Maximum Territorial Extent of New Spain Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
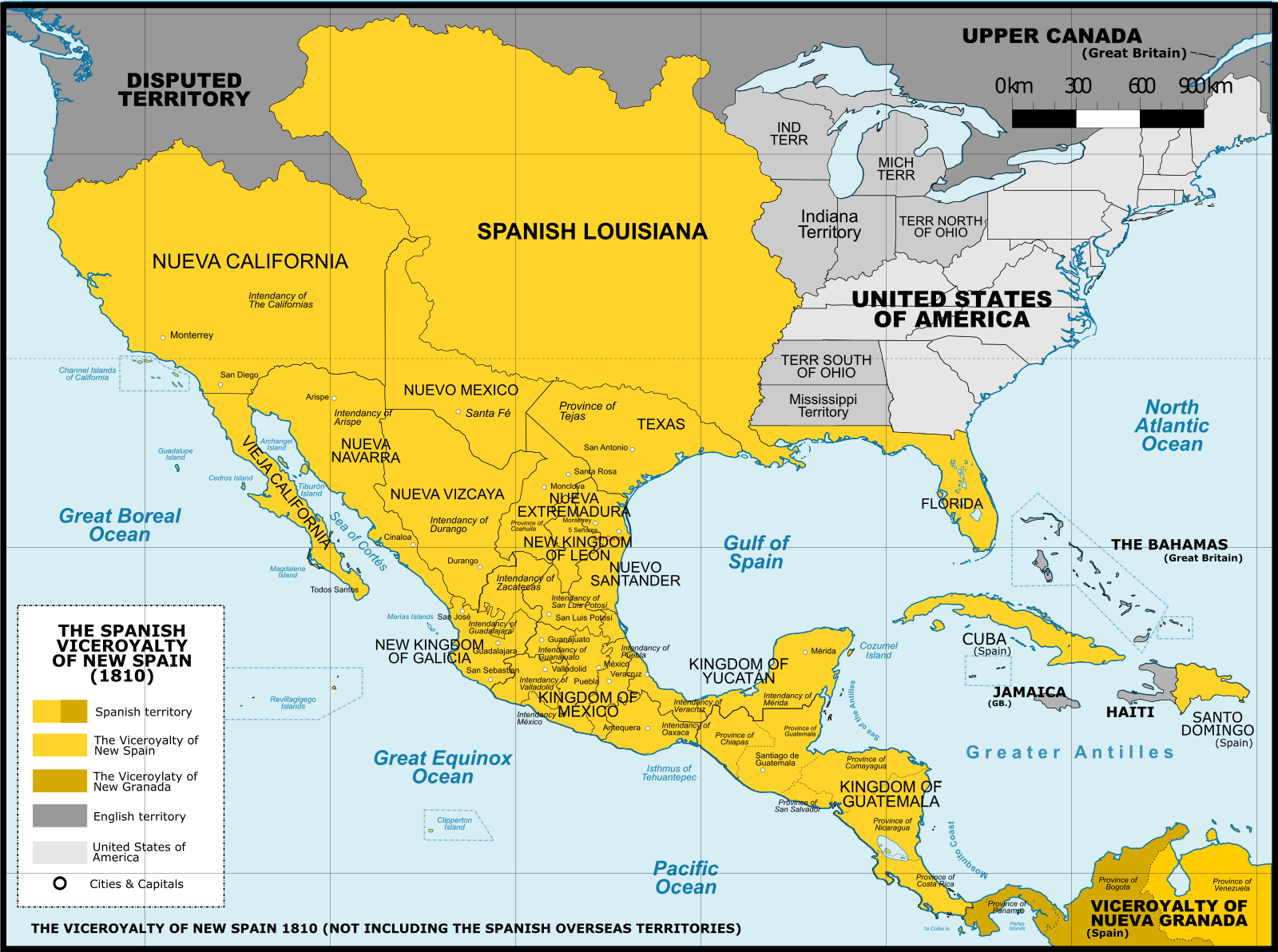
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Maximum Territorial Extent of New Spain" vividly illustrates the vast geographical boundaries that defined New Spain at its zenith during the 18th century. This colonial empire encompassed not just present-day Mexico but also large swaths of what are now the United States, Central America, and even parts of the Caribbean. This visualization provides a crucial understanding of colonial influences on the geopolitical landscape of North America and beyond, highlighting how borders have shifted and transformed over time.
Deep Dive into New Spain's Territorial Extent
New Spain was one of the most significant colonial empires in the Americas, established after the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire in the early 16th century. At its largest, New Spain stretched from the southern tip of what is now Mexico all the way north to present-day Canada, including territories such as Texas, California, Arizona, New Mexico, and even parts of the Great Plains. Interestingly, it also extended south into Central America, covering modern-day Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, El Salvador, and Nicaragua.
At its peak, New Spain was not just a geopolitical entity; it was a melting pot of cultures and economies. The empire was rich in resources, including precious metals like gold and silver, which were mined extensively in regions like Zacatecas and Potosí. The wealth generated from these resources played a crucial role in fuelling the Spanish Crown's ambitions and expanding its influence across the globe.
The administration of New Spain was complex, with a hierarchical system that included viceroys, governors, and local officials who managed various regions. This system allowed for the integration of diverse indigenous populations and the establishment of Spanish culture, language, and religion. The introduction of the encomienda system, which granted Spanish settlers the right to extract labor and tribute from indigenous peoples, had profound social and economic implications.
As you delve deeper into the historical context, it's essential to note the significant trade routes that emerged during this period. The famed Manila Galleons connected New Spain to the lucrative markets of Asia, facilitating an exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas. This route allowed for the flow of silks, spices, and other luxury items into Mexico, which were then transported to Europe. The development of such trade routes not only enhanced New Spain's economy but also established it as a critical hub in the global trade network of the era.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing this map reveals distinct regional characteristics within New Spain that contributed to its complexity. For instance, the northern territories, such as Texas and California, were largely influenced by their proximity to the United States and the later Anglo-American settlement. These regions experienced different socio-economic dynamics compared to southern areas like Guatemala and Honduras, where Spanish influence was more deeply rooted in indigenous cultures and agricultural practices.
In the northern regions, Spanish missions were established to convert indigenous populations and facilitate the expansion of Spanish settlements. In contrast, the southern parts of New Spain were characterized by advanced agricultural economies that relied heavily on indigenous labor. The differences in demographic composition, economic practices, and cultural integration provide a fascinating lens through which to view the historical significance of New Spain's territorial extent.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the maximum territorial extent of New Spain is vital for grasping the historical foundations of present-day North America. The legacy of colonialism can still be felt today in the cultural and linguistic diversity of the region. For example, Spanish remains a dominant language in many parts of Mexico and the southwestern United States, a testament to the enduring impact of New Spain's colonial past.
Moreover, the territorial changes that followed the decline of New Spain, particularly after the Mexican War of Independence and the U.S.-Mexican War, have shaped contemporary borders and national identities. The shifting of boundaries not only redefined the political landscape but also led to complex social dynamics and tensions that continue to play out in various forms.
As we reflect on the historical significance of New Spain, it’s essential to consider current trends, such as the ongoing discussions about cultural heritage, indigenous rights, and the impact of globalization. These issues remind us that the historical narrative of New Spain is not just a story of the past but a living, evolving saga that influences our present and future.
In conclusion, the map of New Spain's maximum territorial extent offers a window into a rich and complex history that has shaped the Americas in profound ways. By understanding this historical context, we can better appreciate the diverse cultural tapestry that characterizes the region today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 14, 2025
- Views
- 28
Comments
Loading comments...