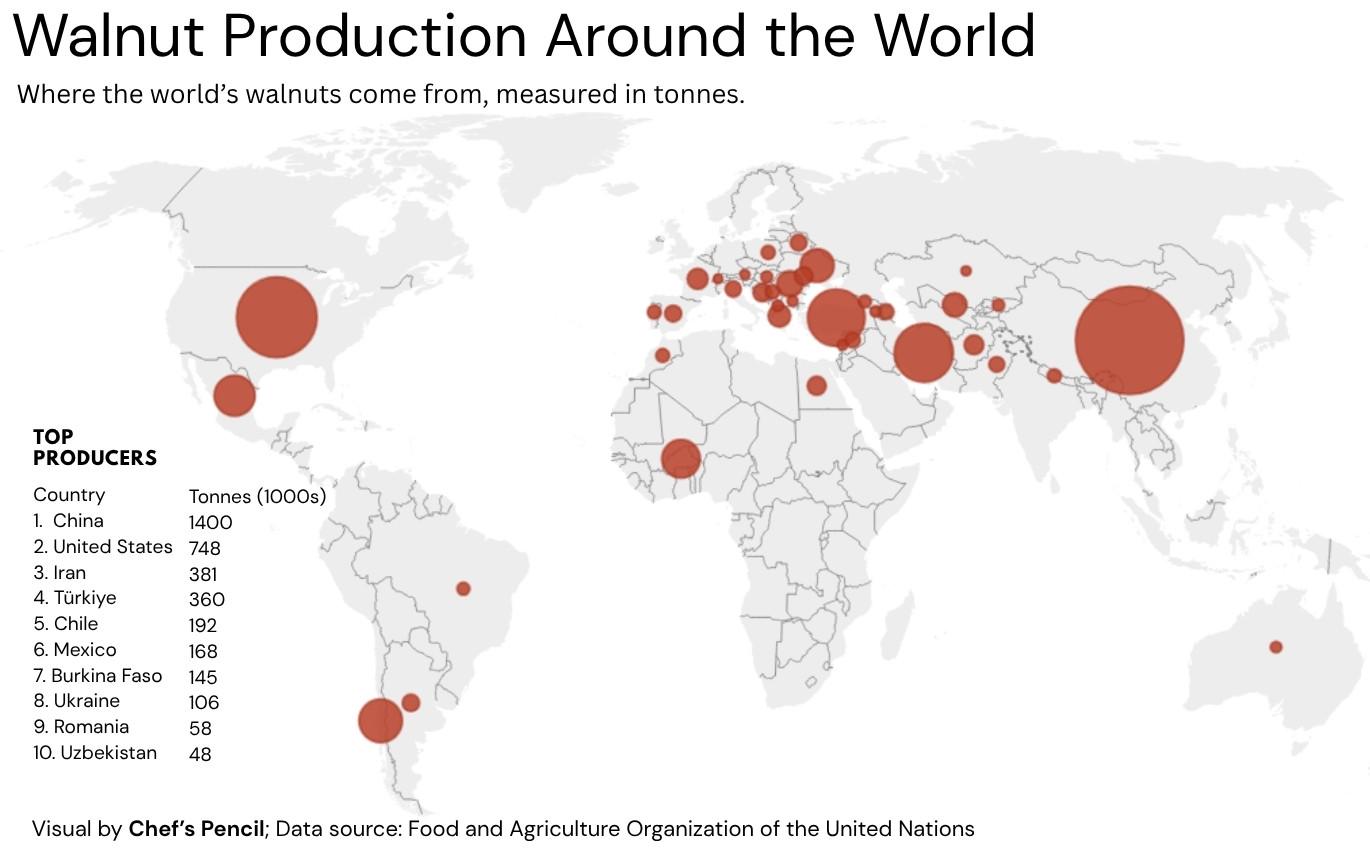
Walnut Production Map: China, U.S., Iran

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map visually represents the global walnut production landscape, highlighting that China, the United States, and Iran collectively account for half of the world's walnut supply. As you explore this map, you'll notice the significant concentration of walnut production in these three countries, which dominate the market and influence global supply chains. However, the story behind walnut production goes beyond mere numbers and locations; it delves into agricultural practices, economic implications, and cultural significance.
