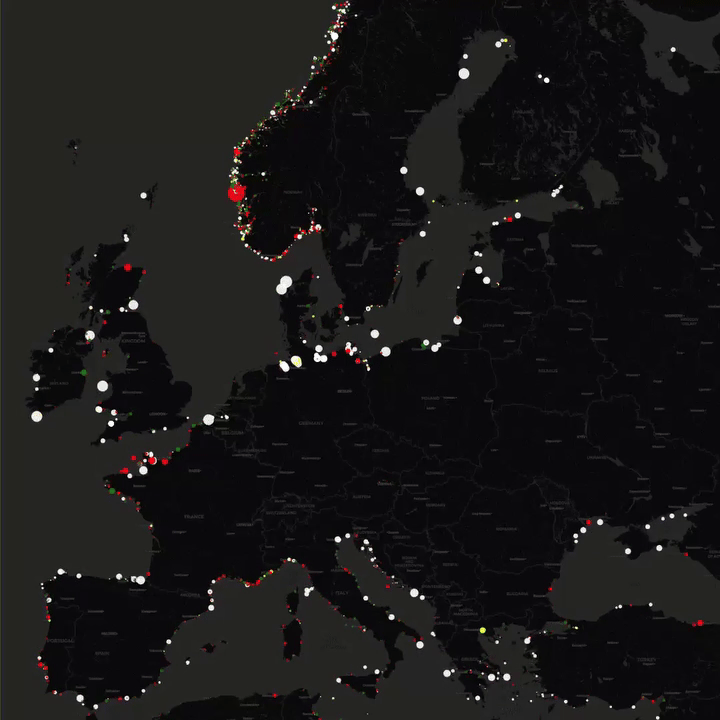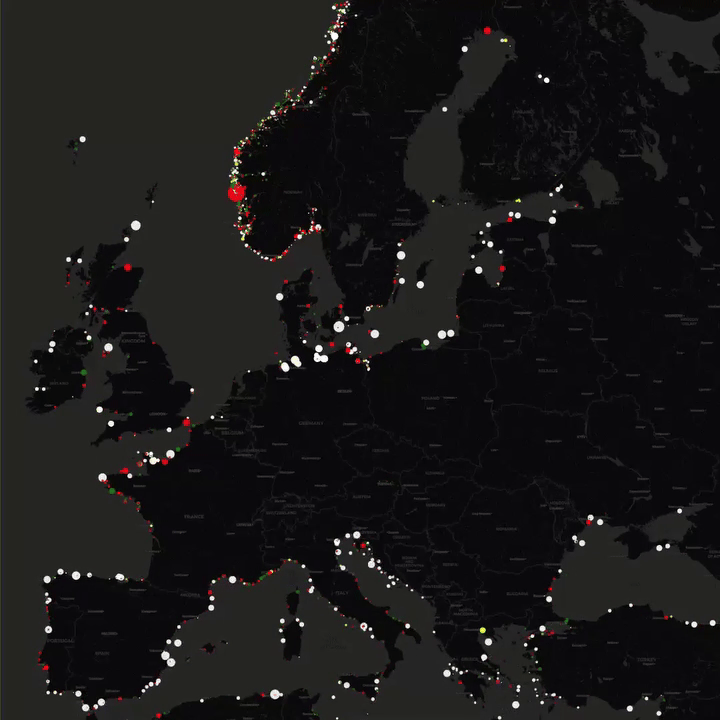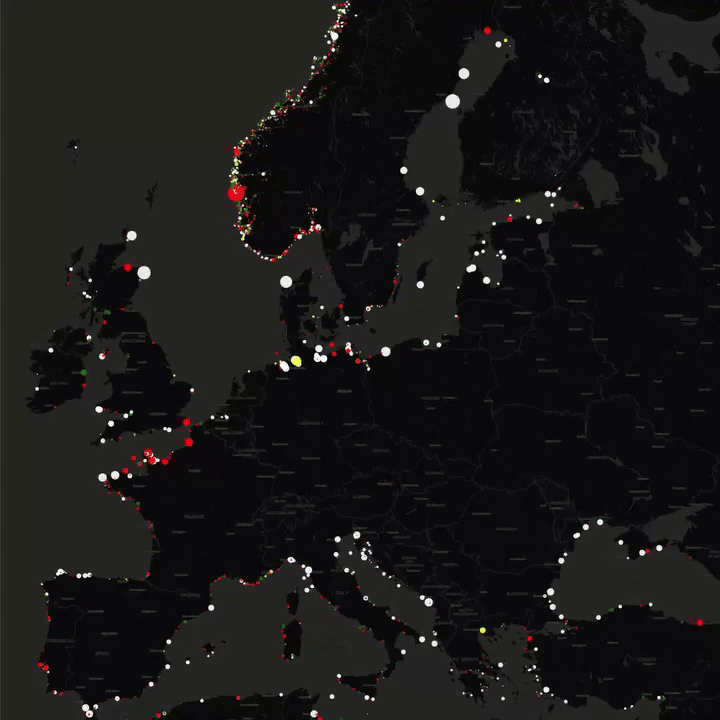
What This Map Shows
This map presents the locations of lighthouses across Europe, illustrating their distribution along coastlines, rivers, and islands. Each lighthouse is marked, allowing viewers to see not only their geographical placements but also to appreciate the historical and navigational significance of these towering structures. Lighthouses have served as vital guides for sailors for centuries, marking dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, and safe entry points to harbors. With this map, we can dive deeper into the rich maritime heritage of Europe and understand the role these lighthouses have played in shaping coastal navigation.
