Polar Balance Map of Earth

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
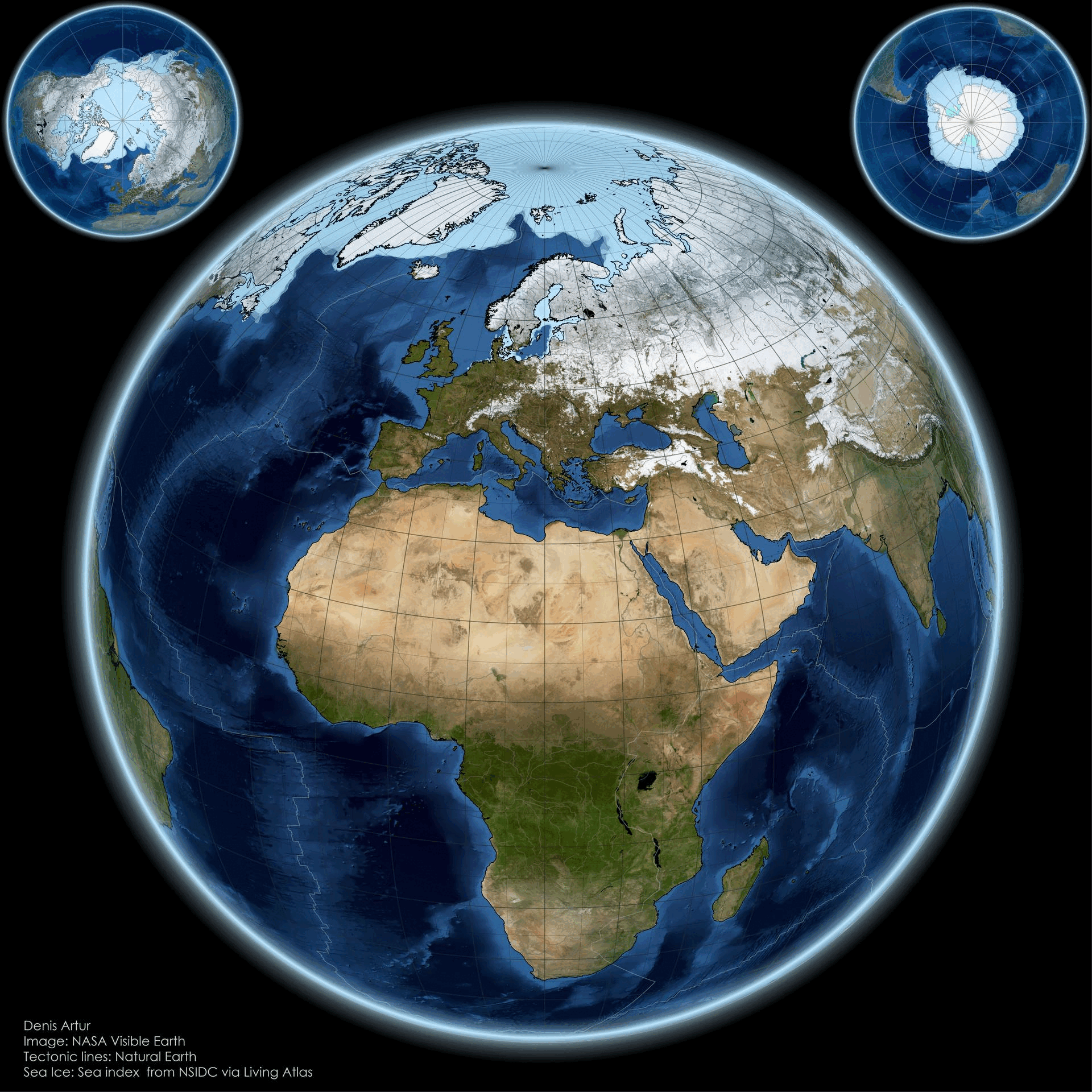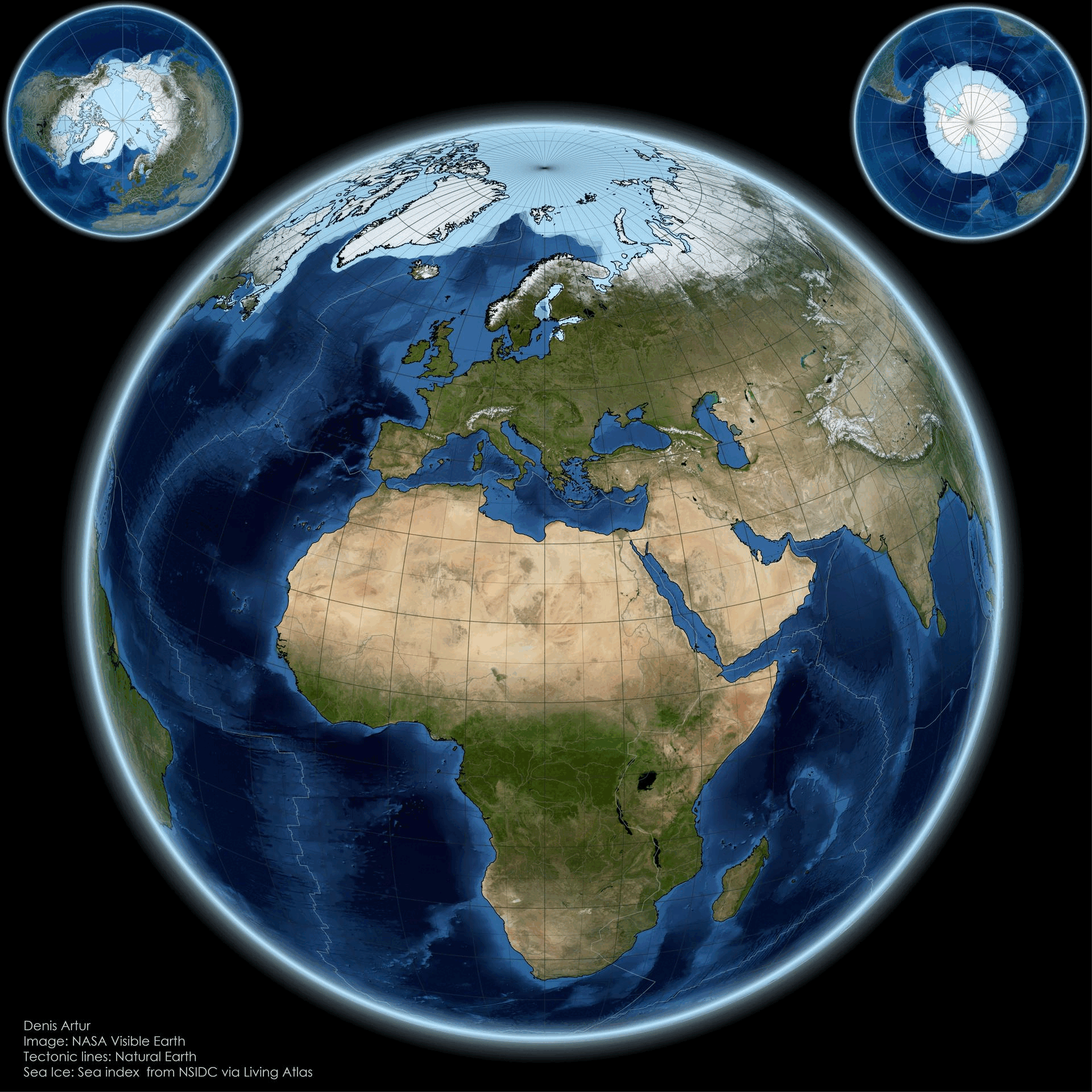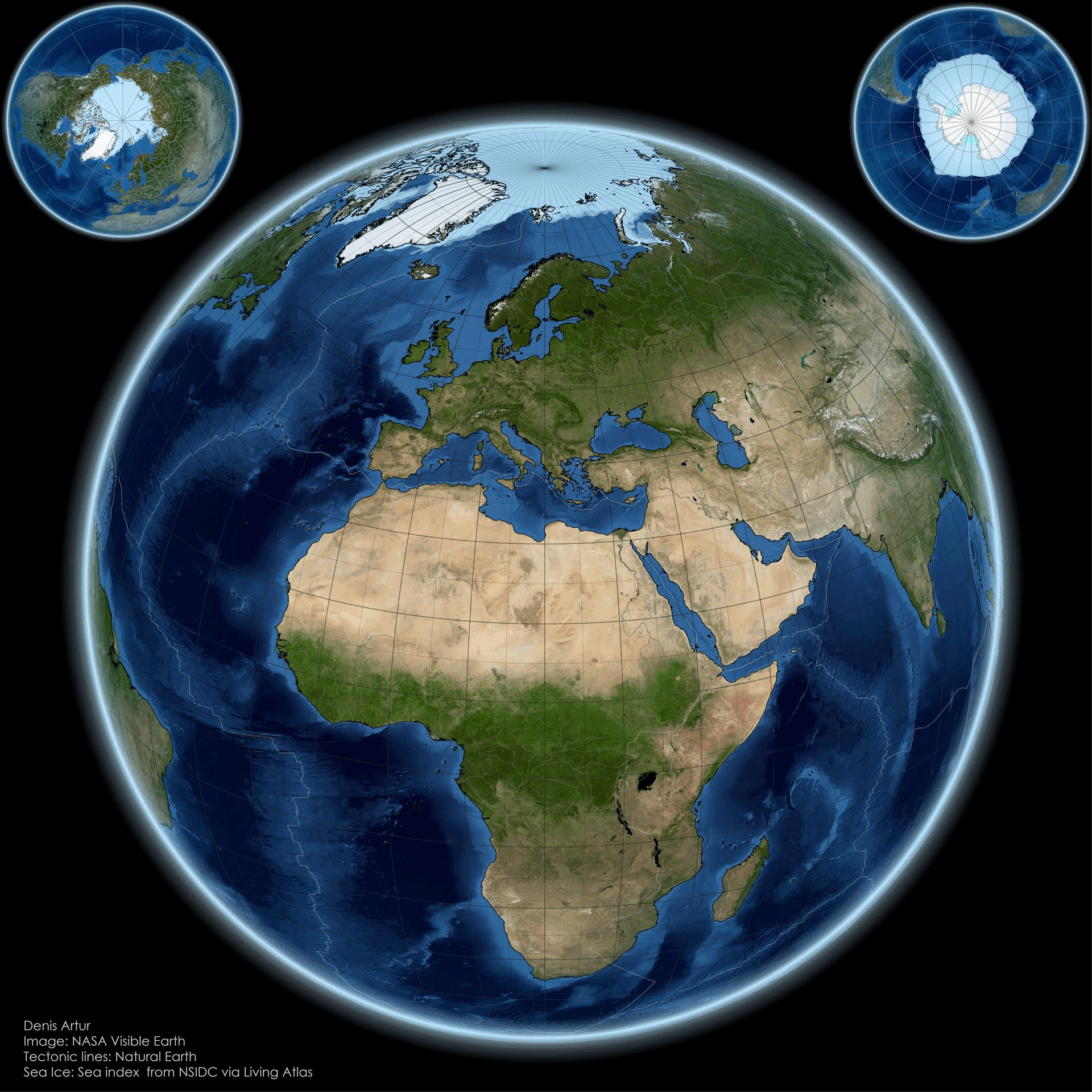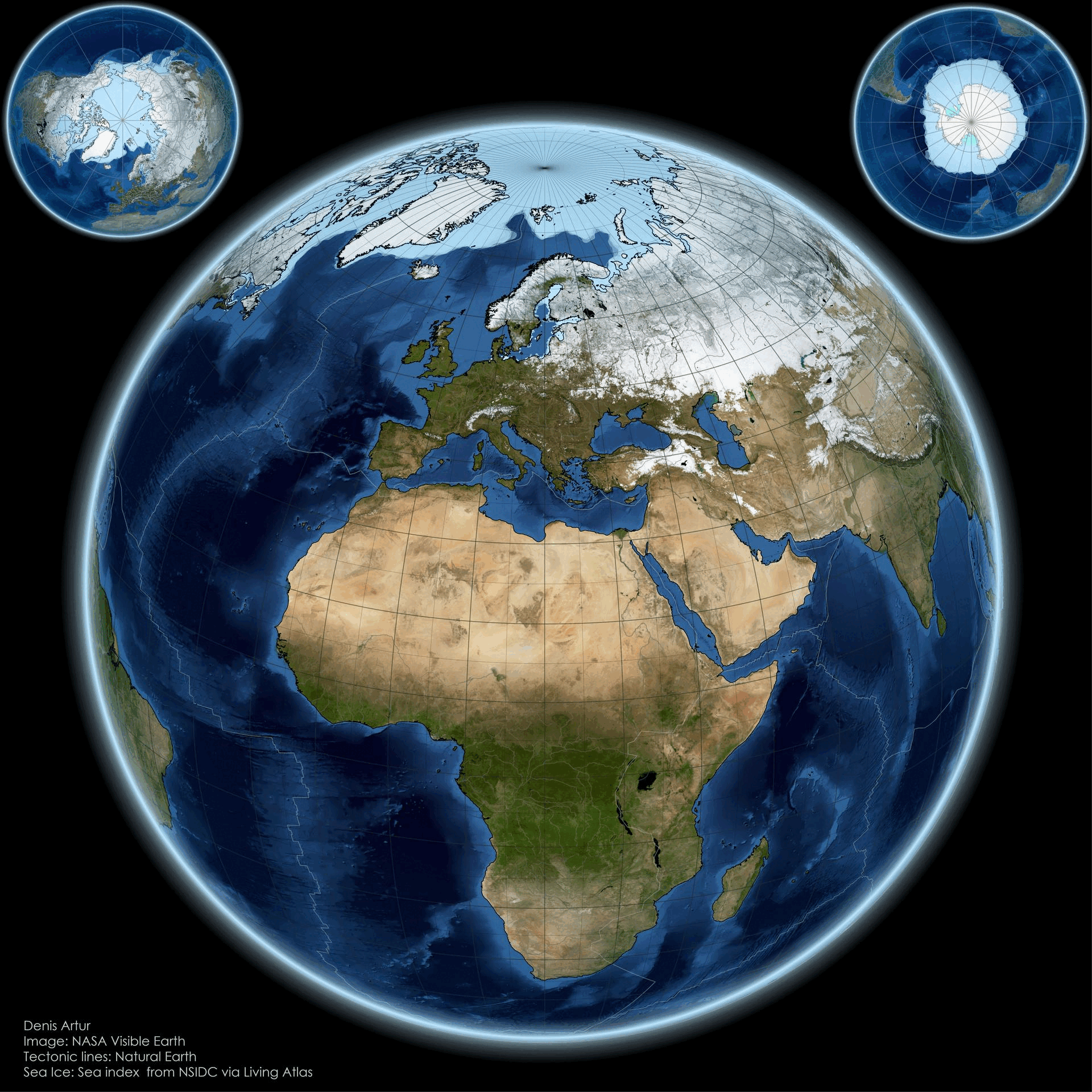
The "From Pole to Pole: Visualizing Earth’s Polar Balance" map presents a striking visual representation of the Earth's polar regions, highlighting the delicate equilibrium between the Arctic and Antarctic environments. This visualization not only delineates geographic boundaries but also illustrates the stark contrasts in climate, biodiversity, and human impact across these two polar extremes. At first glance, one might be drawn to the icy expanses of the Arctic, characterized by its vast sea ice cover and unique ecosystems, while the Antarctic stands as a formidable landmass, enshrined in ice and home to distinctive wildlife.
