Roman Roads to Jerusalem Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
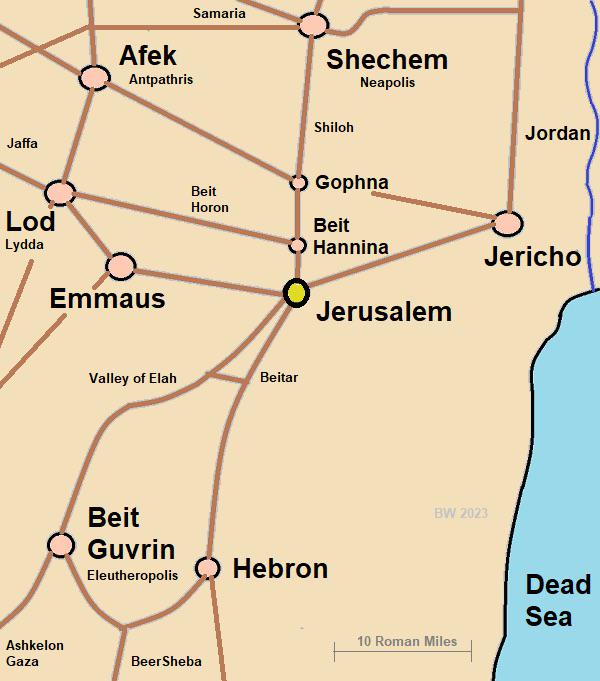
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the main roads that led to Jerusalem during the Roman era, highlighting a fascinating aspect of ancient transportation networks. Interestingly, it reveals that there were five primary routes connecting the city to various regions, significantly outnumbering the two highways available today. These ancient roads were vital for trade, pilgrimage, and military movements, serving as arteries of connectivity in a historically rich area.
Deep Dive into Roman Roads
The Roman roads leading to Jerusalem were more than mere pathways; they were the lifeblood of the region, facilitating interactions among diverse communities and cultures. Each of the five roads had its unique destination and significance:
1. **Northern Road**: This route connected Jerusalem to important cities like Sychem (modern-day Nablus), Caesarea, and Damascus. It was crucial for trade and facilitated pilgrimages to Jerusalem. The presence of these cities along the road indicates a vibrant network of commerce and cultural exchange.
2. **Northeastern Road**: Heading toward the Mount of Olives and Bethany, this road intersected with another leading to Jericho and the Dead Sea. This intersection was strategically important, as it connected Jerusalem with key locations in the Judean wilderness, a region rich in historical and religious significance.
3. **Northwestern Road**: This route led directly to the Mediterranean port of Joppa, which was essential for maritime trade. Joppa served as the gateway for goods and travelers from across the sea, making this road vital for economic and cultural exchanges.
4. **Western Road**: This road split into two paths: one leading back to Joppa and the other heading southwest toward Bethlehem and Hebron. The latter path is particularly noteworthy as it connects Jerusalem with the birthplace of Jesus, underscoring the area's religious importance.
5. **Southwestern Road**: Finally, this road provided access to the Dead Sea, known for its unique geography and mineral wealth. The proximity of the Dead Sea also meant that this road had significant implications for trade, especially in salt and other resources.
What's intriguing is that these roads were engineered with the expertise that characterized Roman infrastructure—straight, durable, and designed to accommodate the movement of not just people, but also goods and armies.
Regional Analysis
Comparing the Roman road network to today’s routes, we find a stark contrast. Today, only two major highways lead to Jerusalem, Highway 1 and Highway 60. Highway 1 runs northwest toward Tel Aviv, while Highway 60 connects Jerusalem to Beer Sheva in the south and Nazareth in the north. These highways serve vital transportation needs but lack the extensive connectivity of their Roman predecessors.
The modern landscape also includes smaller roads like Route 443, 395, and 386, which provide additional routes but are not classified as highways. The reduction in the number of main roads reflects changes in urban development, population distribution, and transportation technology over the centuries. Interestingly, while the ancient roads facilitated movement for various purposes—religious, military, and economic—the contemporary highways primarily serve personal and commercial transport.
Significance and Impact
Why does this comparison matter? Understanding the historical context of Jerusalem's roadways gives us insight into the city's evolution and its role as a cultural and religious center. The Roman road network allowed for the mobility of ideas, people, and goods, shaping the historical narrative of not just Jerusalem but the entire region.
Moreover, as we consider modern implications, the limited number of highways can pose challenges for traffic congestion and urban planning. As Jerusalem continues to grow, the need for efficient transportation solutions becomes increasingly important. Current trends show a rise in urban sprawl, which may necessitate re-evaluating transportation infrastructure to accommodate future growth.
In conclusion, the roads of ancient Jerusalem were more than just routes; they were pathways of history that shaped the city into what it is today. The stark contrast with the present-day highway system invites us to reflect on how our transportation networks influence urban development and connectivity in contemporary society.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 18, 2025
- Views
- 34
Comments
Loading comments...