Deep Dive into Lighthouses
Lighthouses are more than just pretty silhouettes against the skyline; they are essential navigational aids that have kept countless mariners safe. The earliest lighthouses date back to ancient times, with the famed Lighthouse of Alexandria considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Interestingly, the concept of using light to signal safe passage has evolved significantly over the centuries. Today, lighthouses employ advanced technology, often using rotating beams and automated systems to guide vessels safely.
The primary purpose of a lighthouse is to mark dangerous coastlines, safe entry points to harbors, and hazardous shoals. Most lighthouses are painted in distinctive colors and patterns, which help sailors identify them from a distance. For instance, the iconic striped patterns of the lighthouse at Cape Hatteras in the United States are known worldwide. This color coding is crucial, especially in foggy conditions or at night when visibility is poor.
Interestingly, the number of lighthouses in Europe is staggering, with over 1,000 operational lighthouses scattered across its coasts and islands. Countries like France and the United Kingdom boast some of the highest concentrations. France alone has around 200 lighthouses, many of which are strategically positioned to guide vessels through its busy shipping lanes. The United Kingdom, with its rugged coastlines, has also invested significantly in lighthouse technology, with many of its structures equipped with modern light and sound systems to warn approaching ships of potential dangers.
Moreover, each lighthouse has its unique characteristic light, which can signal its identity to sailors. These characteristics include the color, pattern, and rhythm of the light flashes. For example, the Eddystone Lighthouse in England flashes every 10 seconds, whereas the Bell Rock Lighthouse has a different schedule and flash pattern. This variety not only aids in navigation but also adds to the charm and identity of each structure.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map of lighthouses in Europe, regional differences become apparent. For instance, the Mediterranean region, with its calmer seas, features lighthouses that are often more ornate and serve dual purposes as tourist attractions. The coastal lighthouses of Spain, such as the famous La Coruna Lighthouse, not only guide vessels but also draw visitors who wish to explore their history.
In contrast, the northern coasts, particularly in Norway and Scotland, face harsher weather conditions, leading to lighthouses designed for greater durability. The iconic Skerryvore Lighthouse off the coast of Scotland stands as a testament to engineering ingenuity, built to withstand the relentless storms of the North Atlantic.
Scandinavian countries, such as Sweden and Denmark, have also maintained their lighthouses as cultural landmarks, with many becoming heritage sites that celebrate maritime history. The lighthouses in these regions often feature striking architecture, reflecting the local styles and traditions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution and significance of lighthouses in Europe is not just about maritime navigation; it also connects to broader themes such as coastal safety, tourism, and historical preservation. These structures are symbolic of human ingenuity and resilience, standing as beacons of hope against the vastness of the sea.
What's fascinating is that many lighthouses are now being repurposed as tourist attractions, offering visitors a glimpse into maritime history while generating revenue for local communities. They often host museums, cafes, and guided tours, allowing people to appreciate the artistry and engineering behind these landmarks.
As maritime traffic continues to grow, the role of lighthouses remains critical. The need for advanced navigation systems is more pressing than ever, especially with the rise of autonomous shipping technologies. Future projections suggest that lighthouses will continue to evolve, incorporating modern technology while preserving their historical essence. This blend of tradition and innovation will ensure that lighthouses remain integral to maritime safety in Europe for generations to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 7, 2025
- Views
- 118
Comments
Loading comments...