Deep Dive into Walnut Production
Walnuts are more than just a tasty snack; they are a vital agricultural product with rich historical roots. The walnut tree, native to regions of Persia (modern-day Iran), has been cultivated for thousands of years, making walnuts one of the oldest cultivated nuts in human history. Today, walnuts are integral to various cuisines and are celebrated for their nutritional benefits, including high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
Globally, walnut production has seen a remarkable rise, particularly in the last few decades. In 2021, the total walnut production reached approximately 4.2 million metric tons, with China leading the charge by producing around 2.6 million metric tons alone. This is fascinating when you consider that China has not only expanded its production through advanced agricultural techniques but has also invested in improving the quality of its walnut varieties.
The United States, particularly California, is the second-largest producer, contributing roughly 1 million metric tons annually. California’s Mediterranean climate, with its mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, is ideal for walnut cultivation, leading to high-quality nuts that are sought after worldwide. Interestingly, the U.S. walnut industry has also been focusing on sustainable farming practices to meet the growing demand for environmentally friendly products.
Iran, once the global leader in walnut production, now ranks third, producing around 500,000 metric tons. The country is known for its distinct varieties, which are often praised for their flavor and quality. However, Iran faces challenges, including agricultural inefficiencies and economic sanctions, which impact its production capabilities. Despite these hurdles, Iranian walnuts remain a staple in Middle Eastern cuisine and continue to be exported, albeit in smaller quantities than their competitors.
What's compelling is how these three countries have shaped the global walnut market. The interplay between supply, demand, and agricultural practices in these regions directly influences prices and availability worldwide. As consumer preferences shift towards healthier snacks, the demand for walnuts is expected to grow, prompting these countries to potentially increase their production.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing walnut production by region, it’s essential to recognize the agricultural landscape and the socio-economic conditions that influence these outputs. In China, walnut cultivation is heavily concentrated in provinces like Xinjiang and Sichuan, where the climate and soil conditions are favorable. The Chinese government has also implemented policies to encourage walnut farming, seeing it as a way to boost rural economies.
In the United States, California’s Central Valley is the heart of walnut production. Here, farmers utilize advanced irrigation systems and precision agriculture to ensure high yields. However, the region is also grappling with water shortages, raising concerns about the sustainability of walnut farming. The competition among farmers for water resources has led to innovative practices, but it remains a critical issue.
Conversely, Iran’s walnut production is scattered across various provinces, including Kordestan and Zanjan. The country's mountainous terrain can make cultivation challenging, but it also allows for unique walnut varieties to flourish. Despite the challenges posed by sanctions and economic instability, local farmers are finding ways to adapt and continue their traditions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding walnut production is crucial not only from an agricultural perspective but also from an economic and cultural standpoint. Walnuts are increasingly recognized for their health benefits, leading to a surge in demand globally. This demand influences agricultural practices, trade relationships, and economic strategies within the producing countries.
Moreover, the walnut market is reflective of broader agricultural trends, such as the shift towards sustainable practices and the influence of climate change on crop yield. With the global population expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, the pressure to produce more food sustainably will only increase. Countries like China, the U.S., and Iran will play pivotal roles in shaping the future of food production, particularly in high-value crops like walnuts.
In conclusion, the map showing walnut production is not just a representation of where these nuts come from; it encapsulates a complex web of agricultural practices, economic implications, and cultural significance that will continue to evolve in the coming years. As we delve deeper into the world of walnuts, it becomes clear that their impact extends far beyond the kitchen table.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 28, 2025
- Views
- 8
Comments
Loading comments...