Share of Carpathian Mountains Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
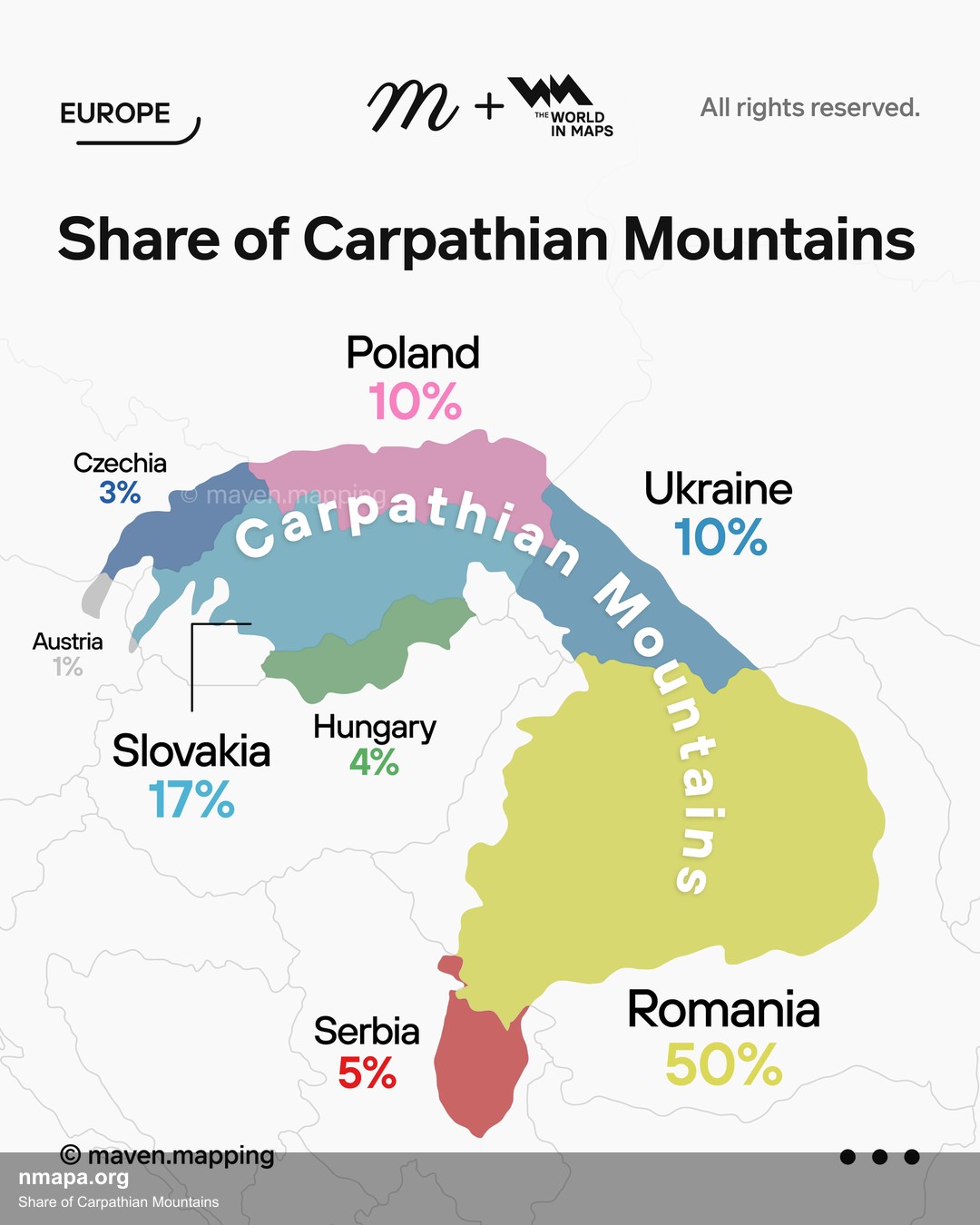
What This Map Shows
The "Share of Carpathian Mountains Map" visually represents the distribution and extent of the Carpathian Mountain range across Central and Eastern Europe. This significant geographical feature stretches through multiple countries, including Poland, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, and Hungary, showcasing the rugged terrain and diverse ecosystems that characterize this region. The map highlights not just the physical boundaries of the mountains but also the surrounding areas that are influenced by their presence. It serves as a useful tool for understanding how these mountains shape the environment, culture, and economy of the regions they span.
