Proximity to Space Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
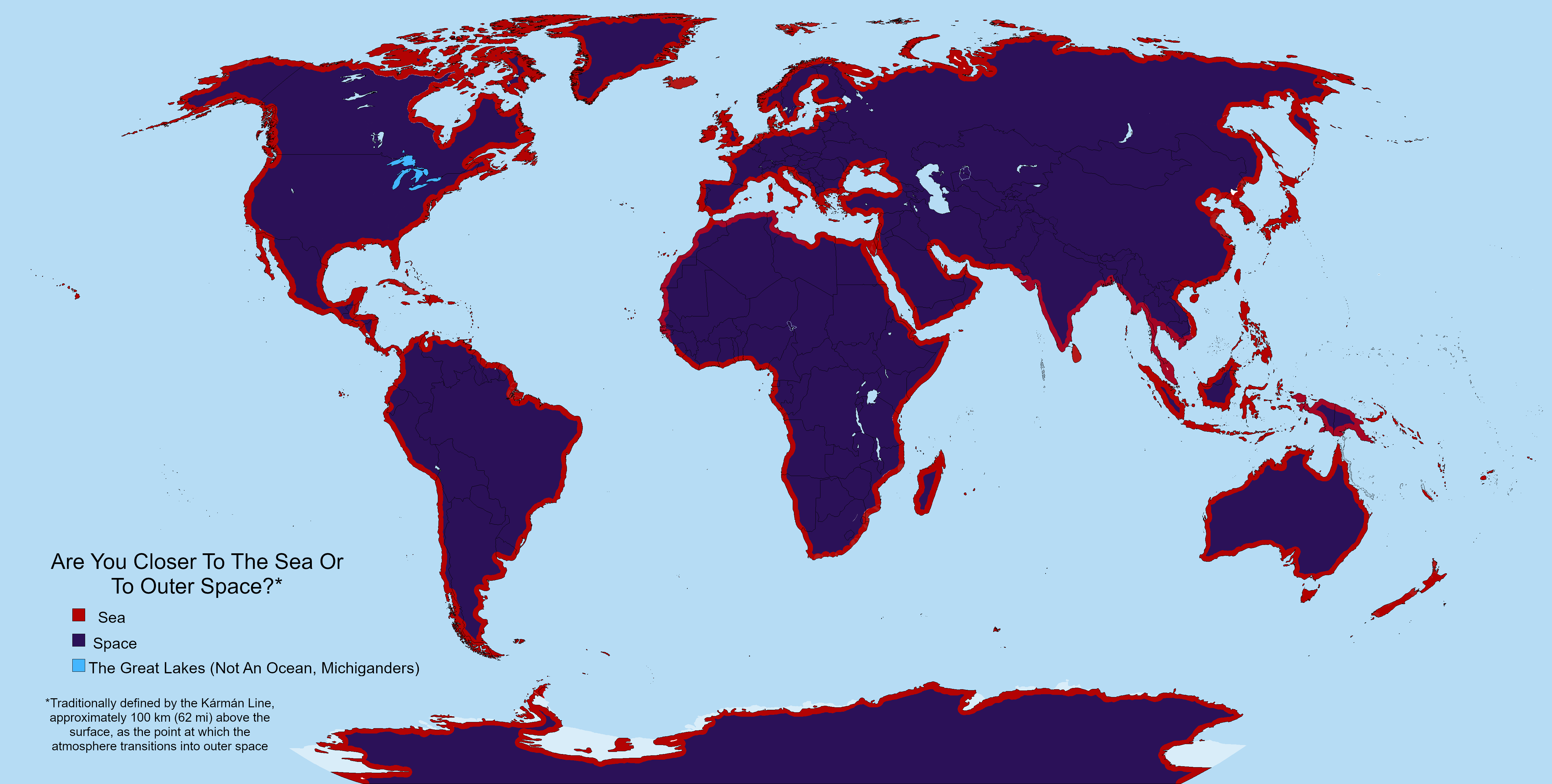
The visualization titled "Space is a lot closer than most people realize" presents an intriguing perspective on the proximity of outer space to our everyday lives. It illustrates the distance from various locations on Earth to the Kármán line, widely recognized as the boundary of space, which sits at an altitude of 100 kilometers (62 miles) above sea level. This map highlights just how accessible space is from different geographical points, emphasizing that, in the grand scheme of the universe, our planet is just a stone's throw away from the vastness beyond.
