Seven Seas Map: Ancient Greek, Arabian & Medieval European Views

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
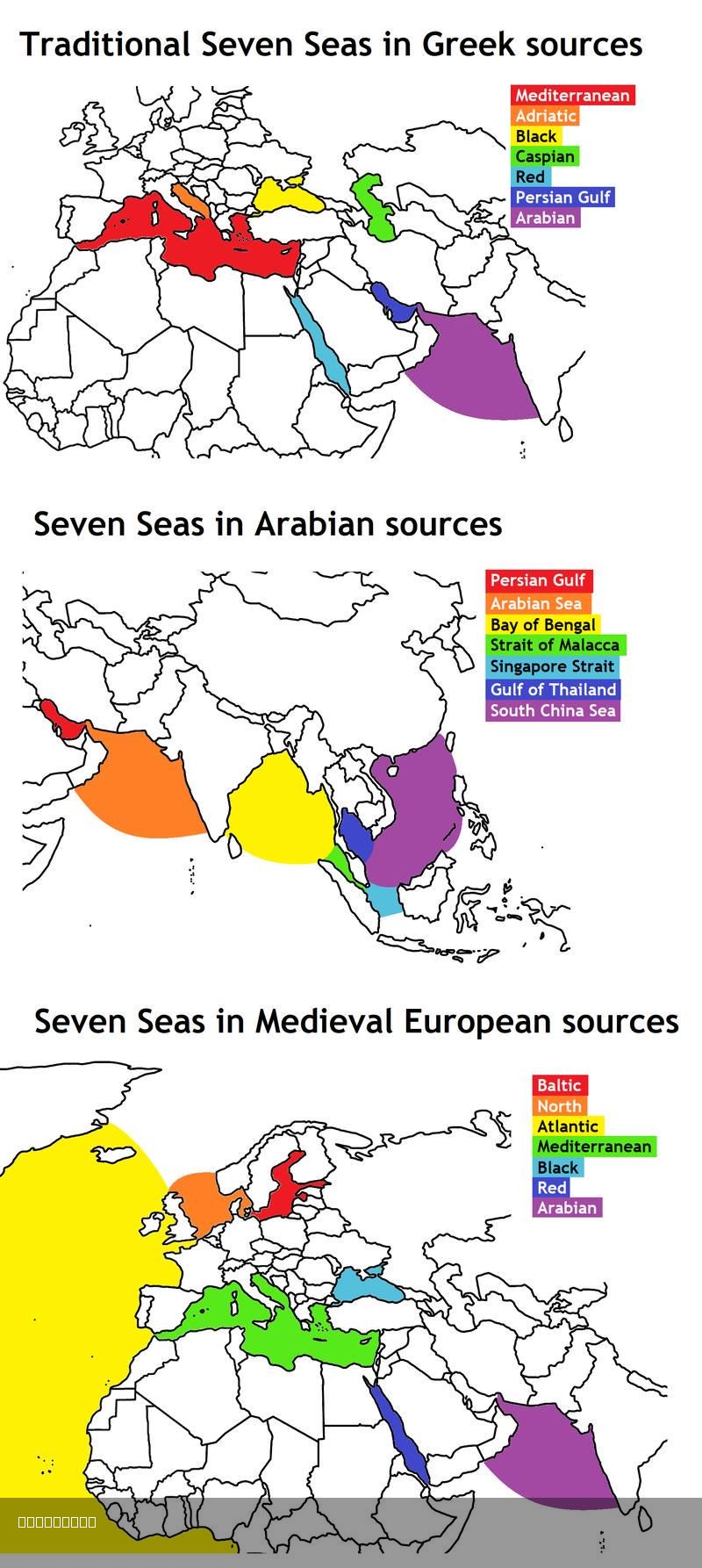
What This Map Shows
The map titled "The Seven Seas From The Ancient Greek, Arabian & Medieval European Points of View" is a fascinating representation that dives deep into the historical perceptions of maritime geography. It illustrates how different cultures interpreted the major bodies of water surrounding their civilizations. From the expansive Mediterranean Sea to the mysterious Indian Ocean, this visualization encapsulates the rich tapestry of maritime exploration and trade routes that shaped human history. It allows us to see not just geography but also the cultural significance attributed to these waters by ancient Greeks, Arab scholars, and medieval Europeans.
Deep Dive into The Seven Seas
The concept of the Seven Seas has evolved over centuries, with each civilization defining its own version based on trade, exploration, and navigational needs. Traditionally, the ancient Greeks identified their Seven Seas based on the regions they navigated most frequently. This included the Aegean Sea, the Ionian Sea, the Adriatic Sea, the Tyrrhenian Sea, the Ligurian Sea, the Gulf of Sidra, and the Red Sea. Each of these bodies played a crucial role in trade, travel, and the exchange of ideas.
Interestingly, the Arabian perspective on the Seven Seas differed significantly. Arab scholars, particularly during the Islamic Golden Age, expanded the geographical understanding of the known world. They included the Arabian Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Mediterranean Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Black Sea, and the Sea of Oman in their definitions. The Arabian Sea, for instance, was vital for trade routes that connected the East to the West, facilitating the exchange of spices, textiles, and knowledge.
Meanwhile, medieval European interpretations reflected a more Eurocentric worldview, influenced heavily by maritime exploration during the Age of Discovery. They often emphasized the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, the Mediterranean, and the various coastal waters surrounding Europe. The significance of the Atlantic Ocean cannot be understated, as it became the gateway for European powers to explore and colonize the Americas.
The Seven Seas thus represent more than just geographical entities; they symbolize the interconnectedness of cultures and economies. These seas were highways of trade and vessels of cultural exchange, shaping societies along their shores.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the Seven Seas by region, we can see striking differences in how each culture interacted with their maritime surroundings. For example, the Mediterranean Sea was a crucial artery for the ancient Greeks, who established city-states along its coast and relied heavily on its waters for trade and military endeavors. In contrast, for Arab traders, the Red Sea served as a vital link to the Indian Ocean, opening pathways to the rich markets of Asia.
In the medieval period, the North Sea became increasingly important as European nations began to expand their naval capabilities. The establishment of trade routes across the North Sea led to economic prosperity for countries like England and the Netherlands. The Baltic Sea, on the other hand, became a battleground for control over vital trade routes, particularly for the Hanseatic League, a commercial alliance of merchant guilds.
Interestingly, while the ancient Greeks and Arab scholars focused more on the surrounding seas, the medieval Europeans began to emphasize the importance of the Atlantic Ocean, which became a focal point for exploration. The Age of Discovery saw European powers such as Spain and Portugal venture into the Atlantic, forever changing the global trade landscape.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the historical context of the Seven Seas is essential for appreciating the development of global trade networks and cultural exchanges that shaped the world as we know it today. The interactions between these seas facilitated not only the exchange of goods but also ideas, technologies, and cultures.
Furthermore, the legacy of the Seven Seas continues to influence modern maritime practices and international relations. Have you noticed that many contemporary shipping routes still align with ancient trade paths established centuries ago? As globalization continues to expand, the importance of these maritime routes remains relevant, impacting economies and cultures worldwide.
Looking ahead, one might wonder how rising sea levels and climate change will affect these historical maritime regions. The Seven Seas are not just historical markers; they are living entities that continue to evolve. Protecting these waters is crucial for maintaining the balance of ecosystems and preserving the rich histories that they embody. As we navigate the complexities of modern maritime navigation and trade, the lessons from the Seven Seas remind us of our shared heritage and interconnected future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 3, 2025
- Views
- 140
Comments
Loading comments...