Deep Dive into the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains, forming the second-largest mountain range in Europe after the Alps, extend for about 1,500 kilometers (932 miles) and consist of three main sections: the Western Carpathians, the Eastern Carpathians, and the Southern Carpathians. This magnificent range is not just a natural barrier; it plays a crucial role in influencing climate, biodiversity, and human activities in the region.
Interestingly, the Carpathians are home to a rich variety of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to this mountain range. The diverse ecosystems range from lush forests at lower elevations to alpine meadows at higher altitudes. The region boasts over 4,000 plant species and a plethora of wildlife, including brown bears, wolves, and lynxes. Have you ever wondered what it takes to maintain such biodiversity? Conservation efforts are ongoing, as the Carpathians face threats from logging, urban development, and climate change.
The climate in the Carpathians varies significantly due to the elevation and geographical location. The western sections receive more precipitation and tend to have a milder climate, while the eastern parts can experience harsher winters. This variation creates unique microclimates that support different types of vegetation and wildlife. For example, in the higher altitudes of the Tatra Mountains, you will find snow-capped peaks and glaciers, while the lower valleys feature temperate hardwood forests.
From a geological perspective, the Carpathians were formed through a combination of tectonic activity and erosion over millions of years. They are predominantly composed of limestone, which contributes to fascinating karst formations, such as caves and gorges. The geological activity continues to shape the landscape, leading to frequent landslides and other natural phenomena.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map's data, it becomes evident that the Carpathian Mountains influence various regions differently. For instance, in Poland, the Tatra Mountains are a focal point for tourism, attracting hikers and winter sports enthusiasts. The area is known for its stunning landscapes and vibrant culture, particularly in towns like Zakopane.
In contrast, the Romanian section of the Carpathians, especially the Southern Carpathians, is characterized by traditional pastoral communities that rely on the land for agriculture and livestock. The Transfagarasan Highway, an engineering marvel snaking through the mountains, draws tourists and showcases the region's natural beauty.
In Slovakia, the High Tatras National Park provides a protected environment for numerous endemic species and offers recreational opportunities, underscoring the importance of the Carpathians for both biodiversity and tourism. However, urbanization in cities like Poprad poses challenges to conservation.
Significance and Impact
The Carpathian Mountains are not just a stunning geographical feature; they play a significant role in the cultural, economic, and environmental fabric of the region. They serve as a natural border, influencing cultural exchanges and economic interactions between the countries they traverse. The mountains also provide essential resources, including timber, minerals, and freshwater, which are vital for the populations living in their shadows.
However, the Carpathians are increasingly facing challenges from climate change, which can alter precipitation patterns and impact the delicate ecosystems. As temperatures rise, the unique biodiversity and habitats may be at risk. Moreover, human activities like deforestation and tourism can further strain these natural resources.
Looking to the future, sustainable tourism and conservation efforts will be crucial in preserving the Carpathians' natural beauty and ecological integrity. Engaging local communities in these efforts can not only protect the environment but also enhance the cultural heritage that the Carpathians represent.
In summary, the Share of Carpathian Mountains Map provides a snapshot of a vital geographical feature that is rich in biodiversity and cultural significance. Understanding the Carpathians' impact helps us appreciate their role in the broader European landscape and underscores the need for responsible stewardship of this precious natural resource.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 2, 2025
- Views
- 164
Comments
Loading comments...