Deep Dive into Earth’s Polar Environments
Let’s delve deeper into what makes these polar regions so unique. The Arctic, primarily composed of ocean surrounded by land, features a complex ecosystem that includes ice-covered waters and coastal areas. Interestingly, the Arctic is warming at a rate nearly twice that of the global average due to climate change. According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center, Arctic sea ice extent has dwindled by about 40% since the late 1970s. This decline not only affects local wildlife, such as polar bears and seals, but also has broader implications for global weather patterns.
In contrast, the Antarctic is a continent covered by a thick ice sheet, which holds about 60% of the world’s fresh water. The Antarctic ice sheet is crucial for regulating sea levels; if it were to melt completely, estimates suggest it could raise global sea levels by over 60 meters. The continent is home to unique species, including Emperor penguins and various seabird species, adapted to its extreme conditions.
What’s fascinating is the biodiversity found in both regions, despite their harsh climates. The Arctic supports a range of species that depend on sea ice, while the Antarctic's isolation has led to unique evolutionary paths for its fauna. For instance, the krill population in the Southern Ocean is vital for the Antarctic food web, serving as a primary food source for whales, seals, and penguins.
The climate of the polar regions is also characterized by extremes. The Arctic experiences seasonal changes profoundly affecting its ecosystems. Summers can be surprisingly warm, leading to a brief but intense growing season for Arctic flora. Conversely, the Antarctic remains colder year-round, with its harsh environment limiting biological productivity.
Interestingly, the polar regions are also experiencing dramatic shifts due to climate change, leading to increased research and monitoring efforts. Scientists are particularly focused on the feedback loops created by melting ice, which further accelerates warming.
Regional Analysis
The map encourages us to consider the regional differences between the Arctic and Antarctic. The Arctic spans several countries, including Canada, Russia, and the United States, each facing unique challenges tied to climate change. For example, the Inuit communities in Canada are experiencing altered hunting patterns as sea ice becomes less predictable. In contrast, the Antarctic, governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, is primarily a research zone with no permanent human inhabitants, yet it is not immune to the impacts of climate change, particularly from melting ice shelves.
Comparing the two regions illustrates the complexity of their climates and ecosystems. For instance, the Arctic’s thawing permafrost releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas, worsening climate change. Meanwhile, the Antarctic's ice loss contributes directly to rising sea levels, posing risks to coastal cities worldwide. By analyzing these regions, we can better understand the interconnectedness of global climate systems, as changes in one area can have cascading effects elsewhere.
Significance and Impact
Why does understanding the polar balance matter? The implications of changes in the polar regions extend far beyond their icy borders. For instance, disruptions in Arctic ecosystems can lead to shifts in global weather patterns, affecting agricultural productivity in temperate zones. Moreover, the melting of Antarctic ice sheets raises pressing concerns for low-lying nations, which may face existential threats from rising seas.
In contemporary discussions on climate policy, the polar regions serve as a bellwether for global climate health. The urgency of addressing climate change is underscored by the visible changes observed in these regions. As scientists project continued warming and ice loss, the need for concerted international action becomes increasingly critical. By engaging with visualizations like the "Polar Balance Map," we can better appreciate the significance of these regions and advocate for sustainable practices that protect our planet.
In conclusion, the polar regions encapsulate the challenges we face in understanding and addressing climate change. As stewards of the Earth, recognizing the importance of the Arctic and Antarctic is essential not only for biodiversity but for the health of our global ecosystem. Have you noticed how the conversation around climate change has evolved? It’s crucial that we keep these discussions alive and informed by the realities depicted in maps like this one.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 15, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...