Welsh Language Distribution Map by Census Districts 1891

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
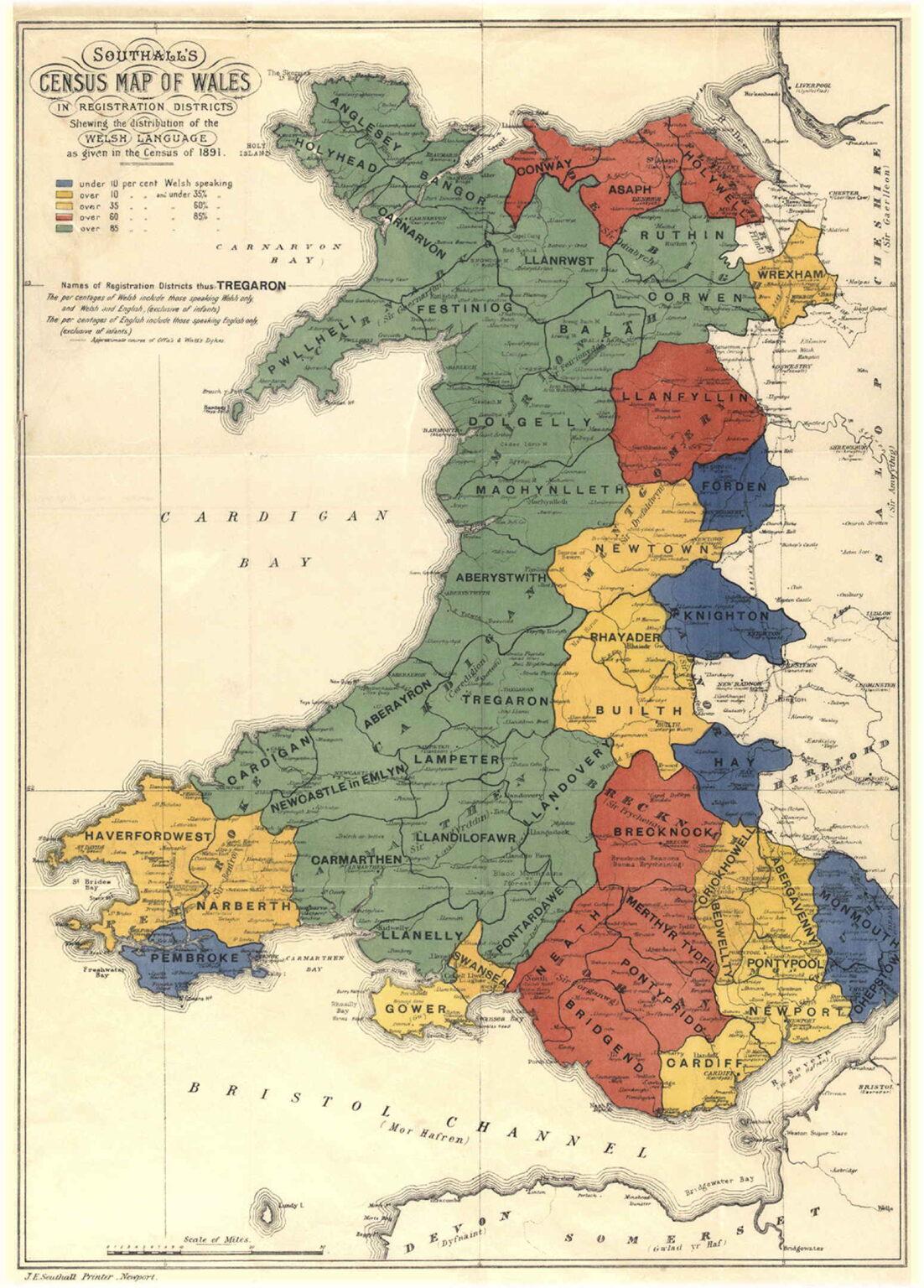
This map illustrates the distribution of the Welsh language across various census districts in Wales, as recorded in the 1891 Census. It categorizes the prevalence of the Welsh language into five distinct groups: areas where less than 10% of the population spoke Welsh, 10-20%, 20-40%, 40-60%, and regions where more than 80% of the population were Welsh speakers. This visualization is not just a representation of language use; it provides a snapshot of cultural identity, societal structure, and regional differences in Wales during the late 19th century.
Deep Dive into the Welsh Language
The Welsh language, or Cymraeg, is a Celtic language that has been spoken in Wales for over a thousand years. Interestingly, the 1891 Census marked a crucial period for the Welsh language, as it was one of the first systematic attempts to gather data on language use within the population. The results reflected not only the linguistic landscape but also the socio-political context of the time.
Historically, Welsh has faced significant challenges, particularly during the 19th century, when industrialization and Anglicization began to take hold. Despite these pressures, the map reveals that a substantial portion of the population continued to speak Welsh, especially in rural areas and the north of Wales. For instance, regions like Gwynedd and Anglesey show overwhelming percentages of Welsh speakers, often exceeding 80%.
This language distribution is closely linked to the cultural identity of the Welsh people. The areas with a higher prevalence of Welsh speakers tended to maintain strong local traditions, folklore, and a sense of community that was deeply rooted in the Welsh language. The map serves as a reminder of the resilience of the Welsh language and its speakers.
Moreover, the census data from 1891 helps us understand the demographics of language use. Regions with less than 10% Welsh speakers, such as parts of industrial south Wales, indicate the impact of English industrialization and migration, where English became the dominant language in workplaces and schools. Conversely, areas with more than 60% Welsh speakers often had a lower degree of industrial development, suggesting a strong retention of cultural heritage.
Regional Analysis
When we examine the map closely, it becomes clear that language distribution is not uniform across Wales. In the north, counties like Gwynedd and Conwy stand out with their high percentages of Welsh speakers. This can largely be attributed to the preservation of Welsh culture, where the language is not only spoken but also taught in schools and used in local governance.
In contrast, the south, particularly in industrial hubs like Merthyr Tydfil and Cardiff, shows a significant decline in Welsh speakers, often falling into the under 10% category. This shift is indicative of the broader societal changes during the industrial revolution, where English became the lingua franca of the burgeoning industries, leading to a gradual erosion of the Welsh language in urban centers.
Interestingly, the town of Aberystwyth emerges as a cultural center in this map, with a healthy percentage of Welsh speakers, reflecting its role as a hub for Welsh literature and education. This town not only served as a university town but also as a bastion for the Welsh language revival efforts that would gain momentum in the 20th century.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of the Welsh language through this map is crucial for several reasons. It highlights the historical context of language use and the socio-cultural dynamics in Wales during a transformative period. The implications of this distribution are still relevant today, as language plays a critical role in cultural identity and community cohesion.
In modern Wales, the Welsh Government has implemented various initiatives to promote the Welsh language, aiming to increase the number of speakers by 1 million by 2050. This goal reflects a broader recognition of the importance of linguistic diversity in preserving cultural heritage. The historical context provided by the 1891 Census serves as a vital reference point for current and future linguistic policies.
As we look at current trends, what's fascinating is how the legacy of the 19th-century census data continues to influence the Welsh language revival. With language education programs and community initiatives, there is a renewed vigor in promoting Welsh, particularly among younger generations. This map, therefore, not only tells a story of the past but also shapes the future of language and identity in Wales.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 25, 2025
- Views
- 10
Comments
Loading comments...