Deep Dive into Proximity to Space
The idea that space is closer than we typically think is both astonishing and thought-provoking. While the average person may envision space as an unreachable frontier, the reality is that many people live within a relatively short distance from it. The Kármán line marks the point where conventional aircraft cannot maintain lift; thus, it serves as a crucial reference for distinguishing between the atmosphere and outer space.
Interestingly, there are numerous factors that contribute to this proximity. For example, high-altitude locations such as Mount Everest, which peaks at 8,848 meters (29,029 feet), bring surrounding areas closer to space. Even cities like La Paz, Bolivia, sit at about 3,650 meters (11,975 feet) above sea level, allowing their residents to experience a unique relationship with the atmosphere.
Moreover, this concept of proximity isn't just about physical distance. It's also about the advancements in aerospace technology that have made space travel more feasible. Space tourism is on the rise, with companies like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic working diligently to offer suborbital flights to civilian passengers. As these ventures develop, the dream of gazing down at Earth from the edge of space is becoming a reality for more and more people.
However, not all regions have the same accessibility to space. For instance, countries with advanced aerospace industries—such as the United States, Russia, and members of the European Space Agency—have the infrastructure to support space exploration and tourism, making the experience more tangible for their citizens. Meanwhile, other regions may lack the resources or technological capabilities to engage with this new frontier directly.
Statistically speaking, the average distance to the Kármán line from any point on Earth is approximately 100 kilometers. However, in practical terms, the closest access points are often located near spaceports and launch sites, which are typically situated in regions with favorable weather conditions and lower population densities to minimize risks during launches.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map regionally reveals interesting variations in proximity to space. For instance, in North America, locations such as Cape Canaveral in Florida and Vandenberg Space Force Base in California serve as launch sites that bring residents closer to the experience of space travel. The distances to the Kármán line from these sites reinforce the notion that space is not beyond reach but rather an attainable destination for those prepared to venture forth.
In contrast, regions in the equatorial belt, such as parts of South America and Africa, play a critical role in space exploration due to the Earth’s rotation. Launching from these locations can provide additional advantages, such as increased velocity from the rotational speed of the Earth, making space travel more efficient. Countries like French Guiana host spaceports that capitalize on this geographic advantage.
Interestingly, urban areas tend to have a more complicated relationship with space due to their dense populations and atmospheric pollution, which can interfere with both the clarity of the sky and the safety of launches. Cities like New York or Tokyo, while far from the Kármán line, are hubs of innovation and technology that contribute indirectly to the space economy through research and development.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the proximity to space is significant for several reasons. Firstly, it challenges our perceptions of Earth and its relationship with the cosmos. The realization that space is just a short distance away can inspire curiosity and a deeper appreciation for both our planet and the universe beyond it. Moreover, as technology continues to evolve, the implications of accessibility to space could reshape various industries, from telecommunications to tourism, and even global collaboration on scientific research.
As we consider the future, the potential for space travel to become more commonplace raises important questions about sustainability and environmental stewardship. How will we balance exploration with the need to protect our planet? Will increased accessibility lead to greater awareness of our responsibilities as stewards of Earth? Current trends indicate that space exploration will become more integrated into our daily lives, with the possibility of a future where space is not just a destination but an extension of our existence.
In conclusion, the proximity of space is not just a geographical fact; it reflects our evolving relationship with technology and exploration. As we stand on the brink of new adventures beyond our atmosphere, it’s essential to remain mindful of both the opportunities and challenges that come with this newfound closeness.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 29, 2025
- Views
- 10
Comments
Loading comments...