Largest Subdivisions in the World Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
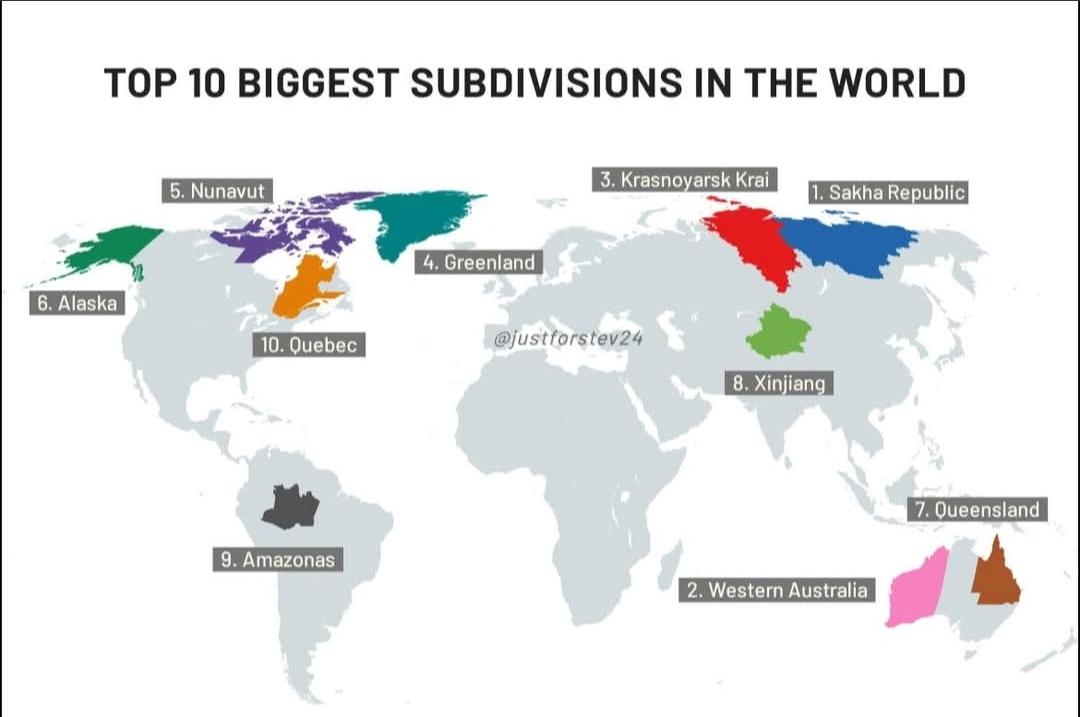
The "Largest Subdivisions in the World Map" provides a comprehensive visualization of the largest political and geographical subdivisions across the globe. These subdivisions can be states, provinces, or territories, depending on the country’s administrative structure. The map highlights not only their sheer size but also allows for an exploration of how these vast areas can influence local governance, economy, and culture.
Deep Dive into the Largest Subdivisions
When it comes to the largest subdivisions in the world, the title often goes to regions that cover vast expanses of land. The largest subdivision by area is the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) in Russia, which spans over 3 million square kilometers. What’s fascinating about Yakutia is its extreme climate; it stretches across a range of latitudes that experience some of the coldest temperatures on Earth. This unique environment affects everything from its population density to economic activities, primarily focused on natural resource extraction, including diamonds and oil.
Another significant player is the Australian state of Western Australia, occupying about 2.65 million square kilometers. It is rich in natural resources and is known for its mining industry, which includes vast deposits of iron ore and natural gas. Interestingly, while Western Australia is enormous, it is sparsely populated, with most of its residents concentrated in the capital, Perth. This stark contrast between area and population density raises questions about urban development and resource management in such large, underpopulated territories.
In Canada, Quebec is the largest province by area, covering over 1.5 million square kilometers. Home to a rich tapestry of cultures, Quebec's unique French heritage shapes its identity and economic interactions. The province is also a leader in the technology and aerospace industries, showcasing how a large land area can provide both challenges and opportunities for development.
These massive subdivisions are not just about size; they also encompass diverse ecosystems, economies, and social structures. For instance, the Brazilian state of Amazonas, covering more than 1.5 million square kilometers, is part of the Amazon Rainforest, one of the most biodiverse areas on the planet. The environmental significance of such regions is immense, influencing global climate patterns and serving as crucial habitats for countless species.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map regionally gives us insight into how different areas manage their vast lands. In Russia, for example, the vastness of Siberia is home to numerous ethnic groups and cultures, each adapted to the harsh environments. Meanwhile, in contrast, the large provinces in Canada, like Alberta and British Columbia, are characterized by their mountainous terrains and rich natural resources, which significantly influence their economies and population distributions.
In Australia, the western part of the continent is primarily arid, affecting settlement patterns. Most of the population lives in coastal cities, leaving the interior largely untouched. This presents unique challenges in terms of resource allocation and infrastructure development. Similarly, in the United States, Texas, the second-largest state, boasts a diverse economy ranging from oil production to technology, reflecting how large subdivisions can develop unique economic identities.
Interestingly, while some subdivisions like Quebec and Western Australia capitalize on their size through resource extraction and population centers, others like the Amazon in Brazil face challenges such as deforestation and climate change, highlighting the importance of sustainable management practices in large areas.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the largest subdivisions in the world is crucial for multiple reasons. First, they often wield significant political power within their respective countries, influencing national policies and resource distribution. Moreover, these areas can serve as microcosms for larger global issues, such as climate change and economic disparity. For instance, the environmental challenges faced by the Amazon rainforest can have far-reaching effects on global biodiversity and climate regulation.
Current trends point toward increasing urbanization within these large subdivisions. As populations grow, cities expand, often leading to conflicts over land use and resources. The future projections suggest that managing these vast areas will require innovative approaches to governance and sustainable development, especially in regions where natural resources are abundant but populations are sparse.
In conclusion, the map of the largest subdivisions is more than just a visual representation; it tells a story of land, culture, and the intricate balance of human interaction with the environment. As we look to the future, the importance of understanding these regions becomes ever more critical in addressing the challenges of our changing world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 14, 2025
- Views
- 26
Comments
Loading comments...